- The paper introduces ReasonEmbed, which integrates innovative data synthesis via ReMixer and adaptive learning through Redapter to enhance reasoning-intensive retrieval.
- It employs a three-stage workflow—conditioned query generation, candidate mining, and relevance annotation—to ensure diverse and challenging training samples.
- Implemented across multiple LLM backbones, ReasonEmbed achieves a record nDCG@10 score of 38.1 on the BRIGHT benchmark, outperforming traditional retrievers.
ReasonEmbed: Enhanced Text Embeddings for Reasoning-Intensive Document Retrieval
Overview
The paper introduces ReasonEmbed, a novel text embedding model designed for reasoning-intensive document retrieval tasks. Unlike traditional retrievers, ReasonEmbed focuses on understanding complex semantic relationships through a combination of synthetic data generation and adaptive learning techniques.
Key Contributions
- Data Synthesis via ReMixer:
ReMixer addresses the limitations of existing synthetic datasets that often result in trivial associations between queries and documents. It employs a three-stage workflow:
- Conditioned Query Generation: Utilizes LLMs to create queries that require intensive reasoning based on diverse corpora.
- Candidate Mining: Searches for documents related to generated queries while excluding source documents to prevent trivial matches (Figure 1).
- Relevance Annotation: Employs a lightweight LLM for annotating document relevance based on multi-step reasoning.

Figure 1: The three-stage data synthesis workflow of ReMixer. The full prompts used in the data synthesis process are available in Appendix~\ref{sec:appendix:data_synthesis}.
- Self-Adaptive Learning using Redapter:
Redapter leverages the concept of reasoning intensity, dynamically adjusting the weight of training samples based on their complexity. This enables the model to focus learning on more challenging reasoning-intensive samples, improving the representation of nuanced semantic relationships (Figure 2).
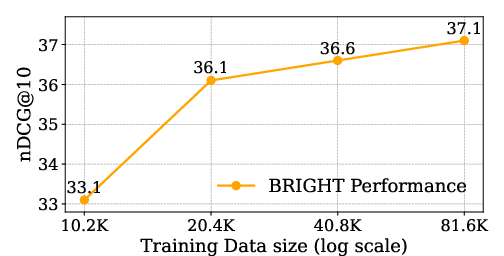
Figure 2: Impact of synthetic data size on retrieval accuracy (using basic contrastive learning for simplicity).
- Implementation Across Backbones: ReasonEmbed is implemented on multiple LLM backbones; notably, the Qwen3-8B variant achieves a record-high nDCG@10 score of 38.1 on the BRIGHT benchmark, showcasing superior performance over existing models.
Implementation Details
- ReMixer Data Synthesis:
- Utilizes LLMs for conditioned query generation to ensure diversity and reasoning demand.
- Employs candidate mining with a focus on excluding the original source documents to avoid trivial matches.
- Incorporates a relevance annotation process refined through a distilled reasoning-LLM for efficient and accurate labeling of document relevance.
- Redapter Training Method:
- Integrates a novel RI-InfoNCE loss function where reasoning intensity scores, computed via powerful LLMs like GPT-4.1-mini, inform the sample weighting strategy.
- The model's initialization from MSMARCO pre-trained checkpoints is fine-tuned with synthesized data, emphasizing reasoning-intensive sample learning.
Experimental Results
ReasonEmbed demonstrates superior performance in reasoning-intensive document retrieval tasks across benchmarks like BRIGHT and R2MED. It significantly outperforms general-purpose retrievers and other tailored methods in tasks requiring deep semantic understanding (Table 1 & Table 2).
Limitations and Future Work
While ReasonEmbed shows remarkable performance, its reliance on existing LLMs for data synthesis and annotation presents potential constraints in reasoning capacity. Future work could address robust scaling to broader domains and explore more advanced multi-agent synthesis methods to further enhance retrieval capabilities.
Conclusion
ReasonEmbed exemplifies the potential of integrating innovative data synthesis and adaptive learning techniques for advancing the capabilities of text embeddings in reasoning-intensive scenarios. The open-sourcing of its resources aims to foster further research in this domain.

