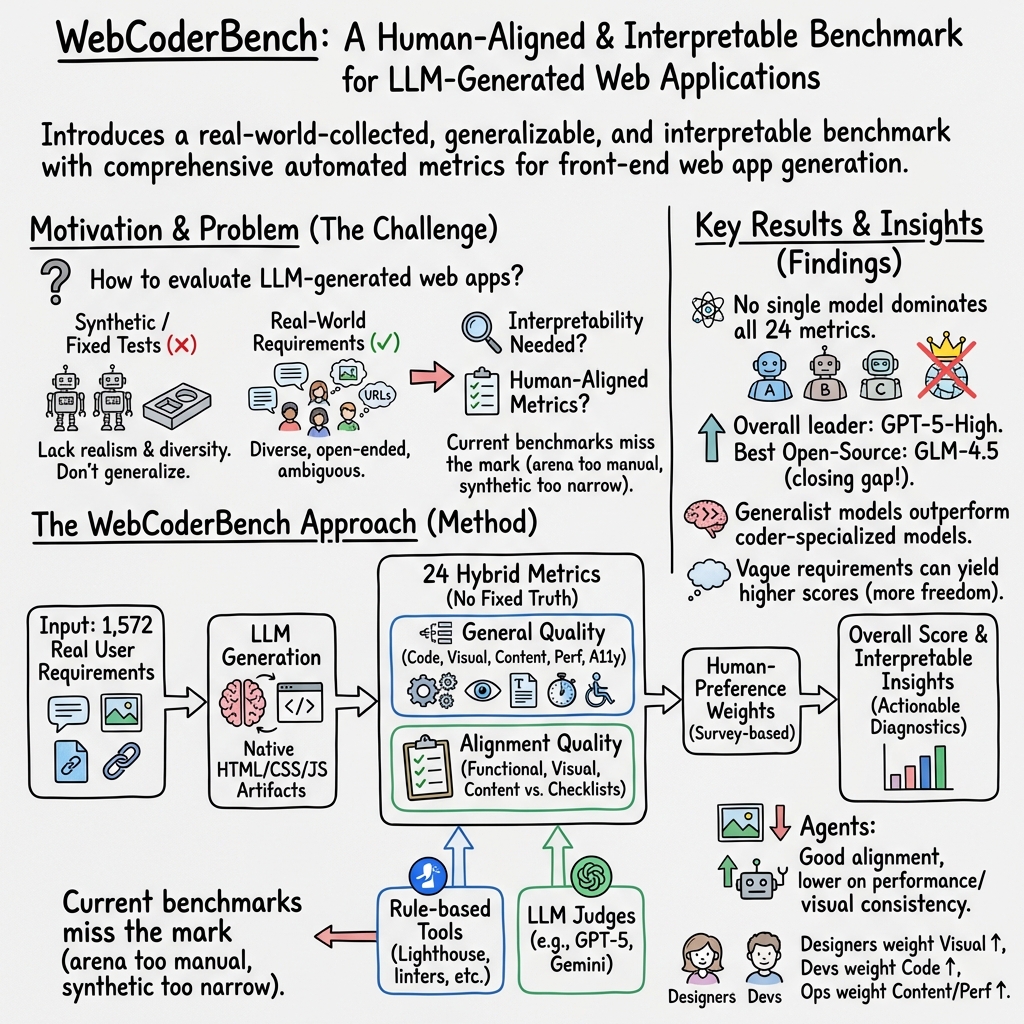
- The paper introduces a benchmark that leverages real-world, multi-turn user requirements to assess LLM-generated web apps.
- It employs a robust framework with 24 metrics across general and alignment quality, incorporating user-driven weights via the Borda Count.
- Evaluation results from 12 LLMs reveal significant performance variations, offering actionable insights for targeted model enhancements.
WebCoderBench: Benchmarking Web Application Generation
Web applications serve as a pivotal domain for demonstrating the capabilities of LLMs in code generation. The paper "WebCoderBench: Benchmarking Web Application Generation with Comprehensive and Interpretable Evaluation Metrics" (2601.02430) introduces WebCoderBench, a benchmark designed to address the challenges of authenticity, generality, and interpretability in evaluating LLMs' ability to generate web applications. This benchmark offers a substantial dataset derived from real-world user requirements, coupled with a robust evaluation framework comprising 24 metrics across various quality perspectives.
Dataset Construction
WebCoderBench emphasizes authenticity by sourcing 1,572 user requirements from an industrial partner's online service. This dataset spans multiple modalities, from textual descriptions to images and URLs, capturing the diverse expression styles of users. The data collection process (Figure 1) involved merging multi-turn requirements into coherent single-turn inputs, ensuring comprehensibility and content anonymization. The curated dataset was further enhanced by establishing ground-truth checklists across functionality, visual design, and content, validated by human experts (Figure 2).
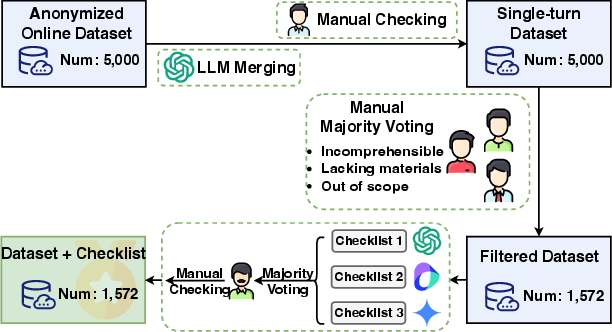
Figure 1: The dataset construction process of WebCoderBench.
Evaluation Metrics
WebCoderBench's evaluation framework is structured around two major quality aspects: general quality and alignment quality, further divided into nine perspectives encompassing 24 metrics (Table 1). This comprehensive structure ensures an objective and quantitative assessment of LLM-generated web applications without reliance on ground-truth implementations.
The benchmark employs rule-based methods and the LLM-as-a-judge paradigm to ensure automated evaluation. General quality covers code, visual, content, performance, accessibility, and maintainability aspects, while alignment quality focuses on meeting user-specified functional, visual, and content requirements.

Figure 2: An example user requirement with its corresponding ground-truth checklists.
Weight Assignment and User Preferences
To reflect human preferences accurately, WebCoderBench integrates preference-aligned weights into its evaluation. This process involved a company-wide survey, leveraging the Borda Count method to calculate weights for each metric based on user importance rankings (Figure 3). This ensures the benchmark's overall score aligns with real-world user preferences, providing actionable insights into user priorities.
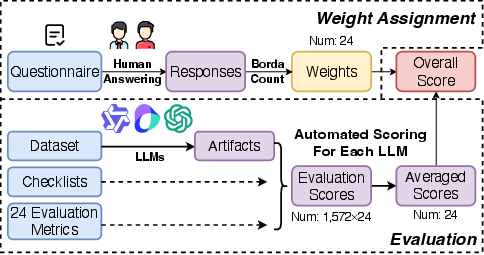
Figure 3: The weight assignment and evaluation workflow of WebCoderBench.
Evaluation Results and Analysis
Experiments conducted with 12 LLMs and 2 LLM-based agents showcased WebCoderBench's efficacy in providing interpretable evaluations (Figure 4). The results indicate significant performance variance across models with no single model leading in all metrics, highlighting opportunities for targeted improvements. The analysis revealed a narrowing gap between open-source and closed-source LLMs and emphasized the rapid pace of model evolution, with newer models consistently outperforming older ones.
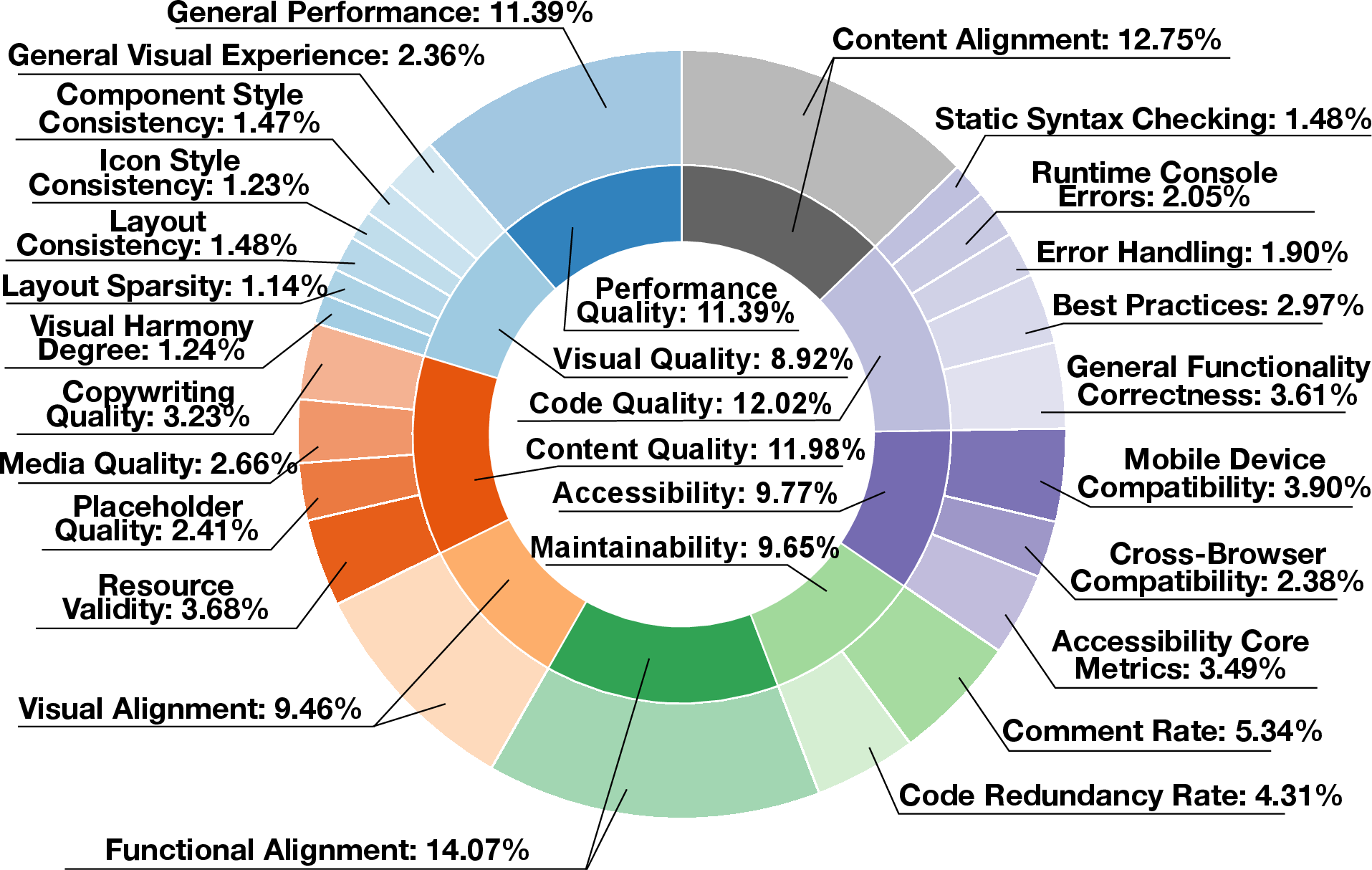
Figure 4: The weight proportion of each perspective and each evaluation metric.
Notably, the evaluation uncovered that models excel in certain areas but lack comprehensive effectiveness across all metrics, reinforcing the specialization trend among current LLMs. User preferences play a crucial role in shaping evaluations, offering developers clear directions for model enhancement.
Conclusion
WebCoderBench provides a robust, interpretable benchmarking framework for LLM-generated web applications, with authenticity and user-centric evaluation at its core. By actively addressing user needs and evolving with the industry, this benchmark sets a new standard for assessing LLM capabilities in web application generation, offering a powerful tool for developers aiming to optimize and refine their models.

Figure 5: The detailed raw scores of 24 evaluation metrics for each LLM and LLM-based agent, with the x-axis indices denoting the IDs of evaluation metrics (corresponding to Table~\ref{metrics table}).