Native Parallel Reasoner: Reasoning in Parallelism via Self-Distilled Reinforcement Learning (2512.07461v1)
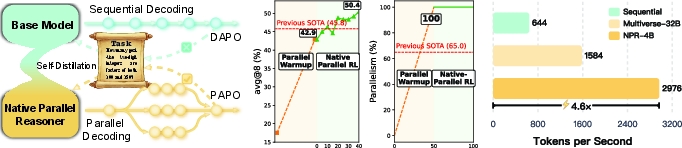
Abstract: We introduce Native Parallel Reasoner (NPR), a teacher-free framework that enables LLMs to self-evolve genuine parallel reasoning capabilities. NPR transforms the model from sequential emulation to native parallel cognition through three key innovations: 1) a self-distilled progressive training paradigm that transitions from ``cold-start'' format discovery to strict topological constraints without external supervision; 2) a novel Parallel-Aware Policy Optimization (PAPO) algorithm that optimizes branching policies directly within the execution graph, allowing the model to learn adaptive decomposition via trial and error; and 3) a robust NPR Engine that refactors memory management and flow control of SGLang to enable stable, large-scale parallel RL training. Across eight reasoning benchmarks, NPR trained on Qwen3-4B achieves performance gains of up to 24.5% and inference speedups up to 4.6x. Unlike prior baselines that often fall back to autoregressive decoding, NPR demonstrates 100% genuine parallel execution, establishing a new standard for self-evolving, efficient, and scalable agentic reasoning.
Sponsor
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Explain it Like I'm 14
Native Parallel Reasoner (NPR) — A simple explanation
What is this paper about?
This paper introduces NPR, short for Native Parallel Reasoner. It’s a new way to teach AI LLMs to “think in parallel.” Instead of solving problems one step at a time, the model learns to split a big problem into smaller parts, work on those parts at the same time, and then combine the results. The goal is to make the model both smarter and faster—without needing a stronger “teacher” model to show it how.
What questions does the paper try to answer?
In everyday terms, the paper asks:
- How can we train an AI to break a problem into pieces and work on those pieces at the same time?
- Can the AI learn this skill by itself (without copying a bigger, better model)?
- How do we make sure this kind of parallel thinking works stably and doesn’t crash or slow down?
How did the researchers do it?
The team built NPR using three main ideas. Think of them like steps in coaching a team to do a group project efficiently.
Before the steps, here are the three big innovations, explained simply:
- Self-distilled training: The model teaches itself by generating its own examples and learning from its best attempts (like practicing and keeping the best runs).
- PAPO (Parallel-Aware Policy Optimization): An improved training rule for trial-and-error that helps the model decide where to branch into parallel paths and how many paths to try.
- NPR Engine: A careful “control center” that makes parallel thinking run smoothly on the computer—no memory errors, no mix-ups about who is doing which part.
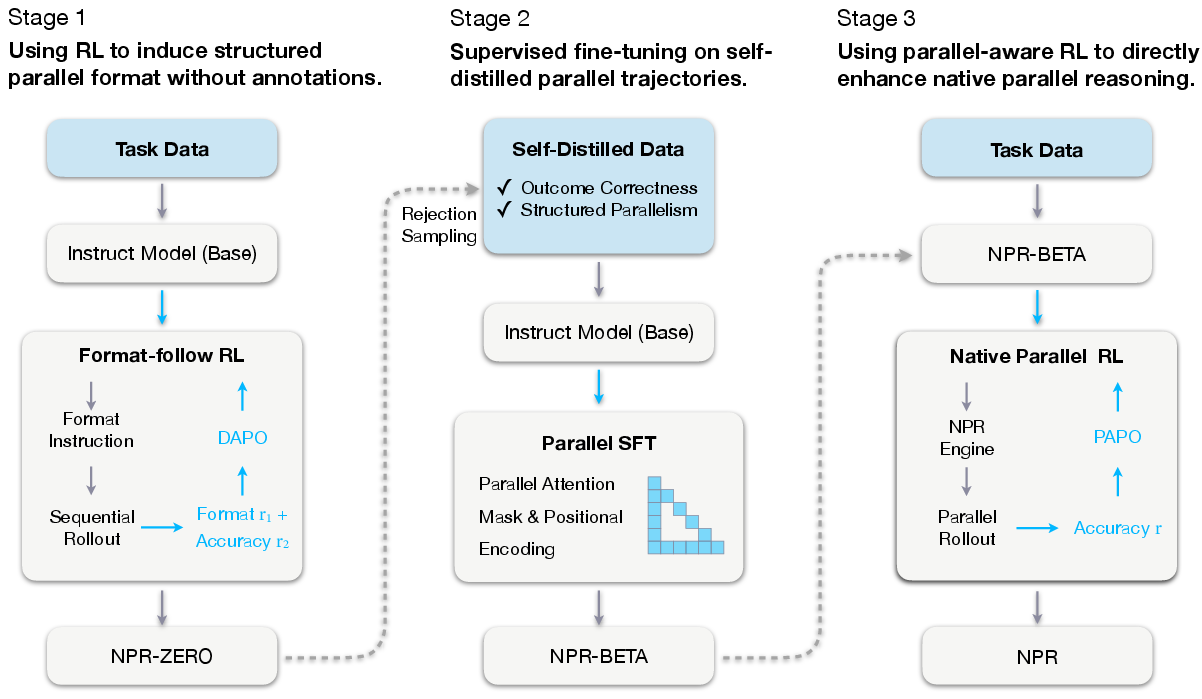
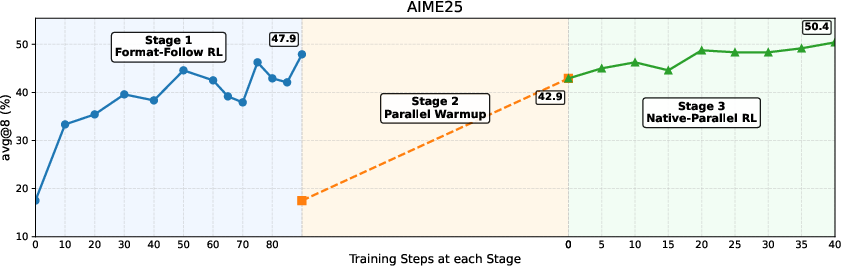
They trained NPR in three stages:
- Stage 1 — Learn the format (like learning the rules of the game)
- The model is taught to think in a simple pattern: make a plan, explore different steps in parallel, then write a takeaway that combines the results.
- It’s rewarded when it follows the structure and gets correct answers.
- The model uses its own outputs to build a training set (self-distillation), so it doesn’t need a teacher model.
- Stage 2 — Make parallel thinking real (not just pretend)
- The model’s “parallel” steps are forced to be truly independent under the hood. This is done by:
- An attention mask: simple rule that says “these steps can’t peek at each other’s work.”
- Positional encoding: simple “address labels” that keep all the steps aligned even if they’re done at the same time.
- The team gathers only good examples (correct and properly structured) to fine-tune the model so it becomes stable at doing true parallel reasoning.
- Stage 3 — Get better at branching using reinforcement learning (trial and error)
- Using PAPO, the model practices choosing where and how to branch into multiple paths.
- The NPR Engine makes this safe and fast—fixing issues like memory leaks, wrong token budgeting (how much to generate), and repetitive text.
- Rewards are simple: correct final answers are good; wrong ones are not. Over time, the model learns smarter branching strategies.
A useful analogy: Think of cooking a meal. Instead of making each dish fully one after another, you prepare the salad while the soup simmers and the bread bakes. Then you bring them all together at the end. NPR teaches the AI to do the “multi-dish cooking” version of problem solving.
What did they find, and why does it matter?
The authors tested NPR on eight reasoning benchmarks (including math contests like AIME and logic tests). Here’s what stood out:
- It’s more accurate: NPR improved scores by up to about 24.5% compared to strong baselines of similar size.
- It’s much faster: Parallel thinking brought speedups up to 4.6× over standard one-step-at-a-time decoding.
- It’s truly parallel: Unlike earlier methods that sometimes secretly fell back to normal step-by-step thinking, NPR ran 100% in real parallel mode across all tested cases.
- It learns without a teacher: The self-distilled data (made by the model itself) performed better than datasets copied from bigger teacher models. This avoids an “intelligence ceiling” where the student can’t surpass the teacher.
Why this is important:
- Faster and smarter reasoning means AI can handle harder problems more reliably.
- Teacher-free training lowers costs and makes progress less dependent on closed, proprietary models.
- True parallel reasoning is a key step toward scalable “agentic” AI—systems that plan, explore multiple options, cross-check themselves, and then act.
What could this change in the future?
If AI can naturally split tasks and explore different solution paths at once, it could:
- Solve tricky math and logic problems more reliably.
- Speed up coding help, planning, and research tasks.
- Make real-time AI assistants more practical, since they can think faster without needing huge computers.
- Encourage the community to build new tools and models that use true parallel reasoning by default, not just imitate it.
In short, NPR shows how an AI can teach itself to think like a well-organized team: plan, divide, explore in parallel, and combine—accurately and quickly.
Knowledge Gaps
Knowledge gaps, limitations, and open questions
Below is a focused list of unresolved issues and missing analyses that future work could address to strengthen and generalize the Native Parallel Reasoner (NPR) framework.
- Limited domain coverage: Evaluation is restricted to math/logic benchmarks (AIME, HMMT, AMC, OlympiadBench, Minerva-Math, ZebraLogic, MATH500). It remains unclear whether NPR’s parallel format and PAPO generalize to other domains (code generation, complex planning, scientific QA, multi-modal tasks, tool-use).
- Teacher-free self-distillation constraints: Stage 2 uses rejection sampling with ground-truth answers for correctness filtering. How to perform parallel warmup and self-distillation on tasks without labeled answers (open-ended generation, real-world agentic tasks) remains unaddressed.
- Aggregation (“Reduce”) strategy: The paper enforces structural tags but does not specify learned or algorithmic policies for merging conflicting branch outputs (e.g., how
<takeaway>resolves contradictions). There is no ablation or evaluation of different aggregation strategies and their effect on accuracy, robustness, and reliability. - Parallel branch dependency modeling: The method imposes independence via attention masks and tags rather than learning the dependency graph . There is no mechanism to infer dynamic inter-step dependencies at runtime, detect spurious independence, or adapt masks when branches are semantically dependent.
- Reward design and credit assignment: PAPO optimizes only final correctness (+1/−1). There is no step-level/branch-level credit assignment, partial correctness scoring, or structure-aware rewards that could improve exploration, branch pruning, and reduce wasted computation.
- PAPO theory and ablations: The stop-gradient reweighting (ratio of
π/sg[π]) lacks formal justification and convergence analysis. There are no ablations isolating contributions of PAPO components (batch-level advantage normalization, removal of importance sampling, special-token gradient preservation) to stability and performance. - Comparison to broader search baselines: NPR is not compared against strong test-time search methods (e.g., Tree-of-Thought, Beam-of-Thought, ReAct, Monte Carlo sampling with reranking) that could exploit parallelism and KV reuse differently. Fair, compute-matched comparisons are missing.
- Generalization across model scales: Results focus on 4B backbones; scalability to larger models (e.g., 7B–70B) and to smaller models is unexplored. It’s unclear whether NPR’s engine fixes and PAPO maintain stability, memory safety, and speedups at higher capacities and branching factors.
- Thinking-mode incompatibility: The paper briefly notes difficulty fine-tuning “thinking tokens” in Qwen3-4B (Thinking) but does not investigate methods to adapt thinking-mode models to native parallelism (e.g., token remapping, dual-format training, latent-thought alignment).
- Format dependence and user-facing outputs: NPR relies on explicit structural tags (
<guideline>,<plan>,<step>,<takeaway>). It is unclear how to deploy parallel reasoning without markup (or with hidden control tokens) and whether such tags degrade user experience or downstream tool compatibility. - Parallelism measurement validity: “100% genuine parallelism” is inferred from tag presence and engine-level constraints. There is no hardware-level concurrency audit (e.g., CUDA kernel concurrency, KV reuse profiling) to prove execution is genuinely parallel rather than fast sequential micro-batching.
- Speedup metrics and granularity: The paper reports tokens-per-second and “up to 4.6×” speedups but lacks detailed latency breakdowns (per-problem wall-clock), memory usage, GPU specs, energy consumption, and sensitivity to branching factor, sequence length, and cache flush events.
- KV-cache reuse quantification: While NPR claims KV reuse advantage over independent sampling, there is no controlled experiment that measures speed/memory gains as a function of branching factor and step structure, nor a comparison to optimized sequential engines with speculative decoding.
- Stability across engines: NPR Engine is built atop SGLang with Multiverse-inspired mechanics; compatibility, performance, and stability on widely used engines (e.g., vLLM, TensorRT-LLM) are not evaluated. Portability and maintenance burden are open concerns.
- Robustness and failure modes: There is no systematic analysis of failure modes (e.g., branch collapse, repetitive loops within
<step>, degenerate parallelism on highly sequential tasks) or defensive policies (branch pruning, anti-repetition strategies beyond fixed coefficients). - Mask/positioning design ablations: NPR adopts Multiverse-style attention masks and positional encoding but does not isolate their contribution. Ablations comparing alternative masking schemes, dynamic mask adaptation, or learned positional strategies are missing.
- Branching policy learning: The work claims “adaptive decomposition” yet does not quantify learned branching policies (e.g., how many branches are chosen per task, when to split/merge, exploration vs. verification) or provide diagnostics on policy changes across training stages.
- Test-time scalability characterization: Results report avg@8 and best@8 but do not explore behavior across k (e.g., k ∈ {2,4,16}) or cost-aware scaling curves (accuracy vs. compute). Practical guidance on choosing k and branching factor per domain/problem difficulty is absent.
- Fairness of baseline data and compute: Comparisons against Multiverse models use different datasets (s1.1-8k vs orz-8k) and base models (Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct vs Qwen3-4B). Compute budgets, training tokens, and inference settings are not matched or fully disclosed, limiting causal attribution.
- Applicability to unlabeled and interactive settings: The pipeline depends on labeled datasets for Stage 2 acceptance filtering and final accuracy rewards in Stage 3. How to extend NPR to interactive environments (tools, web, code execution) with self-verification rewards and no labels is unexplored.
- Security, safety, and reliability: No assessment of robustness to adversarial prompts, branch-induced hallucinations, consistency between branches, or resilience under noisy inputs. Methods for cross-branch contradiction detection and safe aggregation are open.
- Human-centric evaluation: The framework’s impact on interpretability, trust, and usability (e.g., clarity of parallel traces, confidence calibration) is not studied. Human evaluations comparing NPR vs. sequential systems on transparency and error localization are missing.
Glossary
- Agentic AI: AI systems that act autonomously to pursue goals via multi-step decision-making. "emerges as the dominant requirement toward agentic AI"
- Agentic reasoning: Goal-directed, multi-step reasoning characteristic of agent-like AI systems. "has shifted the frontier of AI from semantic fluency to deep, multi-step agentic reasoning."
- Autoregressive (AR) decoding: Token-by-token generation where each token depends on previously generated tokens. "NPR achieves task-dependent speedups, reaching up to 4.6× over autoregressive (AR) decoding."
- Autoregressive (AR) fallback: The tendency of a model to revert from parallel to sequential (AR) generation for better performance. "We observed 30%+ AR fallback on test cases"
- Autoregressive (AR) reasoning: Strict left-to-right token generation with sequential dependencies. "Parallel Reasoning (PR) relaxes the strict left-to-right dependency of AR reasoning"
- avg@8: Average accuracy when evaluating 8 sampled solutions, computed as correct/8. "we report avg@8, which better reflects performance when multiple sampled solutions are available."
- Batch-level advantage normalization: Normalizing RL advantages across an entire batch to stabilize updates. "Batch-level advantage normalization."
- best@8: The best accuracy achieved across 8 sampled solutions for a given problem. "Using best@8 as the metric for test-time scalability"
- Branching factor: The number of concurrent reasoning branches active during parallel generation. "records the active branching factor at each expansion"
- Branching policies: Strategies that decide how and when to split reasoning into parallel branches. "optimizes branching policies directly within the execution graph"
- Cache flush: Forcibly clearing cached data to reclaim memory and reset state. "we perform an immediate cache flush"
- DAPO: A policy optimization objective for language-model RL using group sampling, clipping, and advantage normalization. "We adopt objective functions based on DAPO"
- Dependency graph: A directed graph describing dependencies among reasoning steps, enabling parallel factorization. "can be factorized according to a dependency graph defined over the steps:"
- Execution graph: The structured representation of parallel branches and their control flow during reasoning. "optimizes branching policies directly within the execution graph"
- GRPO: Group Relative Policy Optimization; a PPO variant using grouped rollouts and relative advantages. "Comparison of GRPO-style RL~\citep{grpo} and Parallel-Aware Policy Optimization."
- Group-wise normalization of advantages: Normalizing RL advantages within each rollout group to balance exploration and exploitation. "group-wise normalization of advantages."
- Importance sampling: Reweighting updates by likelihood ratios to correct off-policy bias in RL. "importance-sampling ratios in PPO"
- Indicator-style constraints: Binary filters used to accept or reject sampled trajectories based on correctness and format. "two lightweight, indicator-style constraints"
- Intelligence Ceiling: A limitation on a student model’s capability caused by mimicking a teacher’s distilled behavior. "imposing an 'Intelligence Ceiling' that prevents it from novel, model-intrinsic parallel strategies"
- Key-Value (KV) states: Cached transformer key/value tensors reused to accelerate generation across branches. "shared Key-Value (KV) states"
- KV-cache: The memory structure storing transformer keys and values to speed inference. "KV-cache double-free and memory corruption."
- KV-cache double-free: A memory-safety bug where KV-cache entries are recycled more than once, causing corruption. "KV-cache double-free and memory corruption."
- KV-cache reuse: Reusing shared KV tensors across parallel branches to reduce redundant computation. "permit efficient KV-cache reuse for the shared context inside the NPR Engine"
- Length accounting: Tracking token budgets accurately across parallel branches to avoid exceeding limits. "We extended length accounting to be branch-aware"
- Lite-PPO: A simplified PPO approach for language-model RL with lighter-weight advantage normalization. "We adopt a Lite-PPO~\citep{lite_ppo} style advantage"
- Map–Process–Reduce: A tag-structured schema for planning, parallel execution, and result aggregation. "adopt a simplified “Map–Process–Reduce” schema inspired by Multiverse"
- MapReduce: A distributed-computing paradigm that separates mapping (decomposition) from reducing (aggregation). "The MapReduce paradigm has long underpinned distributed computing"
- Multiverse Attention: An attention design that isolates parallel steps within one forward pass while sharing context. "adopt the core design of Multiverse Attention~\citep{multiverse}"
- Native Parallel Reasoning (NPR): A framework enabling LLMs to generate and evaluate multiple reasoning branches in parallel. "we propose Native Parallel Reasoning (NPR), a framework that enables LLMs to generate and evaluate multiple reasoning branches in parallel."
- Negative log-likelihood: A standard supervised loss that minimizes the negative log probability of target tokens. "The model is trained using standard negative log-likelihood."
- NPR Engine: A re-engineered parallel inference backend ensuring stable, large-scale parallel RL training. "a robust NPR Engine that refactors memory management and flow control of SGLang to enable stable, large-scale parallel RL training."
- On-policy objective: An RL objective that updates the policy using samples drawn from the current policy only. "we eliminate importance sampling and adopt a strict on-policy objective."
- Oracle coverage: The likelihood that at least one sampled solution in a set is correct. "reliably increases oracle coverage at test time"
- PAPO: Parallel-Aware Policy Optimization; an RL objective tailored to optimize native parallel reasoning. "a novel Parallel-Aware Policy Optimization (PAPO) algorithm"
- Parallel attention mask: An attention masking scheme that prevents cross-branch interference among parallel steps. "constructing both the parallel attention mask and the corresponding positional encoding"
- Parallel positional encoding: Position-ID assignments that align and reset positions to support parallel blocks. "Parallel Positional Encoding"
- Parallel reasoning trigger rate: The percentage of evaluated cases in which parallel reasoning is activated. "We quantify a model’s tendency to produce simultaneous, non-sequential reasoning using the parallel reasoning trigger rate"
- Parallel RL: Reinforcement learning conducted under strict parallel-generation semantics and structures. "native parallel RL"
- Parallel semantics: Formal constraints ensuring generation is truly parallel rather than pseudo-parallel. "do not enforce strict parallel semantics"
- Policy Optimization for LLMs: The RL process and objectives used to improve a LLM’s generation policy. "Policy Optimization for LLMs"
- PPO: Proximal Policy Optimization; a widely used RL algorithm with clipped probability ratios. "importance-sampling ratios in PPO"
- Radix-cache mechanism: A cache implementation leveraging radix-tree structures for shared KV storage. "GPU memory leaks caused by radix-cache mechanism"
- Radix-tree: A prefix tree data structure used to share KV paths efficiently among branches. "shared radix-tree KV paths"
- Rejection sampling: Sampling that discards candidates failing correctness or format constraints. "performing rejection sampling on NPR-Zero"
- Repetition penalty: A generation-time penalty discouraging local token repetition within steps. "We apply a mild, selective repetition penalty (coefficient = 1.02)"
- Rollout: Sampling trajectories from a policy for evaluation or training in RL. "collision-free parallel rollouts"
- Self-distillation: Using a model’s own generations to create training data for further fine-tuning. "self-distilled datasets outperform previous teacher-generated trajectories"
- SFT (Supervised fine-tuning): Training a model on labeled data to shape its outputs toward desired formats and answers. "downstream supervised fine-tuning (SFT)"
- Stop-gradient: An operator that blocks gradient flow through a value during backpropagation. "where sg[·] denotes stop-gradient."
- Structured parallel format: A tag-based schema explicitly marking planning, parallel steps, and aggregation. "induce a structured parallel format"
- Supervised Distillation: Training a student model on data distilled from a stronger teacher model. "Reliance on Supervised Distillation."
- Token acceleration: Increasing effective throughput or tokens-per-second via parallel generation. "achieves high reasoning accuracy, genuine parallelism and token acceleration."
- Topological constraints: Structural rules enforcing valid dependency and ordering among parallel branches. "strict topological constraints"
- Wall-clock speedup: Real-world elapsed-time reduction compared to a baseline method. "offers up to 4.6× wall-clock speedup over AR decoding"
Practical Applications
Immediate Applications
Below are real-world use cases that can be deployed now, directly leveraging NPR’s genuine parallel reasoning, PAPO training, and the NPR Engine for stable, high-throughput parallel inference.
- Education — Parallel STEM Tutoring and Exam Prep
- Use case: Deliver multiple solution strategies simultaneously (algebraic, geometric, numerical) for math problems, with cross-verification and concise final answers.
- Workflow: Map (generate diverse plans) → Process (solve each plan independently) → Reduce (choose correct solution, explain discrepancies).
- Tools/products: “Parallel Tutor” module for LMS, chatbot plugins for AIME/AMC practice; integrate NPR-4B checkpoints.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Access to ground-truth answers or auto-checkers; tasks decomposable into independent sub-steps; modest GPU for parallel inference.
- Software — Multi-strategy Code Fixing and Unit-Test Generation
- Use case: Produce several candidate patches and tests in parallel, then automatically select the fix that passes tests.
- Workflow: Map (enumerate suspected root causes) → Process (generate patch+test per cause) → Reduce (run tests, rank patches, present best).
- Tools/products: VSCode/JetBrains extensions with NPR Engine; CI/CD “Parallel Fix” stage; KV-cache reuse for shared context.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Test harnesses and runners; repository access; tasks amenable to branching; controlled token budgets for branches.
- Customer Support — Rapid Triage with Hypothesis Branching
- Use case: Parallel evaluation of potential causes/resolutions for user issues; provide best path with alternatives.
- Workflow: Map (list hypotheses) → Process (draft resolution steps per hypothesis) → Reduce (select likely fix, produce playbook).
- Tools/products: Helpdesk bots with NPR schema tags; integration with knowledge bases; turn-key “Parallel Triage” accelerator.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Reliable KB retrieval (RAG); acceptance metrics replace strict accuracy rewards; guardrails for tone and policy.
- Data Analysis — Parallel Pipelines and Hypothesis Testing
- Use case: Run multiple analytical paths (model choices, feature sets, time windows) simultaneously and pick the best validated insight.
- Workflow: Map (candidate analyses) → Process (execute analyses in parallel) → Reduce (compare metrics, confidence, robustness).
- Sector: Analytics/Finance.
- Tools/products: “Parallel Analyst” notebooks; BI plugins with NPR Engine for branch-aware token accounting.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Connectors to data; domain-specific evaluators; tasks decomposable into independent analytic pipelines.
- Enterprise RAG — Map-Process-Reduce Retrieval at Scale
- Use case: Parallel retrieval and reasoning over document shards; aggregate to final answer with citations.
- Workflow: Map (select retrieval strategies/shards) → Process (reason per shard) → Reduce (cross-check, synthesize, cite).
- Sector: Software/Enterprise Knowledge Management.
- Tools/products: NPR-enhanced RAG pipeline (SGLang backend); branch-aware length budgeting; KV-cache reuse.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Engine-level integration; schema validators; doc-level evaluators for non-ground-truth settings.
- Academic Research — Parallel Literature Review and Synthesis
- Use case: Summarize multiple papers or methods concurrently and produce a reconciled synthesis with explicit comparisons.
- Workflow: Map (select angles: methodology, results, limitations) → Process (summarize per angle/paper) → Reduce (compare, converge).
- Tools/products: “Parallel Review Assistant” for research managers and labs; NPR-Beta for stable structured outputs.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Proxy rewards (e.g., citation coverage, alignment checks) in the absence of ground truth; human-in-the-loop.
- ML Engineering — Teacher-free Self-Distillation and Parallel RL
- Use case: Train small/medium models using NPR’s self-distillation pipeline and PAPO to avoid dependence on stronger teachers.
- Workflow: Stage 1 (format induction with format-aware reward) → Stage 2 (parallel warmup via rejection-sampling) → Stage 3 (PAPO-based RL).
- Sector: AI/Model Training.
- Tools/products: NPR training recipes, PAPO objective, NPR Engine fixes (radix-cache, token ledger, format validator).
- Assumptions/dependencies: Availability of evaluators (accuracy, format checks); stable serving engine; GPU resources.
- Cloud/AI Operations — Throughput and Latency Reduction
- Use case: Deploy NPR Engine to reduce wall-clock latency and increase tokens-per-second for workloads that benefit from branching.
- Workflow: Replace AR decoding with NPR parallel decoding; enable branch-aware token accounting and deterministic cache management.
- Sector: AI Platforms/Inference Serving.
- Tools/products: SGLang-based serving with NPR Engine; per-request branch factor tuning; monitoring for format compliance.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Workloads with parallelizable reasoning; GPU memory budgets; ops observability across branches.
- Logic/Math Apps — Parallel Puzzle Solving and Guided Practice
- Use case: Consumer apps solving logic puzzles or math competition problems with multiple approaches and explanations.
- Workflow: Map (strategy enumeration) → Process (attempts per strategy) → Reduce (verify, explain best).
- Sector: Daily Life/Education.
- Tools/products: Mobile/web apps using bigai-NPR models; lightweight format validators client-side.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Task libraries with correct answers; safe content filters; UX for branch visualization.
- Agent Systems — Single-Actor Parallel Planning
- Use case: Replace multi-agent orchestration with a single NPR-enabled actor that explores breadth in one forward pass.
- Workflow: Map (decomposition into subgoals) → Process (pursue subgoals independently) → Reduce (aggregate and act).
- Sector: Software/Robotics (planning in simulators).
- Tools/products: “Native Parallel Planner” module; reduces inter-agent overhead while maintaining breadth.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Tasks with partial independence; reliable reduce stage for conflicts; integration with task execution APIs.
Long-Term Applications
These applications require further research, scaling, domain adaptation, or regulatory approval before broad deployment.
- Healthcare — Differential Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
- Use case: Explore multiple diagnostic hypotheses and treatment paths in parallel; cross-verify with guidelines and outcomes.
- Sector: Healthcare.
- Tools/products: Clinical Decision Support leveraging NPR’s Map-Process-Reduce reasoning and cross-branch verification.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Regulatory compliance; robust evaluators beyond accuracy (risk, contraindications); integration with EHR; domain-tuned reward functions.
- Finance — Scenario Analysis and Portfolio Optimization
- Use case: Parallel exploration of strategies (hedging, asset mixes, macro scenarios) with risk-adjusted selection.
- Tools/products: “Parallel Strategy Studio” with simulators; PAPO adapted to long-horizon rewards.
- Assumptions/dependencies: High-fidelity simulators; data feeds; governance for model risk; metrics replacing ground-truth rewards.
- Robotics — Task and Motion Planning at Scale
- Use case: Parallel expansion of planning branches (task decompositions, motion trajectories), then reduce with safety and cost criteria.
- Tools/products: NPR-augmented planning stack integrated with classical planners; real-time branch management.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Real-time guarantees; formal safety constraints; cross-domain reward shaping; hardware acceleration.
- Public Policy — Parallel Impact Assessments and Trade-off Analysis
- Use case: Simultaneously evaluate policy options across economic, social, environmental dimensions; produce transparent syntheses.
- Tools/products: Policy labs adopting NPR pipelines for structured option analysis.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Trustworthy data; explainability; strong human oversight; robust validation to avoid hallucinated impacts.
- Scientific Discovery — Hypothesis Generation and Experiment Design
- Use case: Generate and refine diverse hypotheses/experimental setups in parallel; cross-validate with literature and models.
- Tools/products: Lab assistant integrating NPR branches with lab management systems and simulation tools.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Domain ontologies; validation pipelines; incorporation of physical and statistical constraints as rewards.
- Energy — Grid Planning and Contingency Analysis
- Use case: Parallel scenario evaluation for grid stability, dispatch, and demand response; reduce to robust operational plans.
- Tools/products: “Parallel Grid Optimizer” with co-simulation; branch-aware token budgeting for complex plans.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Accurate simulators; safety margins; regulatory audits; HPC/edge co-processing.
- Software Security — Parallel Vulnerability Discovery and Patch Synthesis
- Use case: Search and validate multiple exploit paths and fixes; reduce using static/dynamic analysis outcomes.
- Tools/products: NPR-integrated SAST/DAST workflows; red-team simulators for reward signals.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Reliable code analyzers; sandboxing; high-precision evaluators to prevent false positives.
- Education — Large-Scale Personalized Pathways and Assessment
- Use case: Create parallel learning plans targeting different misconceptions and mastery paths; select adaptive sequences.
- Tools/products: NPR-enabled tutoring platforms with student models and formative assessment rewards.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Fairness and bias monitoring; longitudinal evaluation; privacy-preserving data pipelines.
- AI Infrastructure — Standardizing PAPO and Native Parallel Engines
- Use case: Make PAPO and NPR Engine patterns standard across vLLM/SGLang variants; improve stability and performance for parallel RL.
- Tools/products: Open-source libraries and engine patches; branch-aware token ledgers; cache safety protocols.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Community adoption; compatibility with diverse architectures; benchmarking suites for reliability.
- Safety and Formal Verification — Cross-Branch Proof Checking
- Use case: Couple NPR’s reduce stage with formal methods/theorem provers to verify correctness across branches.
- Tools/products: Hybrid NPR–formal verification systems; domain-specific schemas for provable reasoning.
- Assumptions/dependencies: Integration with proof assistants; domain axiomatization; performance trade-offs for strict guarantees.
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.