- The paper introduces MuonAll, a unified optimizer that extends momentum-based optimization to both one- and two-dimensional model parameters.
- The paper demonstrates that MuonAll achieves competitive performance with AdamW across benchmarks like MMLU and GSM8K while enhancing computational efficiency.
- The paper suggests that integrating advanced matrix norms could further boost fine-tuning and generalization capabilities in large language models.
MuonAll: Efficient Finetuning of LLMs
Introduction
The paper "MuonAll: Muon Variant for Efficient Finetuning of LLMs" explores the performance of the Muon optimizer for supervised finetuning (SFT) on publicly available, pretrained LLMs with sizes up to half a billion parameters. The core innovation of this research lies in the development of MuonAll, a unified optimizer that aims to encompass all model parameters, eliminating the conventional reliance on AdamW for certain parameters.
Background on Muon and MuonAll
The Muon optimizer is a momentum-based optimization algorithm tailored for two-dimensional parameters in neural networks. By implementing orthogonalization via Newton-Schulz iterations, Muon enhances the training efficiency of LLMs. Its updates leverage momentum and gradient information while orthogonalizing updates to address the common inefficiencies pervasive in other optimizers like SGD and Adam.
MuonAll builds upon Muon by generalizing the parameter updates to include one-dimensional parameters. This generalization is achieved by temporarily converting one-dimensional parameters into diagonal matrices for the purpose of optimization, thereby unifying the optimization process within the Muon framework. The key steps in MuonAll include calculating the momentum, applying Newton-Schulz iterations, and reverting one-dimensional parameters back to their original form after optimization steps.
Experiments and Evaluation
To evaluate the effectiveness of MuonAll, the authors conducted SFT experiments on three LLMs: Qwen2-0.5B, SmolLM2-360M, and GPT2-medium. The evaluation centered around several benchmarks including MMLU, HellaSwag, PIQA, ARC-Easy, and others. Each optimizer—AdamW, Muon, and MuonAll—was tested with consistent hyperparameters to ensure comparability.
Qwen2-0.5B
MuonAll showed competitive performance relative to AdamW in benchmarks such as MMLU and GSM8K where MuonAll slightly underperformed compared to Muon alone. However, MuonAll demonstrated improvements over Muon in benchmarks where AdamW was superior, indicating its potential to serve as a standalone optimizer.
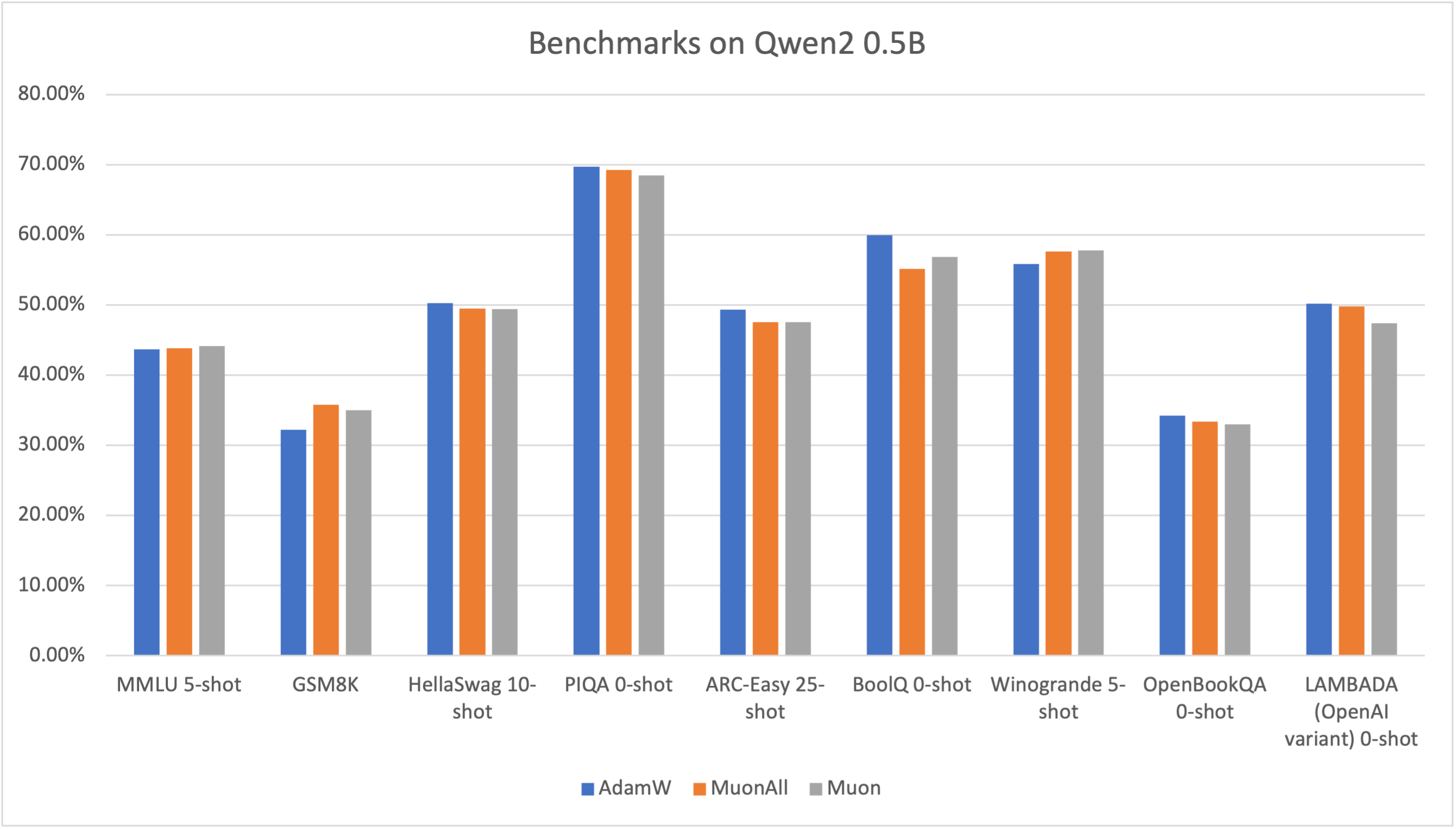
Figure 1: Benchmarks on Qwen2 0.5B
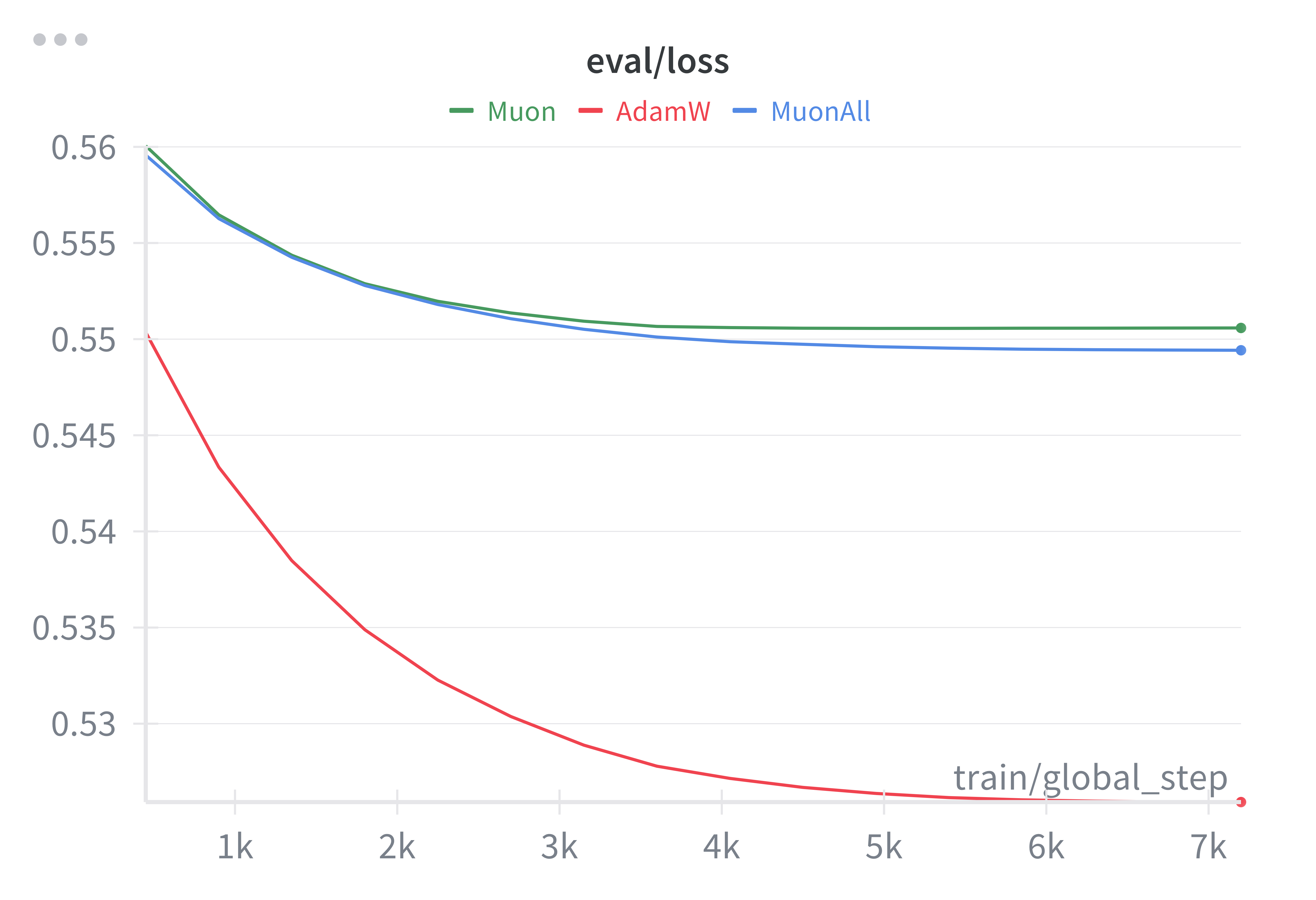
Figure 2: Validation loss on Qwen 0.5B
SmolLM2-360M
With SmolLM2-360M, Muon and MuonAll outperformed AdamW in the MMLU benchmark, showcasing their adaptability and efficiency. MuonAll particularly showed robustness by achieving similar or better results in tasks where AdamW excelled over Muon.
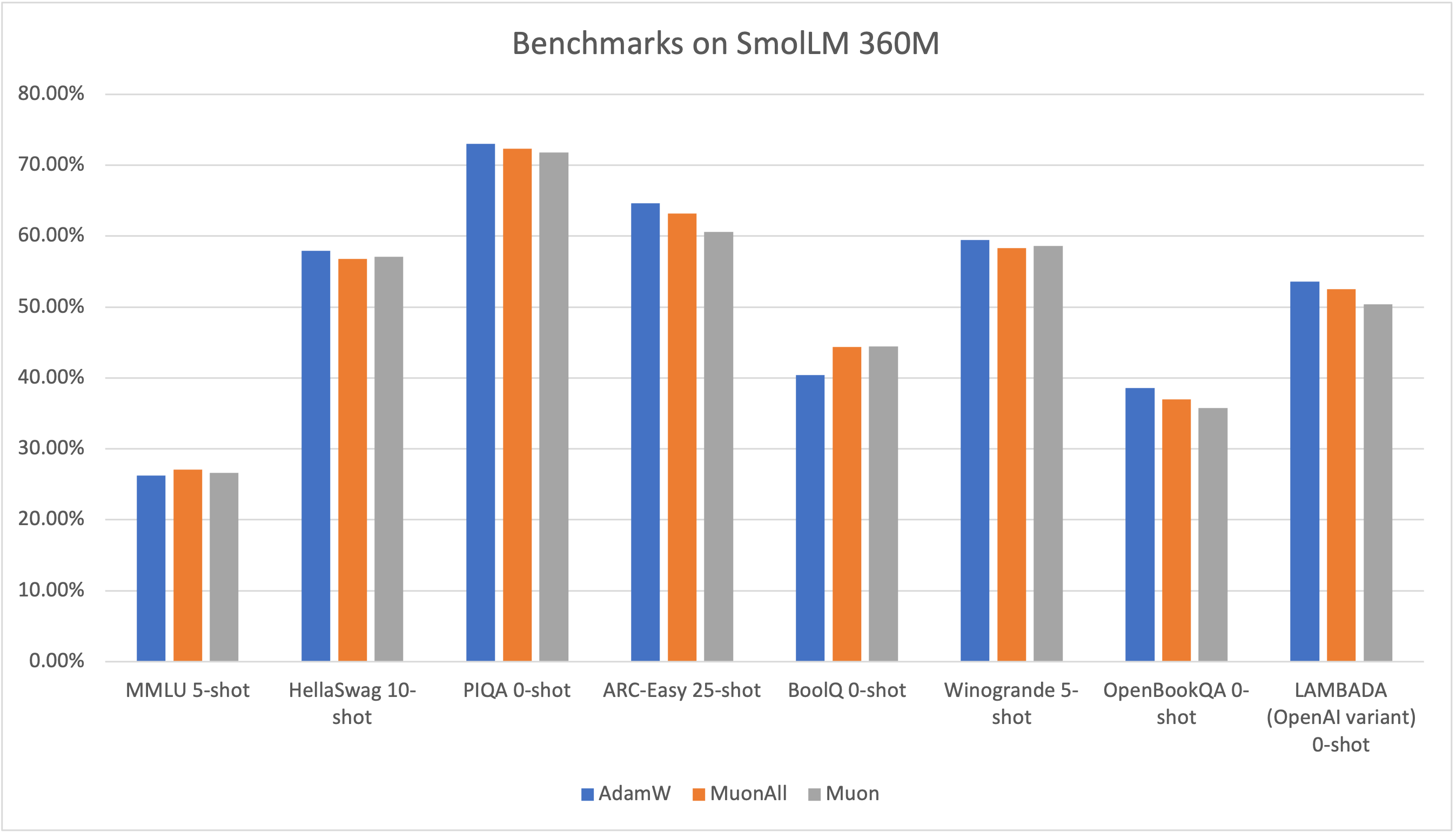
Figure 3: Benchmarks on SmolLM 360M
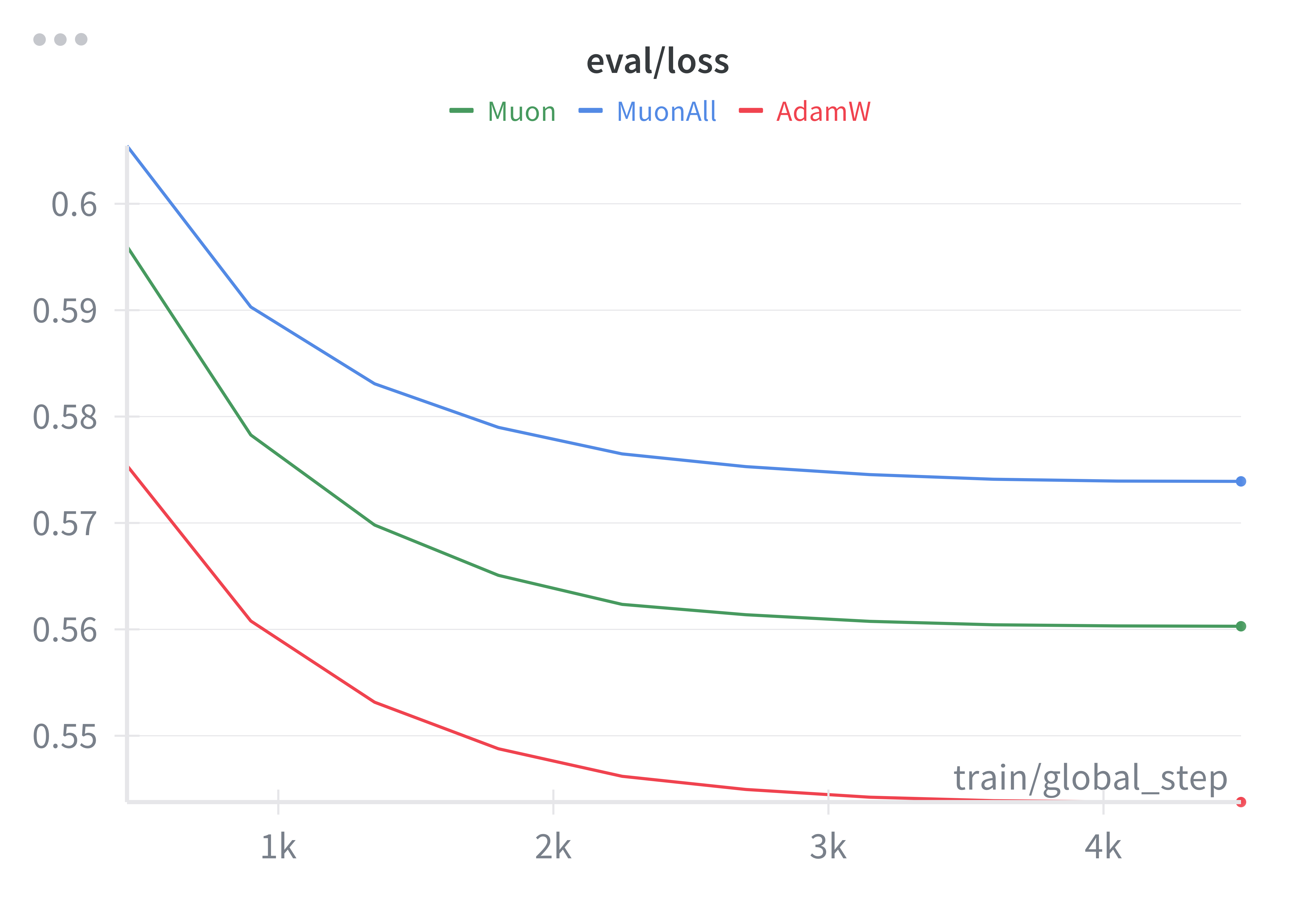
Figure 4: Validation loss on SmolLM 360M
GPT2-medium
For GPT2-medium models, Muon and MuonAll outstripped AdamW on the MMLU benchmark while maintaining competitive scores across others, further highlighting their capacity to contend with traditionally superior optimization methods.
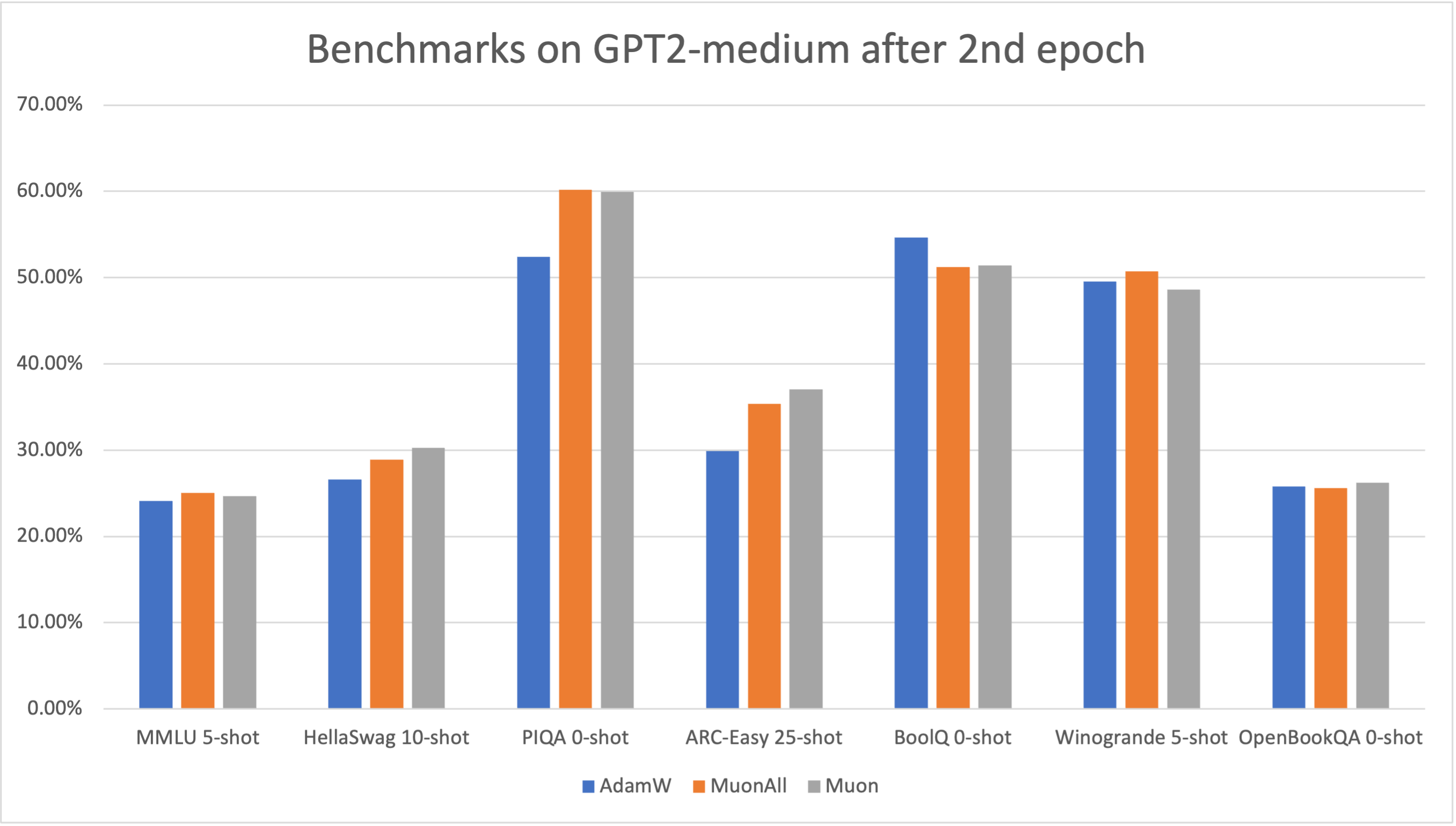
Figure 5: Benchmarks on GPT2-medium after 2nd epoch
Conclusion
The introduction of MuonAll as a comprehensive optimizer for both one-dimensional and two-dimensional parameters marks an important development in the optimization of LLMs. MuonAll aligns closely with AdamW in terms of performance on various natural language processing benchmarks, while providing the computational efficiency through a more cleanly integrated optimization approach.
Future research prospects include exploring the integration of advanced matrix norms such as Schatten-p or trace norms into the Muon framework to further enhance model generalization capabilities and fine-tuning efficiency. Additionally, developing a deeper understanding of the pretraining-fin tuning dynamics using MuonAll could lead to optimized training schemes applicable to a broad range of NLP models.






