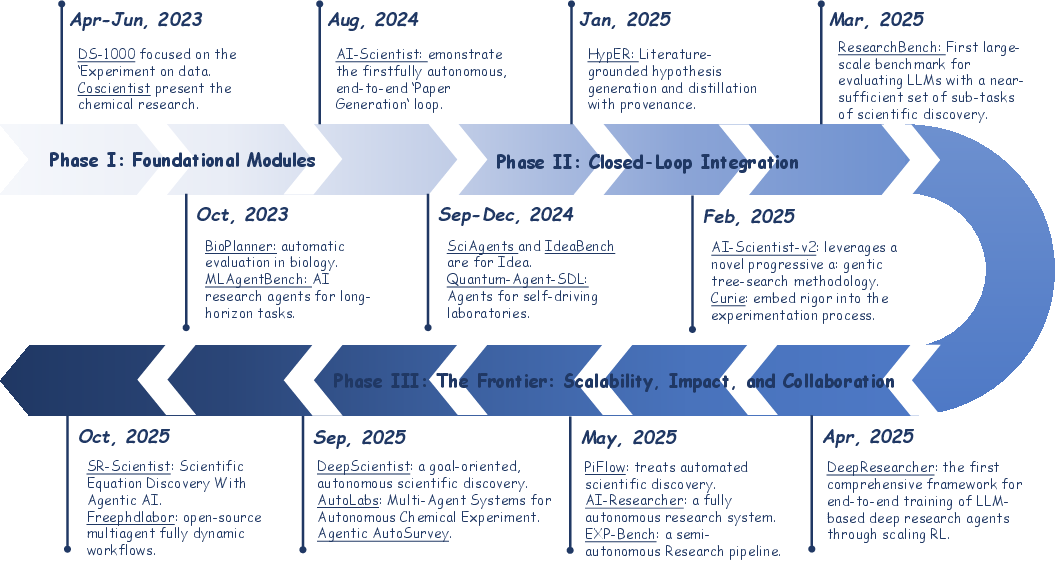
- The paper presents AI Scientist systems that autonomously conduct research, covering the end-to-end process from hypothesis generation to paper publication.
- It outlines a six-stage workflow integrating literature review, idea generation, experiment design, execution, scientific writing, and paper generation.
- The study identifies key challenges in reproducibility, generalizability, and ethical governance, offering a roadmap for scalable and collaborative future systems.
A Survey of AI Scientists
Overview of AI Scientists
"A Survey of AI Scientists" introduces the concept of AI Scientists, systems designed to autonomously conduct scientific research from hypothesis generation to publishing findings. This paradigm, emerging from the integration of LLMs, multi-agent systems, and robotic platforms, signifies a transition from tools aiding human inquiry to AI systems capable of independently originating scientific knowledge. The paper synthesizes developments from 2022 to 2025, categorizing AI Scientist efforts into six methodological stages, mapping them within a historical framework, and providing a comprehensive analysis of the architectural evolution. The work aims to unify fragmented research, providing a roadmap for future AI Scientist systems, addressing challenges in robustness, generalizability, and ethical governance.
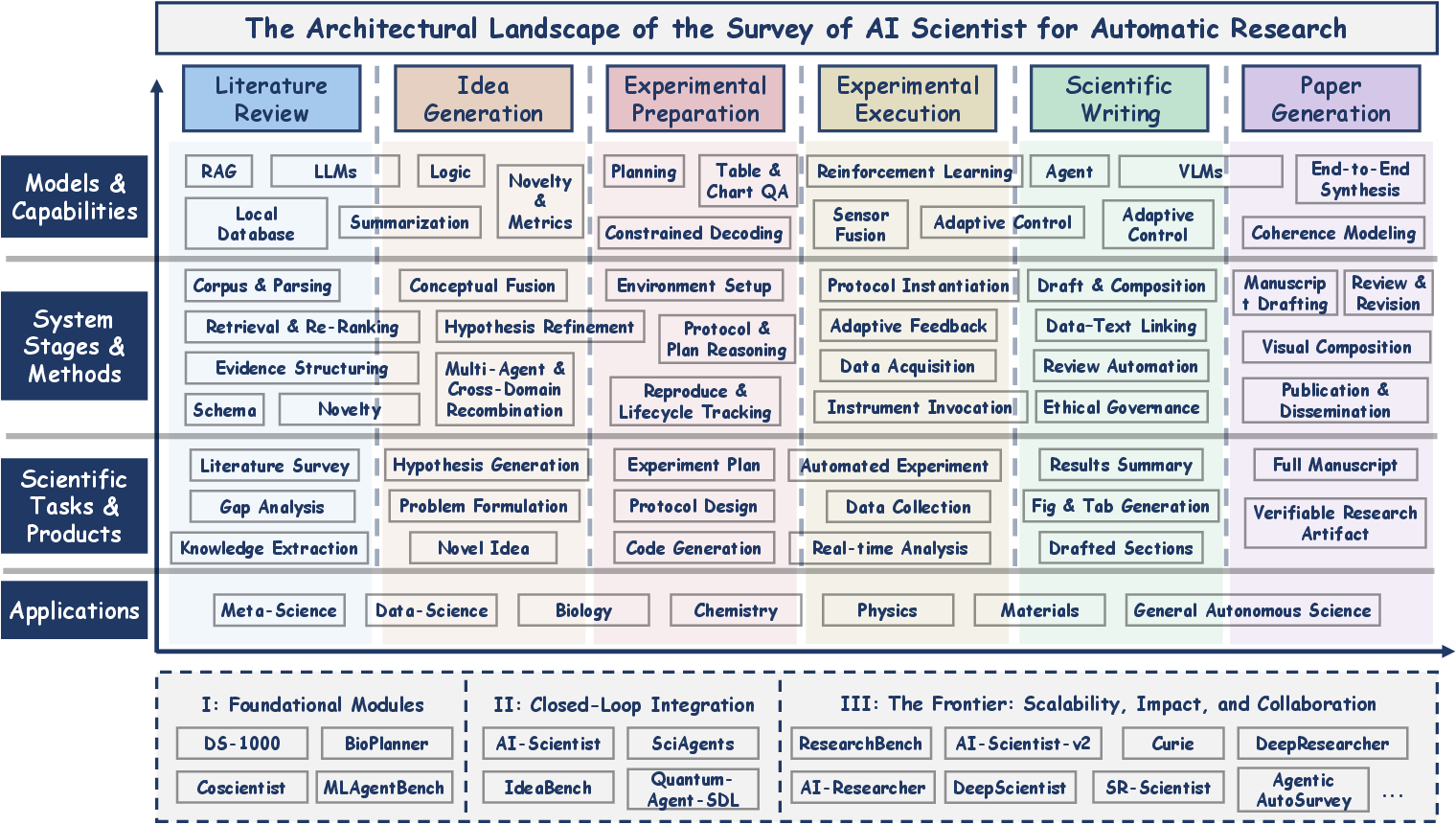
Figure 1: The Architectural Landscape of the AI Scientists for Automatic Research. The main 4x6 matrix maps the six methodological stages of the scientific workflow against layers of abstraction.
Architectural and Methodological Framework
The paper deconstructs autonomous scientific processes into six stages:
- Literature Review: Converts unstructured scientific texts into structured knowledge, enabling AI systems to synthesize research gaps and foundational insights.
- Idea Generation: Uses structured knowledge to foster hypothesis discovery, emphasizing novelty and feasibility.
- Experimental Preparation: Translates hypotheses into executable plans, incorporating protocol design and reproducibility tracking.
- Experimental Execution: Utilizes closed-loop control for real-time experimentation, adaptive planning, and empirical data validation.
- Scientific Writing: Transforms experimental findings into structured narratives, ensuring citation-grounding and ethical compliance.
- Paper Generation: Integrates all stages into autonomous manuscript creation, including drafting, visualization, revision, and publication.
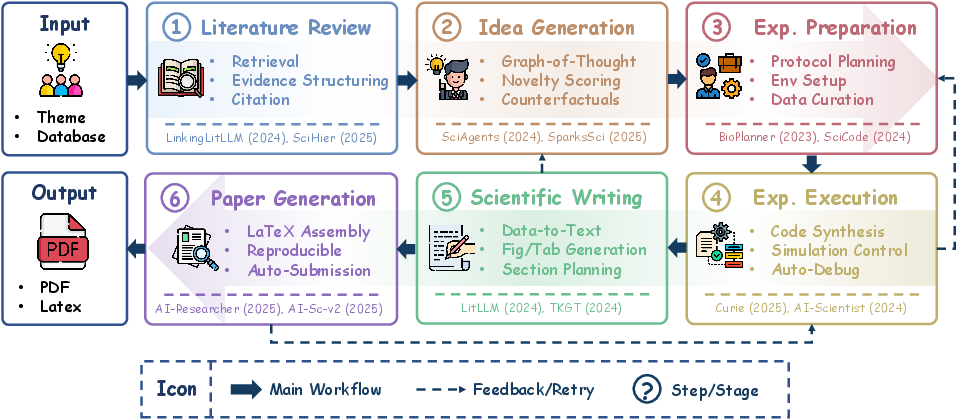
Figure 2: End-to-end workflow of an AI Scientist system. The stages represent the closed scientific loop, from knowledge synthesis to validated reports.
Evolutionary Trajectory
The research categorizes the evolution of AI Scientists into three phases:
Applications and Implications
AI Scientist systems are being applied across diverse scientific domains:
- General Systems: Offer domain-independent frameworks for automating full scientific workflows. Examples include The AI Scientist v1 and v2, focusing on cross-disciplinary research automation.
- Domain-Specific Systems: Specialized in chemistry, biology, physics, and social science, showcasing significant advancements in automated experimentation and discovery protocols.
The paper addresses implications of AI Scientists, highlighting challenges in reproducibility, cross-domain generalization, and ethical governance. Suggested future directions include enhancing reproducibility-by-design, uncertainty quantification, modular architectures, and ethical frameworks for AI-generated science.
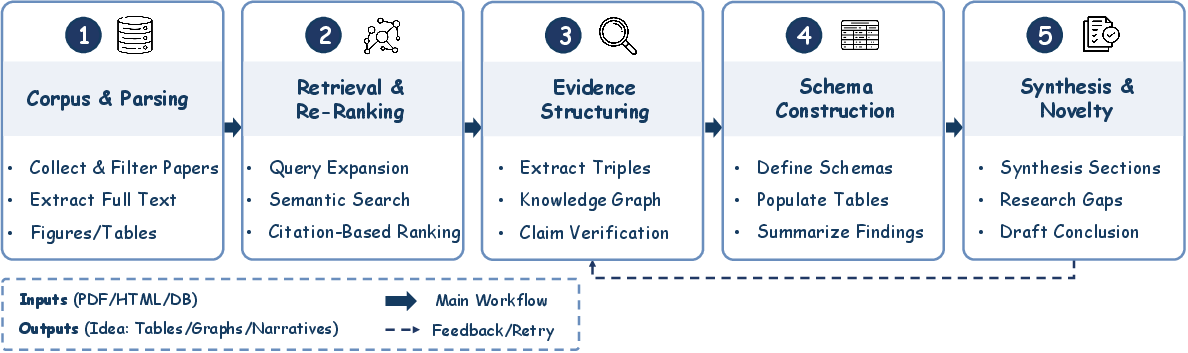
Figure 4: Pipeline for Automated Literature Review. The workflow transforms scientific data into structured knowledge through iterative refinement.
Conclusion
"A Survey of AI Scientists" provides a comprehensive synthesis of AI Scientist research, highlighting methodological advancements and the paradigm shift towards autonomous scientific discovery. The paper identifies critical challenges and future directions emphasizing the importance of scalability, collaboration, and governance in AI systems' integration into scientific inquiry. These systems promise to augment human creativity and systematic exploration, redefining traditional scientific processes.
Through structured analysis and a forward-looking agenda, the survey serves as a roadmap for developing trustworthy AI partners in scientific discovery, fostering innovative collaboration between humans and AI systems.