- The paper introduces a novel framework where LLM agents iteratively refine strategies through an experience-driven lifecycle.
- The methodology combines offline self-distillation of strategic principles with online interaction and reinforcement learning for enhanced decision-making.
- The framework significantly outperforms traditional agent baselines on multi-hop question-answering benchmarks, showcasing improved adaptability and robustness.
EvolveR: Self-Evolving LLM Agents through an Experience-Driven Lifecycle
Introduction
The paper "EvolveR: Self-Evolving LLM Agents through an Experience-Driven Lifecycle" (2510.16079) presents a novel framework aimed at addressing the inherent limitations of current LLM agents. Traditional LLM agents are adept at tool use and reasoning but falter when it comes to learning from past interactions, treating each task as an isolated episode. This inability to build upon previous experiences restricts their capability to refine problem-solving strategies iteratively. EvolveR introduces a self-improving mechanism, enabling agents to learn from their own experiences through a structured, closed-loop lifecycle comprising Offline Self-Distillation and Online Interaction phases.
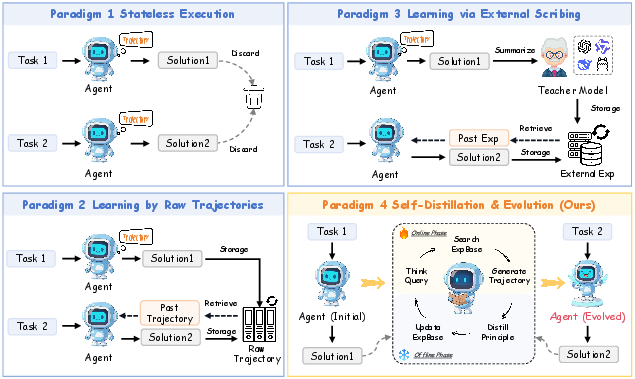
Figure 1: An illustration of four major paradigms for LLM agent learning. (1) Stateless Execution; (2) Learning by Raw Trajectories; (3) Learning via External Scribing; (4) EvolveR.
Methodology
EvolveR's lifecycle consists of two main phases:
Offline Self-Distillation: In this phase, agents distill interaction trajectories into a repository of abstract, reusable strategic principles. This involves transforming raw data into structured insights that can guide future decisions. The distillation process not only abstracts knowledge but also employs semantic deduplication and integration to maintain a high-quality experience base, enriched through empirical utility evaluation using dynamic scoring.
Online Interaction: Agents engage with tasks by retrieving distilled principles to enhance their decision-making process. This phase serves as a testbed for applying strategic wisdom, generating informative trajectories for the next cycle of distillation. The core novelty here is the strategic adaptation based on retrieved experience, aligning the agent's internal reasoning with proven strategies to streamline exploration.
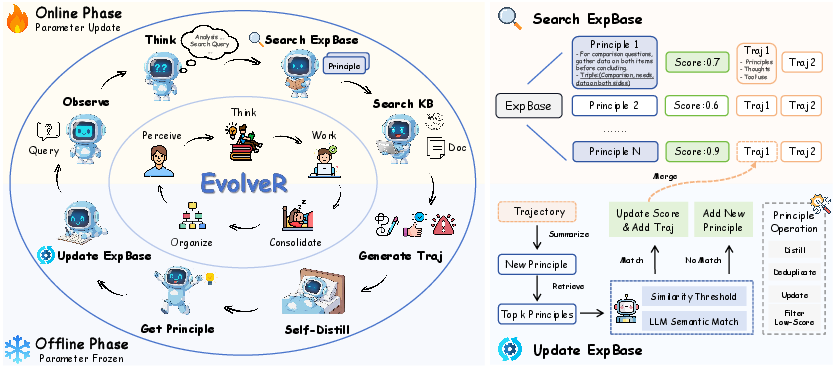
Figure 2: Overview of the EvolveR framework's experience lifecycle.
Experience Lifecycle and Policy Evolution
EvolveR's lifecycle is driven by a reinforcement learning mechanism that updates the agent's policy based on performance metrics derived from online interaction trajectories. The reward function balances task success and procedural correctness, integrated into Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) for efficient learning. Key operations such as strategic principle retrieval during deliberative reasoning loop, trajectory generation, and the iterative policy optimization fortify an evolutionary loop, allowing agents to continuously transform and refine strategies.
Numerical Results
EvolveR's efficacy is demonstrated through extensive empirical studies on multi-hop question-answering benchmarks. The framework significantly surpasses existing agentic baselines, validating the transformative potential of experience-driven evolution. The ablation studies provide further insights into the core components, highlighting that while smaller models benefit from external teacher-based distillation, larger models excel through self-distillation due to enhanced cognitive alignment. This scaling insight underscores EvolveR's adaptability and robustness across varied model architectures.
Several parallels exist between EvolveR and previous works in continual learning and reinforcement learning for LLM agents. Continual learning traditionally focuses on preserving knowledge, whereas EvolveR emphasizes active acquisition and refinement, akin to frameworks utilizing reflective reasoning and external memory. In reinforcement learning domains, EvolveR advances beyond stateless approaches by internalizing strategic principles that guide reasoning processes, enhancing autonomy and adaptive learning.
Conclusion
EvolveR provides a comprehensive blueprint for the development of autonomous LLM agents capable of self-evolution. By integrating experience-based strategic distillation within a closed-loop lifecycle, agents can not only leverage external data but also internalize the consequences of their actions for continuous improvement. This paradigm shifts focus from merely accessing knowledge to gradually constructing and refining expertise, promising a future of more adaptable, intelligent systems. Future developments might explore refined optimization techniques to further mitigate noise in experiential internalization, enhancing agent autonomy and strategic learning.
The implications are substantial, with potential advancements in agentic interpretation, personalization, and steerability. However, these advancements necessitate careful considerations regarding alignment and safety. As agents evolve independently, ensuring robust value alignment through strategic reward function design becomes imperative, introducing new challenges in AI development.



