- The paper extends the MDP framework to model LLM agents with multi-turn dialogues, tool integration, and stochastic feedback for effective RL training.
- Agent-R1's modular framework supports diverse environments by incorporating intermediate rewards and action masks to optimize multi-step interactions.
- Empirical studies on multi-hop question answering demonstrate significant performance gains, with GRPO achieving the highest accuracy among compared algorithms.
Agent-R1: Training Powerful LLM Agents with End-to-End Reinforcement Learning
Introduction
The development of LLMs has ushered in an era of advanced natural language processing capabilities, enabling substantial progress in tasks requiring high-level reasoning and interaction. This paper explores the potential of employing Reinforcement Learning (RL) to further evolve LLMs into autonomous agents proficient in actively interacting with environments. The central challenge addressed by the paper revolves around adapting RL methodologies, traditionally effective in static tasks, for the dynamic, multi-turn, interactive scenarios necessitated by LLM agents.
Reinforcement Learning in LLM Agents
The paper systematically extends the Markov Decision Process (MDP) framework to model LLM agents by capturing their complex behaviors in multi-turn dialogues and interactions with environments. This adapted MDP formulation includes:
- State Space: Unlike static models, LLM agents maintain comprehensive dialogue histories and environmental feedback, enabling informed decision-making across turns.
- Action Space: Token generation by agents can trigger external tool utilization, expanding beyond traditional text production.
- State Transition Probability: Introduces stochastic environmental feedback that influences the subsequent states beyond deterministic token generation.
- Reward Function: Enhances traditional sparse reward systems with intermediate process rewards to guide agents through complex interactions effectively.
These extensions lay the foundation for RL training in agentic environments, setting the stage for more efficient learning processes and strategic decision-making in LLM agents.
Agent-R1 Framework
Agent-R1 is introduced as a modular, flexible, and user-friendly RL framework designed to streamline the training of LLM agents. The framework is capable of integrating various environment interfaces, task scenarios, and computational resource requirements, exhibiting adaptability to diverse applications.
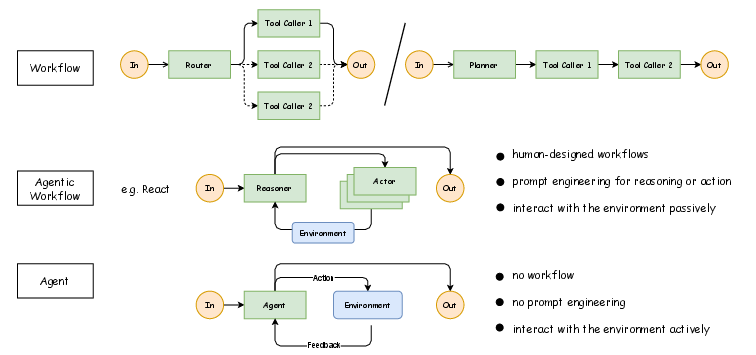
Figure 1: Comparison of workflows, agentic workflows, and autonomous agents. Workflows rely on human-designed routing or planning, while agentic workflows (e.g., ReAct) introduce iterative reasoningâacting loops. Fully autonomous agents remove predefined workflows and interact with the environment proactively through an end-to-end actionâfeedback cycle.
Central to Agent-R1 are two core components: Tool and ToolEnv, designed to facilitate interactive rollouts, crucial for RL-based training. Tools execute atomic actions, bridging agents with external capabilities, while ToolEnv orchestrates and interprets these interactions to refine the agent's learning pathway.
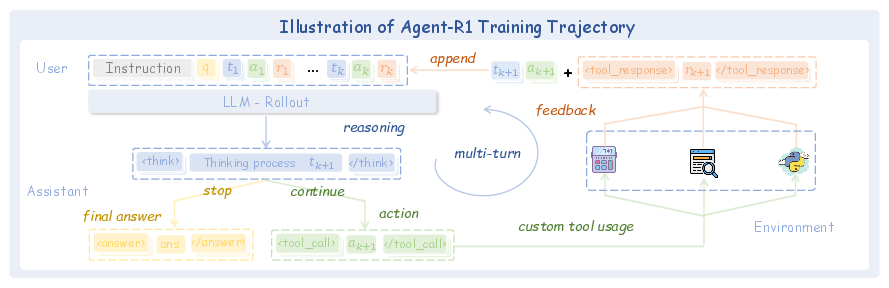
Figure 2: Illustration of the Agent-R1 training trajectory. The agent performs multi-turn reasoning and tool-based actions during rollout, receives environment feedback, and appends tool responses to form the next state. This trajectoryâcontaining thinking steps, actions, and feedbackâserves as the basis for reinforcement learning updates in Agent-R1.
The framework's modularity allows rapid adaptation to different environments, thus supporting the deployment of LLM agents across a wide spectrum of interactive settings.
Empirical Study
The empirical section of the paper assesses Agent-R1's impact by applying it to the multi-hop question answering task, demonstrating its proficiency in executing complex reasoning across documents. The paper validates Agent-R1's RL frameworks using algorithms like PPO, GRPO, REINFORCE++, and others in comparison to established baselines.
Results indicate significant performance improvements, with GRPO achieving the highest average Exact Match score, highlighting the framework's potential in refining agent training through RL.
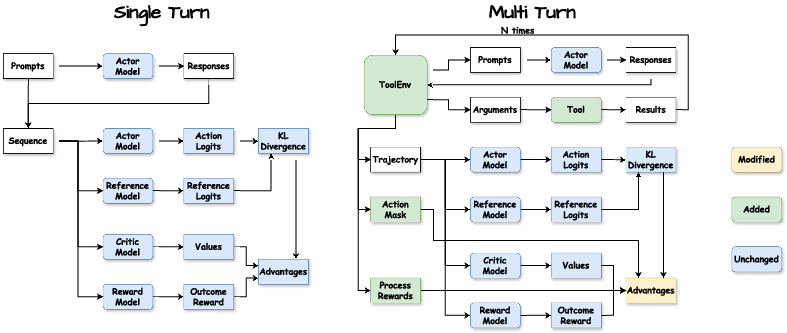
Figure 3: Flow diagram of Single-Turn RL and Multi-Turn RL(Agent-R1) in generation stage.
A comprehensive ablation analysis confirms the importance of the framework's policy optimization mechanisms, particularly the inclusion of action and advantage masks, demonstrating marked influence on learning outcomes and subsequent agent efficiency.
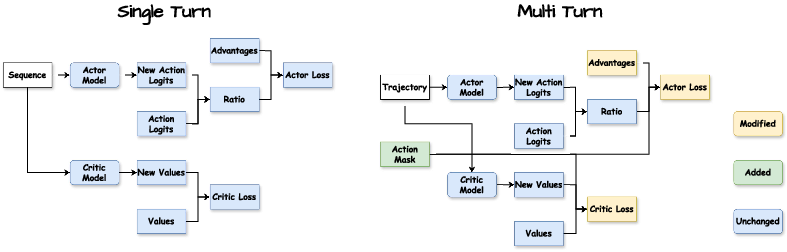
Figure 4: Flow diagram of Single-Turn RL and Multi-Turn RL(Agent-R1) in learning stage.
Conclusion
The paper offers substantial advancements in the training of LLM agents through Reinforcement Learning by providing a systematic extension of the MDP framework tailored to agentic needs. Agent-R1 serves as a pioneering platform exhibiting scalability, flexibility, and integration capabilities necessary for the development of sophisticated autonomous agents. This work not only highlights immediate benefits in agent performance but also lays robust groundwork for future research and development in AI, driving towards more general and adaptable intelligent systems. As AI continues to evolve, the insights from Agent-R1’s design and experiments will play a decisive role in shaping the trajectory of LLM agent capabilities.





