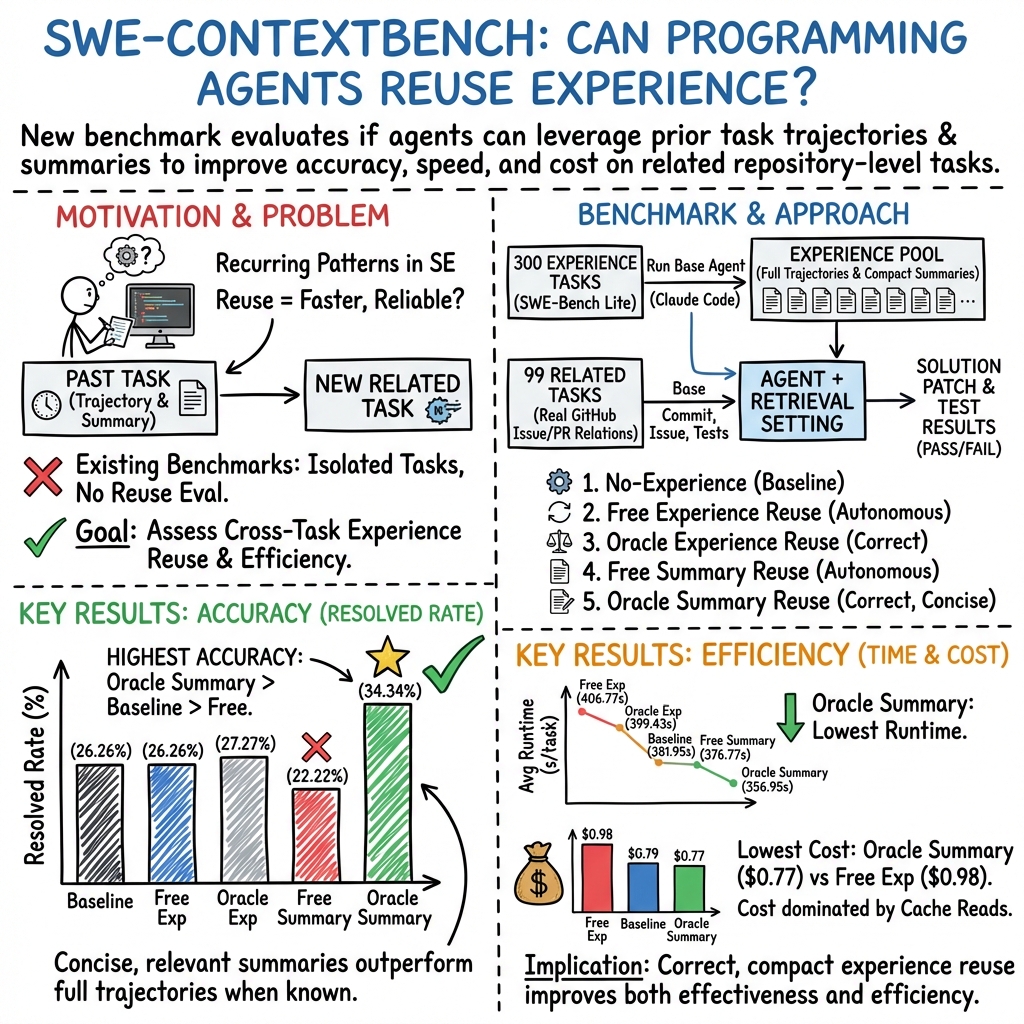
SWE Context Bench: A Benchmark for Context Learning in Coding
Abstract: LLMs are increasingly used as programming agents for repository level software engineering tasks. While recent benchmarks evaluate correctness in realistic codebases, they largely treat tasks as independent and do not assess whether agents can reuse experience across related problems. As a result, the ability of agents to accumulate, retrieve, and apply prior experience, as well as the efficiency gains from such reuse, remains difficult to measure. We introduce SWE-ContextBench, a benchmark designed to explicitly evaluate experience reuse in programming agents. Built on SWE-Bench Lite, SWE-ContextBench augments 300 base tasks with 99 related tasks derived from real dependency and reference relationships among GitHub issues and pull requests, forming task sequences with shared context. The benchmark evaluates agents along three complementary dimensions: prediction accuracy, time efficiency, and cost efficiency. Using SWE-ContextBench, we study multiple experience reuse settings, including oracle guided and autonomous retrieval, as well as full execution trajectories and compact summaries. Our results show that correctly selected summarized experience improves resolution accuracy and substantially reduces runtime and token cost, particularly on harder tasks. In contrast, unfiltered or incorrectly selected experience provides limited or negative benefits. These findings highlight the importance of experience representation and retrieval quality, and position SWE-ContextBench as a principled benchmark for studying experience reuse in programming agents.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Practical Applications
Immediate Applications
Below is a concise set of practical, deployable use cases that leverage the paper’s findings on experience reuse, summary-based memory, and efficiency metrics.
- Software/DevOps (industry): Pre-procurement benchmarking of code agents using SWE-ContextBench to compare accuracy, time, and cost
- Tools/workflows: CI job that runs agents on the 99 related tasks; dashboard reporting “Resolved,” FAIL_TO_PASS, PASS_TO_PASS, runtime, and token cost
- Assumptions/dependencies: Repositories have runnable test suites; reproducible environments; access to agent APIs and token accounting
- Developer tooling (industry): VSCode/JetBrains plugin that records fix trajectories and auto-generates compact “Fix Cards” (summaries) for reuse on related issues
- Tools/products: Experience pool manager; trajectory recorder; summary generator; retrieval panel that suggests relevant past fixes
- Assumptions/dependencies: Teams allow logging of agent actions; storage for summaries; basic issue/PR linking in repos
- Agent orchestration (software): Cost- and time-aware “memory gate” that prioritizes using concise summaries over full trajectories and includes a fallback to baseline solving
- Tools/workflows: Policy engine that triggers summary-first prompts; token budget monitor; guardrails for unhelpful memory (disable misleading summaries)
- Assumptions/dependencies: Reliable token usage metrics; configurable orchestration; stable API pricing
- QA/Testing (software): Automated guardrails using FAIL_TO_PASS and PASS_TO_PASS as acceptance criteria for AI-generated patches
- Tools/workflows: CI checks that require all FAIL_TO_PASS tests to pass and enforce no regressions on PASS_TO_PASS
- Assumptions/dependencies: Comprehensive tests; patch application pipeline; clear separation of test vs solution patches
- Open-source maintenance (industry/academia): GitHub Actions that mine and surface related issues/PRs to seed an experience pool and encourage better linkage for reuse
- Tools/workflows: Reference-analyzer action; “related-issues” labels; auto-generated summary comments on merged PRs
- Assumptions/dependencies: Project maintainers adopt templates and linking practices; access to GitHub metadata
- AI platform/model cards (industry): Publishing efficiency-aware benchmark results (accuracy, time, cost) for coding agents
- Products: Model cards that report SWE-ContextBench metrics and retrieval strategies tuned for summary-first reuse
- Assumptions/dependencies: Benchmark license compatibility; vendor transparency; periodic re-runs for updates
- Engineering management/Finance (industry): Token and runtime budgeting for agent workloads grounded in benchmark-derived efficiency profiles
- Tools/workflows: Budget planners; cost dashboards; SLAs that include efficiency targets (e.g., max runtime per task)
- Assumptions/dependencies: Predictable workloads; known pricing; alignment between engineering and finance
- Documentation/Knowledge management (industry): Auto-generated “summary of fix” sections stored in a team knowledge base to accelerate future triage
- Tools/products: Knowledge base integration; semantic search over summaries; “experience reuse” tags
- Assumptions/dependencies: Adoption in PR templates; quality summarization; data retention policies
- Security (industry): Minimizing broad context exposure by favoring concise, vetted summaries over full logs to reduce accidental leakage
- Tools/workflows: Secret scanning on trajectories; retrieval gating policies; summary sanitization steps
- Assumptions/dependencies: Security tooling integrated into CI; privacy constraints; access control on memory stores
- Education (academia): Course labs using SWE-ContextBench to teach efficiency trade-offs in agent-assisted software engineering
- Tools/workflows: Assignments contrasting baseline vs summary reuse; analysis of retrieval quality effects on outcomes
- Assumptions/dependencies: Compute quotas; dataset access; reproducible environments
Long-Term Applications
Below are forward-looking use cases that build on the benchmark’s insights and require additional research, scaling, or ecosystem development.
- Production memory OS for agents (software): Organization-wide “Agent Knowledge Graph” that mines relations among issues/PRs and serves high-quality, compact experience to agents
- Tools/products: MemOS-like memory supervisor; graph-based retrieval; continual summarization and deduplication
- Assumptions/dependencies: Scalable storage/compute; robust entity/linking; governance around data provenance and access
- Domain-adapted experience-reuse benchmarks (robotics/healthcare/finance/energy): SWE-ContextBench-style datasets for sequential, related tasks (e.g., maintenance logs, clinical triage, incident resolution)
- Products: ContextBench variants with validated outcomes beyond code; sector-specific test harnesses
- Assumptions/dependencies: High-quality, privacy-compliant datasets; standardized evaluation protocols; domain experts for curation
- Industry standards and certifications (policy/industry): Efficiency-aware benchmarks adopted in procurement and compliance to ensure responsible agent deployment
- Tools/workflows: Consortium-backed specs for accuracy/time/cost reporting; reproducibility requirements; audit trails
- Assumptions/dependencies: Multi-stakeholder participation; regulatory alignment; shared reference implementations
- Learned retrieval/ranking approximating oracle selection (software/ML): Models that predict the “right summary” to present, trained on task relationship signals and resolution outcomes
- Tools/products: Retrieval models with efficiency rewards; confidence calibration; drift monitoring
- Assumptions/dependencies: Labels for relatedness; safe RL policies; continuous evaluation
- Knowledge marketplaces (industry): Secure exchange of anonymized “experience summaries” between companies/teams to accelerate fixes across similar stacks
- Tools/products: Licensing and anonymization frameworks; federated search; IP-safe sharing protocols
- Assumptions/dependencies: Legal agreements; privacy tech; standardized summary schemas
- Continuous-learning agents with memory management (software): Agents that accumulate, compress, and selectively forget experience to stay efficient on large, evolving codebases
- Tools/workflows: Compression policies; usefulness scoring; automatic pruning and refresh strategies
- Assumptions/dependencies: Stable criteria for “useful experience”; robust telemetry; safe forgetting mechanisms
- Repository hygiene and refactoring for reuse (software): Automated suggestions to restructure issues/PRs and tests to maximize reuse potential and evaluability
- Tools/products: Reference-mining bots; linkage recommendations; test coverage diagnostics tied to FAIL_TO_PASS/PASS_TO_PASS distribution
- Assumptions/dependencies: Developer buy-in; minimal disruption to existing workflows; support from platform APIs
- Sustainability reporting (energy/policy): Efficiency-focused agent design tied to compute/energy metrics, enabling greener AI development practices
- Tools/workflows: Energy-to-token cost mapping; sustainability dashboards; efficiency targets in OKRs
- Assumptions/dependencies: Reliable conversion of compute to energy; organizational commitment to ESG goals
- Financial planning for AI operations (finance/industry): Dynamic budget allocation models using efficiency metrics to forecast agent operating expenses and ROI
- Tools/products: Scenario planners; cost simulators; efficiency SLAs
- Assumptions/dependencies: Stable pricing; observability over workloads; integrated finance/engineering processes
- Standardized curricula and assessments (academia/education): Programs emphasizing experience reuse strategies, retrieval quality, and efficiency metrics in AI+SE education
- Tools/workflows: Benchmark-aligned assignments; capstone projects building memory-augmented agents; shared evaluation rubrics
- Assumptions/dependencies: Broad adoption of datasets/benchmarks; institutional support; accessible compute resources
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.