- The paper presents DPPO, a metacognitive framework that iteratively alternates between RL for weakness detection and SFT for targeted skill refinement.
- It achieves a 54.3-point gain on VSI-Bench while maintaining performance on general benchmarks, demonstrating high data efficiency and minimal forgetting.
- The approach unifies preference learning strategies to scale embodied VLMs, enabling robust generalization and adaptive self-improvement in complex tasks.
Introduction
Embodied intelligence—integrating perception, reasoning, multimodal understanding, and real-world interaction in artificial systems—remains challenged by two principal bottlenecks: limited embodied data and the inefficiency of current learning paradigms. Existing approaches in vision-language modeling either pursue ever-larger heterogeneous datasets or architecturally-driven continuous control, yet both are limited by their reliance on passive, static datasets and lack mechanisms for adaptive self-improvement. The paper "Bridging VLMs and Embodied Intelligence with Deliberate Practice Policy Optimization" (2511.16602) introduces Deliberate Practice Policy Optimization (DPPO), a metacognitive training framework that iteratively combines reinforcement learning (RL) for weakness diagnosis with supervised fine-tuning (SFT) for the targeted refinement of discovered deficiencies. This unified meta-learning "metaloop" achieves continual, data-efficient capability acquisition.

Figure 1: Overview of DPPO, demonstrating the iterative RL–SFT metaloop and its adaptive dynamic data curation based on model weaknesses.
DPPO operationalizes metacognition through dynamic alternation between two phases:
- RL phase for exploratory weakness detection: Rollouts under the current policy uncover persistent error modes and skill gaps using difficulty-aware sampling and multi-objective reward functions. Trajectories are assigned success metrics and sampled preferentially to reveal model limitations.
- SFT phase for targeted competence expansion: RL-exposed weaknesses are distilled using high-quality supervision, either from reference teacher models or curated expert data, along with general data for catastrophic forgetting mitigation.
This process forms a persistent loop, dynamically rebalancing data difficulty and preventing skill drift through multi-source replay. The DPPO framework is formally unified under preference learning, where SFT and RL are cast as special cases (single positive vs. ranked preferences) within a probabilistic modeling objective. This grounding both integrates and generalizes previous post-training paradigms (direct preference optimization, rank-based RL fine-tuning, hybrid alignment schemes).
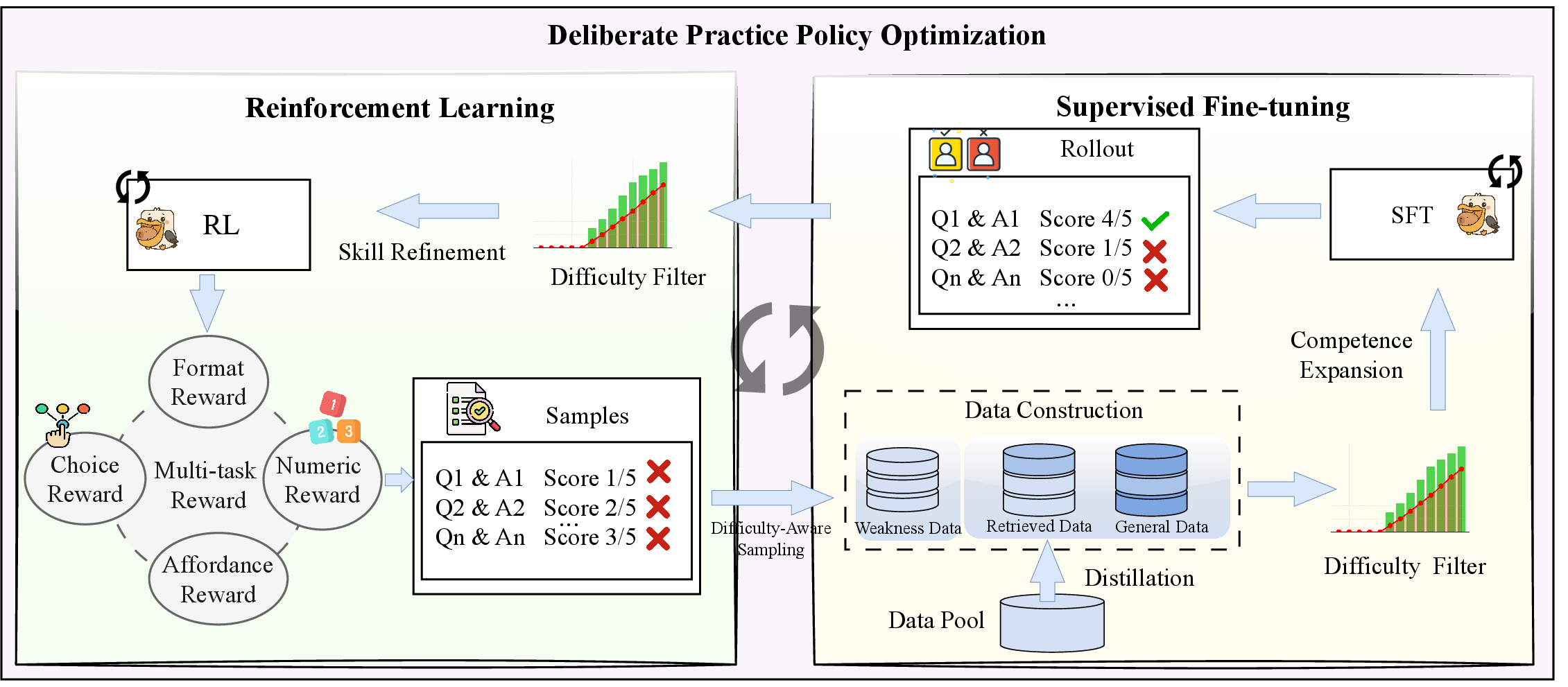
Figure 2: Schematic of the training pipeline, showing iterative rollout logging and difficulty-aware data selection for rapid ability gains and stable alignment.
Empirical Evaluation
Experimental Setup
DPPO is instantiated on Pelican-VL 1.0, a family of vision-language embodied models (up to 72B parameters). Training employs a curated multimodal dataset constructed for four embodied AI core capabilities: spatial/physical reasoning, temporal/scene understanding, perception/grounding, and decision/task planning. Training proceeds in metaloop cycles, starting with short-horizon tasks and incrementally expanding temporal context length to promote generalization across increasingly complex embodied interactions.
Over three metaloop cycles, Pelican-VL exhibits monotonic improvements in embodied benchmarks, with general-domain performance (MVBench) remaining stable, indicative of minimal catastrophic forgetting. Difficulty-aware sampling during RL phases accelerates competence acquisition in harder benchmarks.

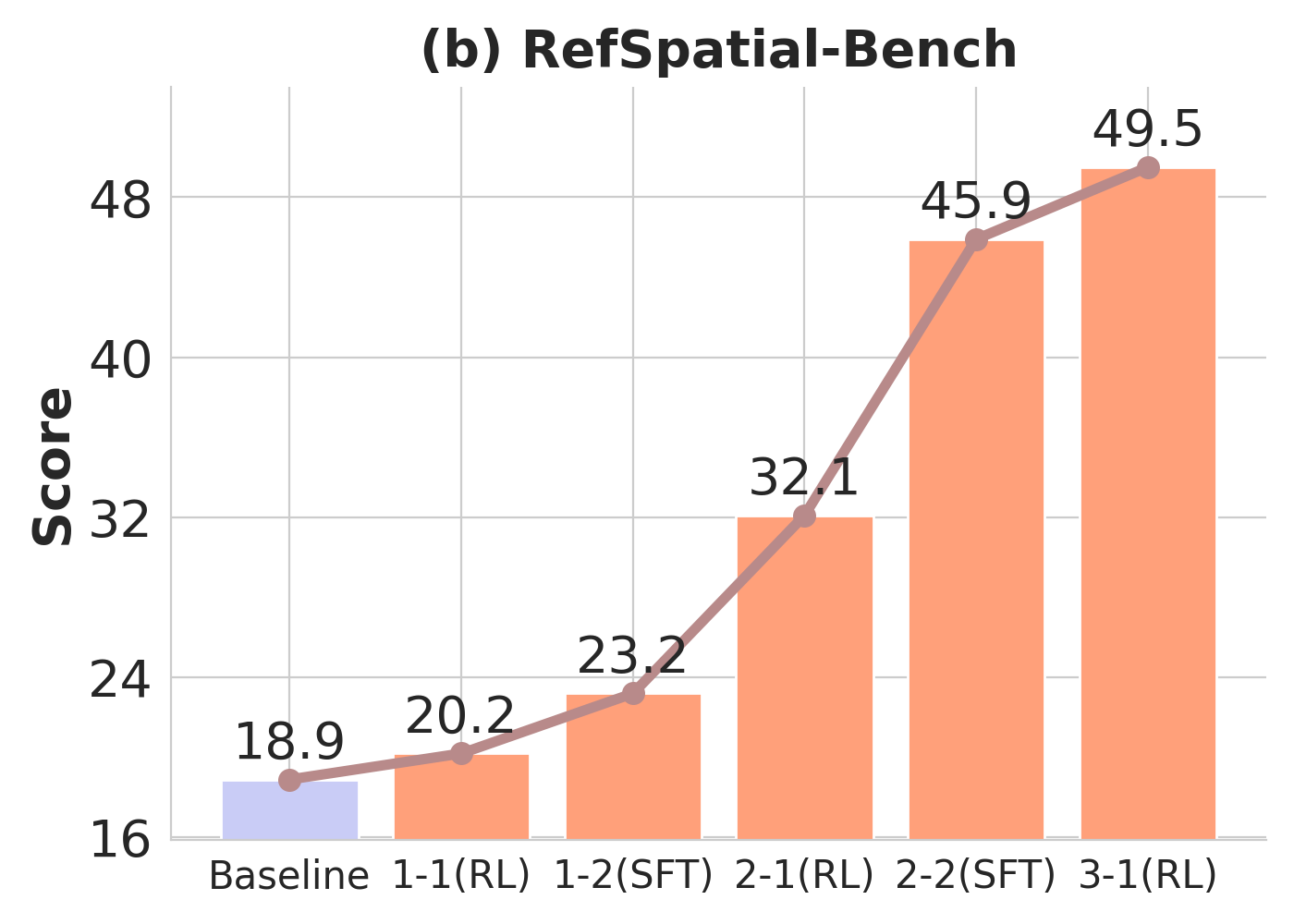



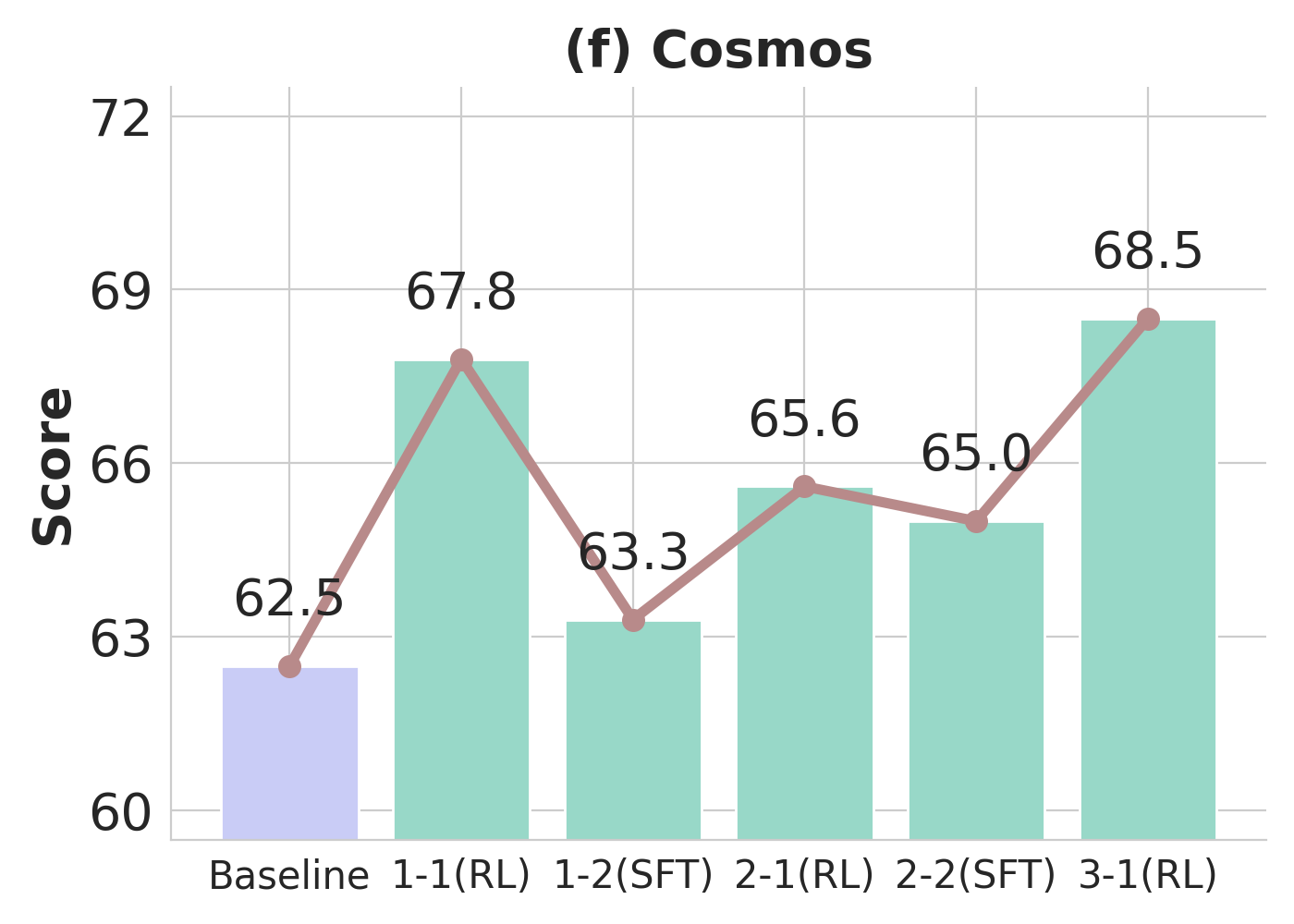
Figure 3: Performance trajectory of Pelican-VL 72B through training loops, illustrating compounding gains in embodied skills and stable behavior on general datasets.
Progressive RL training induces marked distributional shifts in model capabilities, measured by reductions in unsolved task fractions and movement of trajectory embedding centroids (visualized via t-SNE).




Figure 4: Distributional shift in task mastery during RL—a steady reduction in unsolved tasks and increased coverage of solution space.

Figure 5: Trajectory embedding centroid evolution across DPPO metaloop cycles, showing how distinct benchmarks induce task-specific representation changes.
Ablation and Catastrophic Forgetting
A critical result is that DPPO achieves a 54.3-point performance gain on VSI-Bench with only a 1.9-point drop on MMStar (a general benchmark), outperforming both standalone SFT and RL baselines. Classical RL exhibits substantial performance collapse on out-of-domain data, whereas DPPO’s adaptive replay and rebalancing curtail this issue significantly.

Figure 6: Comparison of SFT, RL, and DPPO—DPPO simultaneously yields superior performance gains on in-domain tasks and negligible forgetting on general data.
Scaling and Benchmark Comparisons
On an extensive battery of benchmarks, Pelican-VL 1.0 achieves:
- 20.3% improvement over its base model
- 10.6% higher average than open-source 100B-parameter scale models
- On some tasks, outperforms closed commercial models exceeding 200B parameters
This validates both the alignment and scaling efficiency of the DPPO framework, establishing competitive or superior performance in real-world embodied reasoning and planning tasks.


Figure 7: Radar plot showing Pelican-VL 1.0 (72B) compared to other models across nine embodied reasoning dimensions; DPPO leads in Physical, Quantitative, and Decision reasoning even versus larger-scale models.
Implications and Prospects
Theoretically, DPPO demonstrates that alternating RL and SFT can be rigorously framed as preference learning, supporting unified objective optimization and revealing their complementary roles. Practically, DPPO transforms rare, high-value feedback into systematic skill acquisition—maximizing sample efficiency and enabling continual, diagnostic model improvement without growing data dependence. The integration of automatic weakness detection, targeted data curation, and staged curriculum design is crucial for future scalable, self-improving robotic agents.
The release of Pelican-VL and DPPO, along with an open benchmarking and diagnostic framework, has substantive potential to catalyze reproducible research in embodied AI. This could accelerate transitions toward self-evolving, modality-generalist intelligence with tighter simulation-to-real transfer, reduced capital/resource costs, and more robust generalization.
Conclusion
The DPPO framework is a metacognitive "training engine" for embodied vision-LLMs. It unifies RL and SFT under a dynamic, preference-optimized loop, achieving state-of-the-art data efficiency, capability generalization, and catastrophic forgetting avoidance. Numerical results underscore substantial performance advantages over both SFT and RL, as well as closed-source models at much larger scale. DPPO’s theoretical grounding and practical pipeline constitute a new foundation for the development of scalable, adaptive, and diagnostically intelligent embodied agents. Future developments may include fully autonomous self-improving ecosystems, more granular diagnostic tools, and tighter hardware-in-the-loop learning integrations, driving progress toward the realization of general-purpose embodied AI.

















