- The paper presents a novel CoT-based Synthesizer that merges multiple candidate answers, addressing pitfalls of Best-of-N and Self-consistency methods.
- The methodology employs diverse response generation and logical analysis to synthesize coherent answers even from flawed candidate responses.
- Experimental results demonstrate significant improvements in reasoning tasks, with smaller models attaining competitive accuracy against larger LLMs.
The paper introduces the CoT-based Synthesizer, a novel method aimed at improving the performance of LLMs on complex reasoning tasks by synthesizing answers from multiple candidate responses. This approach addresses limitations in existing inference scaling methods such as Self-consistency and Best-of-N, which fail to produce correct answers when all candidate responses are incorrect.
Introduction
LLMs have made significant strides in NLP; however, they often struggle with complex reasoning tasks requiring precise answers. Traditional methods like Best-of-N select the highest-scoring answer, but these methods evaluate candidate responses independently, missing potential relationships between them. Self-consistency selects the most frequently generated response, relying on exact matches which limits applicability in open-ended tasks. The proposed CoT-based Synthesizer leverages CoT reasoning to synthesize superior answers by analyzing complementary information from flawed candidate responses, even when none is correct. Figure 1 visually highlights the capability of synthesizing correct answers from incorrect candidate responses.
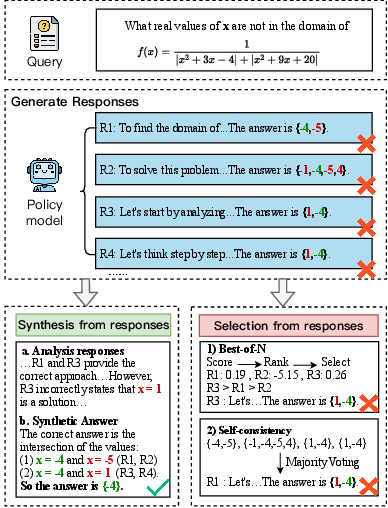
Figure 1: An example of our method in mathematical reasoning. Even when the policy model generates all incorrect responses, our method can still leverage their strengths to produce the correct answer.
Methodology
Synthesizer Inference
The CoT-based Synthesizer involves several stages to generate and improve responses:
- Diverse Response Generation: Using a high sampling temperature and Top-P sampling, the policy model generates diverse candidate responses, ensuring relevant and coherent responses.
- Response Analysis and Synthesis: The Synthesizer investigates candidate responses to discern logical coherence and synthesizes them into a high-quality response. This process entails analyzing the frequency, relevance, and accuracy of responses, enabling the construction of a coherent answer even when no candidate is fully correct.

Figure 2: An overview of our method. (1) Synthesizer Inference: The policy model generates diverse candidate responses, which are analyzed and synthesized by the CoT-based synthesizer to produce a high-quality final response. (2) Data Generation Pipeline: The pipeline combines a diverse response generation process using a sampling LLM with query-response relationship analysis to construct high-quality synthetic data. (3) Synthesizer Training: The generated dataset is then used to train the model via SFT to enhance reasoning and synthesis capabilities.
Data Generation Pipeline
To complement Synthesizer Inference, a robust data generation pipeline is essential for training. This involves generating synthetic responses using sampling LLMs and filtering them to ensure quality, thereby creating diverse datasets for training smaller models effectively.
Synthesizer Training
The constructed dataset is used to train models on synthesis tasks, enhancing their capability to leverage provided candidate responses accurately. This training enables the model to synthesize coherent outputs, improving inference accuracy significantly.
Experiments
The evaluation of the CoT-based Synthesizer across various NLP benchmarks and models demonstrates significant performance enhancements over existing methods. The Synthesizer allows smaller models like Llama3-8B-Instruct to achieve better accuracy even when handling complex reasoning tasks with larger LLMs such as GPT-4o.
Conclusion
The CoT-based Synthesizer represents a substantial advancement in inference scaling strategies. By synthesizing candidate responses through CoT-based analysis, it overcomes the limitations of traditional methods, significantly enhancing LLM performance across reasoning tasks. The automatic data generation pipeline ensures lightweight and efficient model training, making it widely applicable to various NLP applications. The success of this method suggests promising directions for future research in improving LLM reasoning capabilities and synthesis efficiency through further scaling and optimization.



