- The paper introduces WorldMM, a unique multimodal memory agent that integrates episodic, semantic, and visual memories for enhanced long video reasoning.
- It employs an adaptive retrieval strategy to dynamically fuse multi-scale temporal and visual information, effectively addressing context capacity limitations.
- Experimental results demonstrate an 8.4% performance improvement over state-of-the-art methods in perceptually and relationally complex video reasoning tasks.
A Detailed Analysis of "WorldMM: Dynamic Multimodal Memory Agent for Long Video Reasoning"
Introduction
The paper "WorldMM: Dynamic Multimodal Memory Agent for Long Video Reasoning" (2512.02425) addresses the challenges presented by video LLMs when tasked with understanding extremely long video sequences. Current video LLMs exhibit competence when dealing with short clips but encounter difficulties when scaling up to videos spanning several hours or days. This is attributed to limited context capacity and loss of important visual details during abstraction. While memory-augmented methods have offered a degree of mitigation through textual summaries, they lack the complete integration of visual evidence required for effective reasoning. WorldMM introduces a novel approach by constructing multiple types of memory—episodic, semantic, and visual—to facilitate dynamic retrieval and reasoning from long video streams.
Multimodal Memory Construction
WorldMM builds three types of memory: episodic memory, which indexes factual events across multiple temporal scales; semantic memory, which updates conceptual knowledge continuously; and visual memory, which preserves scene-based information. This architecture addresses two main limitations of existing models: the failure to incorporate visual information during retrieval and prediction and the restriction caused by fixed temporal scales of event retrieval.
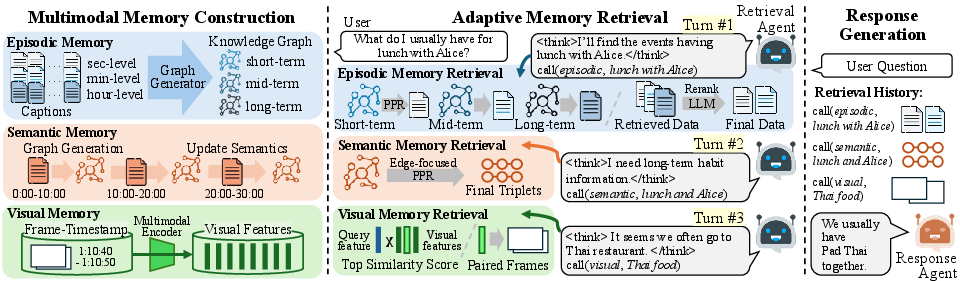
Figure 1: Overview of WorldMM showcasing its three complementary memory types and adaptive retrieval methodology.
Episodic Memory
Episodic memory consists of temporal knowledge graphs formed by parsing video segments into captions and then triplets detailing entity-action relationships. This multilayered approach enables the model to represent events over various temporal scales: seconds, minutes, and hours.
Semantic Memory
Semantic memory evolves by integrating high-level conceptual knowledge through triplet-based embeddings that ensure continuity and coherence across temporal divisions of the video. This construction is crucial for understanding relationships and habitual actions.
Visual Memory
Visual memory complements text-based memories by segmenting video streams into short, fixed-length parts, indexed either via features or timestamps. It facilitates retrieval by grounding text in visual context, essential for tasks requiring nuanced spatial reasoning.
Adaptive Memory Retrieval
WorldMM leverages an adaptive retrieval agent to dynamically integrate information from these diverse memories, optimizing the query handling process. The retrieval mechanism is iterative, focusing on progressively enhancing its strategy until the sufficient detail is collected to address the user query.
Episodic Retrieval Strategy
The episodic retrieval is achieved through a coarse-to-fine, multi-scale scouting approach. Captions are initially retrieved based on their relevance to the input query's context, and then further refined through cross-scale analysis.
Enrichment through Semantic Memory
Semantic retrieval evaluates edge-based relationships within graphs to extract long-term reasoning and knowledge specific to entities and their interactions. This approach substantially enriches understanding when reasoning over complex, interrelated behavioral or conceptual queries.
Visual Contextualization
Visual retrieval works on two modalities: feature-level cues guided by semantic similarity, and timestamp-based access for direct retrieval of relevant visual frames. This dual-mode capability ensures that the model can reveal visually grounded insights without overwhelming irrelevant contextual data.
Experimentation Results
Across five benchmarks that span durations from hours to weeks, WorldMM demonstrates a significant improvement in performance, achieving an average 8.4\% higher score than current state-of-the-art methods. Specifically, advantages were noted in categories reliant on perceptual and relational understanding, where visual and semantic memories are diversely leveraged.

Figure 2: Memory type utilization across categories in EgoLifeQA: illustrating diverse application of multimodal memory types.
Moreover, WorldMM stands out for its capacity to retrieve information at varying granular levels over comprehensive temporal spans, evidenced by its superior temporal intersection over union (tIoU) scores in scenarios where context integration was critical for accurate reasoning.



Figure 3: Average tIoU performance highlights WorldMM's superior ability to dynamically integrate temporal scopes in reasoning.
Conclusion
WorldMM sets a new benchmark for long video reasoning by offering a robust framework for integrating multimodal memories through adaptive retrieval systems. Its unique memory structure facilitates reasoning that is both temporally comprehensive and multimodally rich. Future avenues in AI research could explore extensions of this approach to encompass more varied types of multimedia content, further pushing the boundaries of context-rich AI reasoning. The promise of WorldMM lies in its potential applications ranging from interactive AI glasses to autonomous household robots, all benefiting from its sophisticated contextual understanding. However, ethical considerations of privacy and data security require stringent regulation as deployment broadens.




