- The paper presents a novel framework that employs latent-level collaboration among heterogeneous experts to enhance multi-LLM performance.
- It uses a lightweight router to select top-K experts and aggregates hidden states via cross-attention, significantly improving in-distribution and out-of-distribution accuracy.
- The approach maintains computational efficiency by keeping pre-trained backbones frozen, scaling accuracy with more experts while minimizing overhead.
Mixture of Thoughts: Learning to Aggregate What Experts Think, Not Just What They Say
Introduction
In the field of LLMs, leveraging the specialization of each model is pivotal for achieving superior performance across various domains such as mathematics, coding, and general reasoning. Existing multi-LLM frameworks are constrained by either routing a query to a specific expert, aggregating outputs through costly exchanges, or fusing homogeneous model weights into a singular entity. The "Mixture of Thoughts" (MoT) introduces a novel framework of latent-level collaboration among heterogeneous experts within an efficient global routing mechanism.
Methodology
MoT utilizes a lightweight router to select the top-K most relevant experts and designates one as the primary expert responsible for final output generation. The remaining experts contribute through interaction layers which collaborate at a hidden state level rather than output aggregation. These layers integrate hidden states into a shared latent space where cross-attention facilitates the primary expert to aggregate insights from other active peers.
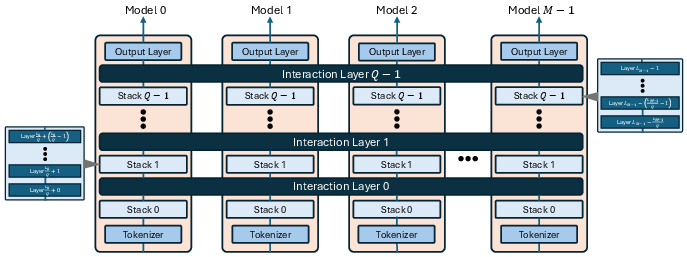
Figure 1: Heterogeneous expert integration in MoT. Each expert with Lm layers is divided into Q stacks, enabling Q levels of interaction. After each stack, routed experts project hidden states into a shared latent space; the primary expert aggregates these via cross-attention before proceeding.
The framework keeps pre-trained expert backbones frozen, thereby reducing the complexity and computational overhead typically involved in multi-turn exchanges or parameter fusion approaches.
Results
Across five in-distribution benchmarks, MoT achieves considerable performance improvements, surpassing the state-of-the-art systems by +0.38% and +2.92% in average accuracy over routing and aggregation-based methods, respectively. For example, MoT outperformed the single model baseline by +10.95% in in-distribution tasks and improved robustness with +9.03% better accuracy in out-of-distribution benchmarks.

Figure 2: Accuracy radar plot across OOD and ID tasks, showing MoT outperforming base models and state-of-the-art routing baselines.
The efficiency preserved through the single-pass inference aligns computation costs closely with routing baselines, enabling practical deployment without iterative overhead.
Analysis and Discussion
Robustness:
MoT maintains effectiveness despite expert dropouts during inference, which is crucial for real-world applications where model availability might fluctuate due to network or hardware issues.
Scalability:
The model composition experiment illustrates that accuracy improvements scale with the number of experts, reflecting MoT's capability to leverage diverse expert knowledge dynamically.
Parameter Efficiency:
Despite the performance gains, the additional parameter burden introduced by MoT's architecture remains minimal, reinforcing the practicality of integrating latent-space collaboration.
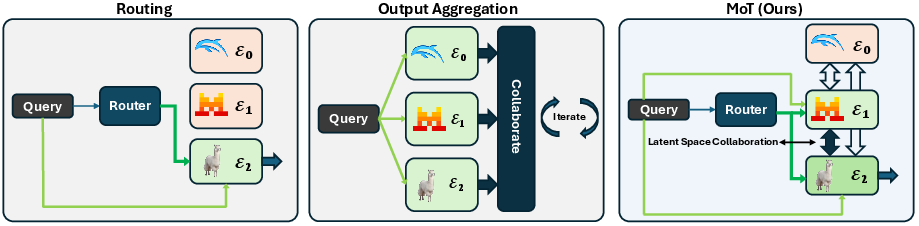
Figure 3: Prior paradigms (routing, output aggregation) vs. our MoT schematic. Dark green lines are for selected experts.
Conclusion
Mixture of Thoughts offers a significant enhancement to the collaborative capacities of multi-LLM systems, providing both refined accuracy and computational efficiency. By maintaining a fine-grained interaction at the latent level while preserving expert specialization, MoT sets the stage for future explorations where broader collaboration across diverse datasets and models can be achieved without sacrificing independence and specialization. The full implementation details and code are publicly available, enabling replication and further research.




