- The paper demonstrates the design of a honeypot that leverages LLMs to simulate realistic LDAP interactions for improved threat detection.
- It details a custom architecture and dataset creation process essential for fine-tuning the model to generate accurate LDAP responses.
- Results show a 100% syntax pass rate and robust simulation performance, indicating significant potential for advanced cybersecurity defenses.
Design and Development of an Intelligent LLM-based LDAP Honeypot
The paper "Design and Development of an Intelligent LLM-based LDAP Honeypot" explores the implementation of a deception tool leveraging LLMs to simulate the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). LDAP is pivotal in managing identity and access information in many organizational infrastructures, thus making it a lucrative target for cyber attackers. The proposed honeypot aims to enhance cybersecurity measures by evolving traditional honeypot techniques with AI-driven adaptability and flexibility.
Introduction
LDAP is widely used for querying directory services that store sensitive credential information. This information is often exploited in attacks targeting identity management systems, with methods ranging from direct LDAP injections to indirect exploits like the Log4Shell vulnerability. Misconfigurations in LDAP servers can expose networks to unauthorized access, making robust security measures essential.
Traditional honeypots have limitations in adaptability and complexity, prompting the integration of LLMs for more effective deception capabilities. The paper proposes an LLM-based honeypot to enrich threat detection and analysis, contributing effectively to defense strategies against such intrusion attempts.
System Design and Architecture
The architecture of the LLM-powered honeypot includes a local listener that processes incoming LDAP requests by converting them into JSON format, forwarding them to a remote service hosted on Google Colab. The service, utilizing a fine-tuned LLM, generates responses that are retransformed into LDAP format before being returned to the client. This workflow highlights the system's ability to simulate realistic LDAP server interactions with attackers.
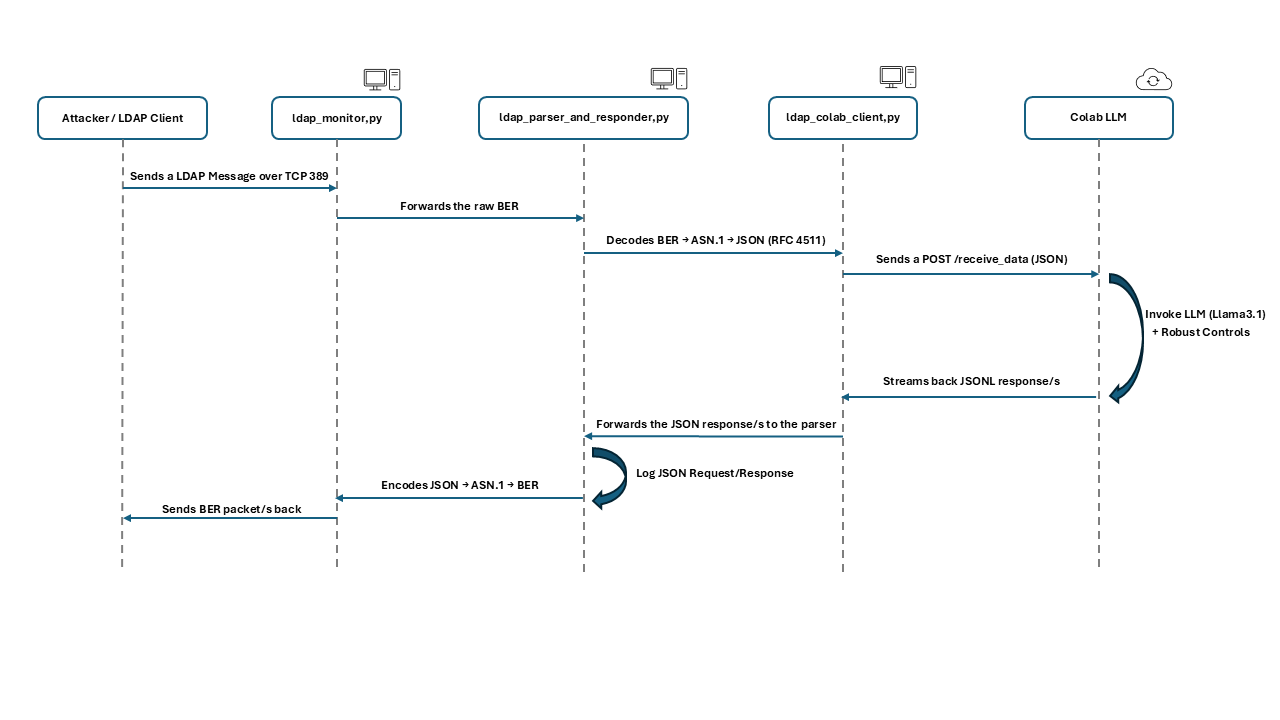
Figure 1: Overview of the Honeypot-LLM LDAP system architecture.
The choice to fine-tune an LLM, rather than use vendor-provided APIs, allows greater output control and system realism, albeit at a higher implementation cost. The paper underscores the importance of maintaining session context and managing encrypted communications for realism, noting these as areas for future development.
Dataset Creation
Creating a dataset was crucial given the absence of publicly available LDAP traffic data. The authors generated LDAP traffic using OpenLDAP servers and captured it in different file formats, later processing it into a unified CSV format. This dataset encompasses diverse operations, including authentication, queries, modification, and deletion commands.
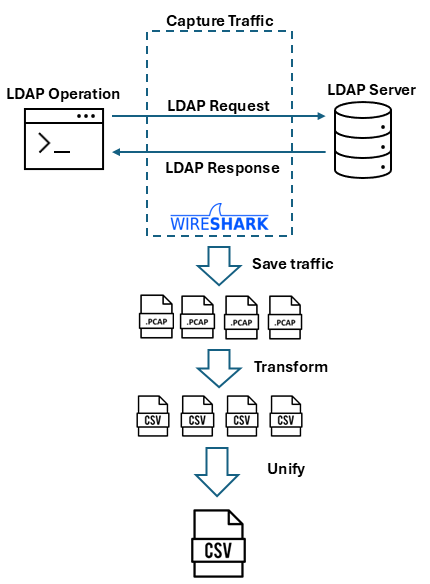
Figure 2: Dataset Creation Process
The dataset facilitates fine-tuning by providing realistic examples of LDAP interactions, aiming for optimal LLM performance when simulating various LDAP scenarios.
Evaluation and Results
The paper employs a custom evaluation framework tailored for the honeypot. This approach considers syntax, structure, key fields, and completeness, emphasizing realistic protocol simulation. Results show that the fine-tuned model yields substantial improvements in all metrics, particularly in structural consistency and request-response pairing.
While syntactically correct outputs were maintained, the fine-tuned model demonstrated robustness in operations beyond the capabilities of the baseline. Notably, it achieved a 100% Syntax Pass Rate, confirming its reliability in producing parseable JSON responses, and performed significantly better in complex LDAP operations like searches.
Conclusion and Future Directions
The research presents a pioneering use of LLMs in developing a honeypot for LDAP, addressing gaps in the literature and offering a robust tool for threat intelligence. While successful in simulating accurate LDAP interactions, the paper acknowledges potential enhancements that include handling encrypted traffic and exploring alternative LLMs for real-time response capabilities.
The foundation laid by this paper opens avenues for refined deployment strategies in cybersecurity defenses, suggesting that continued evolution of AI-powered honeypots can offer notable advances in protecting identity and access management systems. Future efforts may fine-tune session persistence and expand dataset diversity to ensure comprehensive coverage of potential attack scenarios.



