- The paper introduces X-Fusion, which integrates a vision tower with frozen LLMs via a dual-tower design, preserving robust language capabilities while processing images.
- It demonstrates that using cleaner image-to-text samples and targeted vision data enhances both image generation and understanding, with faster convergence noted in smaller models.
- Experimental results showcase X-Fusion's scalable integration of pretrained vision features, offering an efficient framework for unified multimodal AI.
X-Fusion: Introducing New Modality to Frozen LLMs
Introduction
The paper "X-Fusion: Introducing New Modality to Frozen LLMs" (2504.20996) proposes an innovative framework designed to extend the utility of pretrained LLMs by integrating multimodal tasks, specifically focusing on vision, without disrupting their existing language capabilities. The framework, named X-Fusion, uses a dual-tower design which incorporates modality-specific weights. This integration approach ensures that while the LLM parameters remain frozen, visual information can be processed for both understanding and generation. The paper highlights experimental evidence demonstrating X-Fusion's superior performance in multimodal tasks compared to other architectures.
Architectural Design Details
X-Fusion's architectural novelty lies in its dual-tower design. This configuration maintains the integrity of the LLM's language processing capabilities while introducing a vision-specific processing tower. The design comprises two separate components for each model layer: the frozen text transformer block and the trainable vision transformer block. The text tower processes language inputs using pretrained weights, while the vision tower facilitates the assimilation of visual data. Importantly, the text and vision towers can, in principle, have asymmetric architectures, allowing flexibility in model design.

Figure 1: We introduce X-Fusion - a novel framework that adapts pretrained LLMs (e.g., LLaMA) to new modalities (e.g., vision) while retaining their language capabilities and world knowledge.
Experimental Insights
Detailed experiments provide insights into optimizing the training of multimodal models. X-Fusion explores the impact of noise levels during training, demonstrating that cleaner images in the image-to-text samples enhance both image generation and understanding tasks. Furthermore, the inclusion of understanding-focused data improves generation quality. Feature alignment, particularly with smaller models, also accelerates convergence. The integration of pretrained representations for vision feature regularization offers additional pathways to enhance performance, especially beneficial in smaller architectures.
Performance metrics from experiments show that X-Fusion not only surpasses other baselines in image generation but also maintains competitive performance in image understanding tasks, all while preserving the intrinsic language capabilities of the LLM.
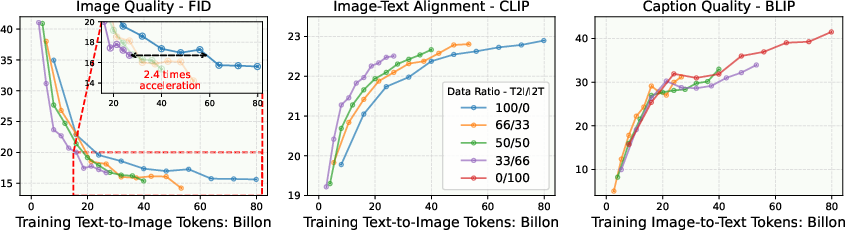
Figure 2: Performance of image generation and understanding at various data ratios. Increasing visual understanding data improves visual generation performance.

Figure 3: Performance of image generation and understanding at various noise limits in the image-to-text samples. Providing clear images for image-to-text samples enhances visual generation and understanding simultaneously.
Practical Implications and Future Directions
X-Fusion represents a significant step toward efficient integration of multimodal capabilities into LLMs, paving the way for more comprehensive AI models capable of processing and generating both verbal and visual content. Its flexible dual-tower design not only allows for scalability but also promises lower computational costs, addressing a major limitation of training large multimodal models from scratch.
Looking ahead, the paper suggests potential extensions of X-Fusion, including the application of the X-Fuse layer, transfer learning from pretrained diffusion models, and fine-tuning for specific downstream tasks. These directions suggest avenues for further enhancing model performance, particularly in terms of visual quality and multimodal feature synthesis.

Figure 4: Interactive Generation. Our X-Fusion model can follow user instructions to understand, generate, or edit images.
Conclusion
X-Fusion innovatively bridges the gap between language processing and vision tasks within LLMs, offering an efficient and scalable solution for multimodal integration. With strong experimental backing, the framework stands out for its ability to retain language capabilities while incorporating new modalities, making it a promising candidate for further developments in unified multimodal AI systems. As the landscape of AI continues to expand into diverse modalities, X-Fusion's approach is poised to inform future research and applications in building versatile and comprehensive AI models.





