- The paper introduces a novel graph-guided LLM framework that transforms codebases into directed heterogeneous graphs for improved code localization.
- It employs agent-guided search tools such as SearchEntity and TraverseGraph to enable effective multi-hop reasoning across complex code dependencies.
- Experimental results demonstrate up to 92.7% file-level accuracy and an 86% reduction in API costs compared to state-of-the-art models.
LocAgent: Graph-Guided LLM Agents for Code Localization
Introduction
Code localization is a pivotal task in software maintenance, focusing on identifying where modifications must be made within a codebase to resolve issues. The complexity arises from bridging natural language descriptions of problems with specific code elements, which demands reasoning across hierarchical structures and multiple dependencies. LocAgent is a framework that enhances code localization by employing graph-based representation techniques to parse codebases into directed heterogeneous graphs. This graph-based approach facilitates powerful multi-hop reasoning, enabling LLM agents to locate relevant code sections accurately and efficiently.

Figure 1: Code localization across four common programming scenarios. Given a codebase and an issue description, the goal of code localization is to identify the relevant code snippets that require modification to resolve the issue.
Methodology
Graph-Based Code Representation
LocAgent transforms codebases into directed heterogeneous graphs that encapsulate files, classes, functions, and their dependencies. This representation facilitates the creation of sparse indexes for optimizing the exploration of structures and content searches within large repositories. Nodes represent code entities (directory, file, class, function), and edges delineate relationships (contain, import, invoke, inherit). By capturing both explicit and implicit code relationships, LocAgent supports efficient traversal and reasoning across complex code structures, enabling agents to pinpoint code that requires updates even when it is not directly mentioned in issue descriptions.

Figure 2: Overview of LocAgent framework. LocAgent first parses the given codebase to build a graph-based code representation with various types of entities and relations. It then constructs sparse indexes for exploring structures and searching content. Using these indexes, it performs agent-guided searches that combine the graph and tools.
Agent-Guided Search
LocAgent introduces a set of unified tools that leverage graph representations for agent-guided code exploration. It includes SearchEntity for keyword-based code retrieval, TraverseGraph for multi-hop exploration, and RetrieveEntity for fetching detailed code entities. These tools facilitate efficient codebase navigation and autonomous agent operation, thereby improving accuracy and speed in finding localization targets. This system supports iterative exploration, enhancing an agent's ability to reason through complex dependencies that are crucial for resolving software issues effectively.
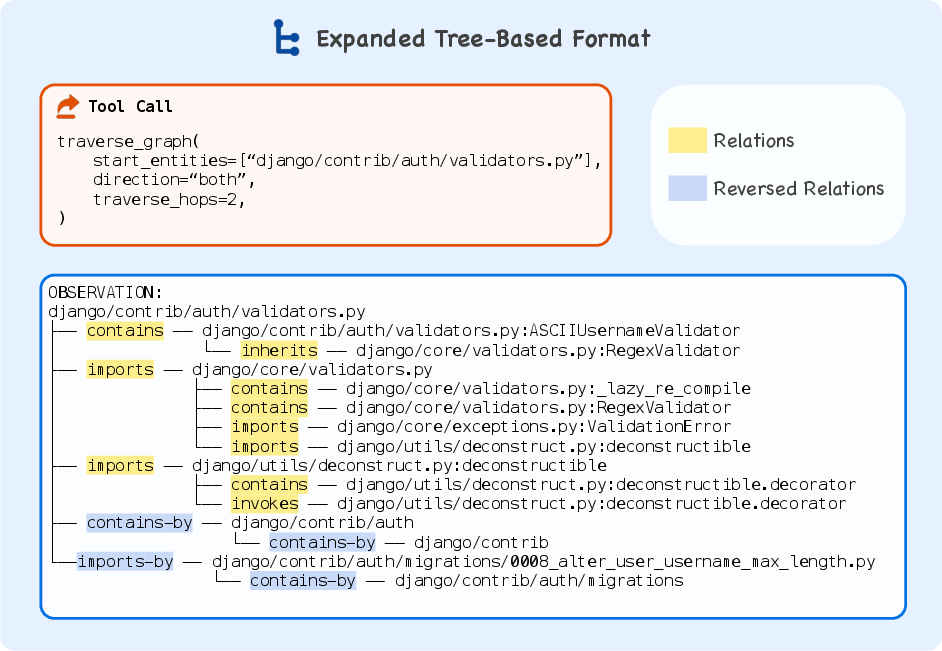
Figure 3: A truncated example of the expanded tree-based format for the output subgraph of tool TraverseGraph.
Experimental Results
LocAgent significantly improves localization accuracy across various complexity levels. Using benchmarks like SWE-Bench-Lite and Loc-Bench, the framework demonstrated substantial gains in accuracy (up to 92.7% for file-level localization) while reducing API costs by approximately 86% compared to state-of-the-art models like Claude-3.5. LocAgent's agent-driven, graph-based exploration proved robust even as task difficulty increased, maintaining competitive performance across different categories of code issues.

Figure 4: Performance analysis at different difficulty levels for file- and function-level localization. All agent-based methods and Agentless use Claude-3.5 as the localization model.
The fine-tuning of Qwen-2.5-Coder-Instruct models revealed enhancements in localization capabilities, matching or exceeding the performance of proprietary LLMs at a fraction of the cost. This fine-tuning was accomplished using successful trajectories from both Claude-3.5 and Qwen models, establishing a high-quality dataset for model refinement. The distilled models offer a practical alternative for real-world deployment scenarios where cost efficiency and data security are paramount.

Figure 5: Comparison of performance between the original and fine-tuned Qwen models. The metrics used are file-level Acc@5 and module/function-level Acc@10.
Conclusion
LocAgent advances code localization by integrating heterogeneous graph representations and agent-guided search strategies. This methodology streamlines codebase navigation, improves localization accuracy, and dramatically reduces operational costs. Future work may explore adapting LocAgent to diverse programming languages and further enhance model training with varied datasets to broaden its applicability and robustness in software engineering domains. These developments promise significant contributions to automated code maintenance, providing meticulous and efficient code localization strategies essential for evolving software ecosystems.






