- The paper introduces WaferLLM, a novel system leveraging a custom PLMR model to harness wafer-scale parallelism for significant inference throughput improvements.
- It proposes scalable algorithms like MeshGEMM and MeshGEMV, achieving up to 200x better utilization and 606x faster GEMV performance compared to GPU-based systems.
- The research demonstrates practical innovations such as prefill and decode parallelism and a KV cache shift method to effectively manage non-uniform memory and limited routing resources.
WaferLLM: LLM Inference at Wafer Scale
Introduction
"WaferLLM: LLM Inference at Wafer Scale" introduces WaferLLM, a novel system designed specifically for wafer-scale AI accelerators. Traditional inference systems primarily optimized for GPUs fail to leverage the full potential of wafer-scale integration, which integrates a vast number of AI cores in a mesh-based architecture with large distributed memory and extremely high bandwidth.
Architectural Overview
WaferLLM is underpinned by the PLMR device model, which is tailored to capture unique hardware characteristics of wafer-scale architectures. This model highlights four key properties crucial for efficient system design:
- Massive Parallel cores (P): Enabling fine-grained partitioning to manage millions of cores.
- Non-uniform memory access Latency (L): Mitigating the latency variations across extensive NoC hops.
- Constrained local Memory (M): Ensuring efficient memory usage given limited on-chip core memory.
- Limited Routing resources (R): Carefully managing communication paths within the mesh topology.

Figure 1: Key components in LLM inference on wafer-scale architecture.
Innovations in Wafer-Scale Parallelism
WaferLLM introduces innovative strategies for achieving wafer-scale parallelism:
- Prefill Parallelism: Employs mesh-based partitioning to maximize core utilization, replacing GPU-based GEMM operations with new PLMR-compliant distributed GEMM.

Figure 2: Prefill parallelism plan for massive-scale mesh architectures.
- Decode Parallelism: Utilizes a fine-grained tensor replication strategy to enhance parallelism and minimize communication overhead during the autoregressive token-by-token generation phase.
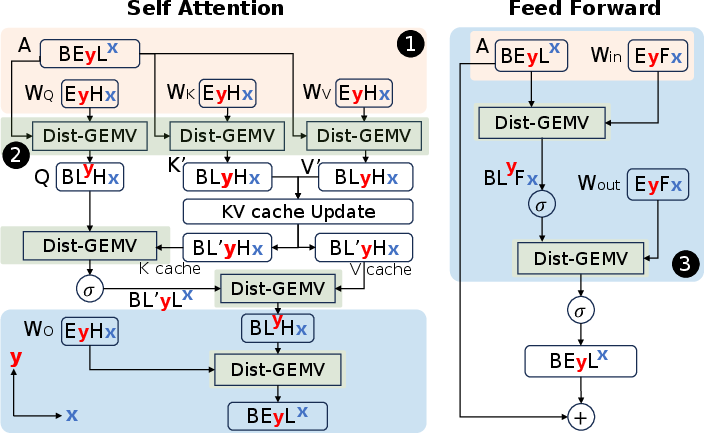
Figure 3: Decode parallelism plan, ensuring minimal communication costs.
- Shift-based KV Cache Management: Proposes a novel KV cache shift method for balanced core utilization, overcoming the skewed resource usage typical in GPU systems.

Figure 4: Comparison between KV cache concatenation and KV cache shift methods.
Scalable Algorithms for Efficient Inference
WaferLLM advances the field with two scalable algorithm variants tailored for wafer-scale accelerators:
Trailing traditional systems like T10 and Ladder, WaferLLM demonstrates a profound increase in inference throughput, boasting impressive improvements in both energy efficiency and computation speed:
- Achieves up to 200x better utilization of wafer-scale accelerators compared to existing systems.
- Delivers 606x faster GEMV operations than advanced GPU implementations, while significantly reducing energy costs.
Micro-benchmarks: MeshGEMM yields 2-3x speedup over leading GEMM algorithms such as SUMMA and Cannon.
Conclusion
WaferLLM effectively harnesses the unique capabilities of wafer-scale accelerators, achieving significant enhancements in LLM inference performance. As wafer-scale computing evolves, WaferLLM's methodologies pave the way for future developments in AI model deployment, emphasizing the role of massive parallelism and distributed architectures. Continued advancements in wafer-scale technology and corresponding software ecosystems are expected to further enhance inference capabilities, making WaferLLM a critical asset in AI computation.







