- The paper presents a unified checkpointing system that offers automatic online resharding and decoupled storage architecture for efficient LLM development.
- It introduces asynchronous tensor merging and zero redundant loading to handle irregular tensor sharding and reduce I/O overhead.
- Experimental results exhibit up to 529x reduction in checkpoint stalls and 3.5x faster loading times, emphasizing the system's efficiency across various frameworks.
ByteCheckpoint: A Unified Checkpointing System for Large Foundation Model Development
Introduction
The paper presents ByteCheckpoint, a PyTorch-native checkpointing solution designed to address the complex checkpointing needs of LLMs. Given the scale and diversity of LLM training practices, ByteCheckpoint facilitates automatic online checkpoint resharding and supports multiple training frameworks and storage backends efficiently.
Motivation and Challenges
Checkpointing LLMs is critical for ensuring fault tolerance in environments where models span thousands of GPUs. Traditional systems often assume consistent parallelism during save and load operations, which poses limitations when adapting checkpoints to varying GPU availabilities and task requirements. ByteCheckpoint overcomes these limitations by providing seamless integration across different parallelism strategies, including TP, DP, and PP, and frameworks such as FSDP and Megatron-LM.
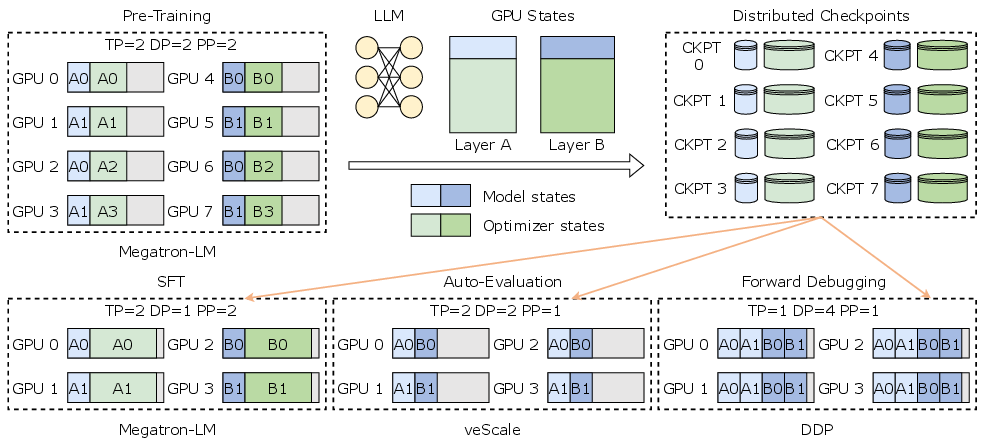
Figure 1: Various checkpoint resharding requirements in real-world LLM production. Users may use different parallelism strategies and training frameworks to save/load checkpoints for their tasks. We only show GPU states here for simplicity.
System Design
ByteCheckpoint's architecture is centered on a disaggregated storage system that separates data and metadata. This decoupling allows it to efficiently manage and transform checkpoints regardless of the training framework.

Figure 2: Storage architecture of ByteCheckpoint. In this example, distributed checkpoints are saved with four training processes.
Automatic Online Resharding
The system supports online resharding, where checkpoints saved under one configuration can be loaded into a different parallel configuration without the need for manual intervention. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for tasks that necessitate frequent changes in GPU allocation.
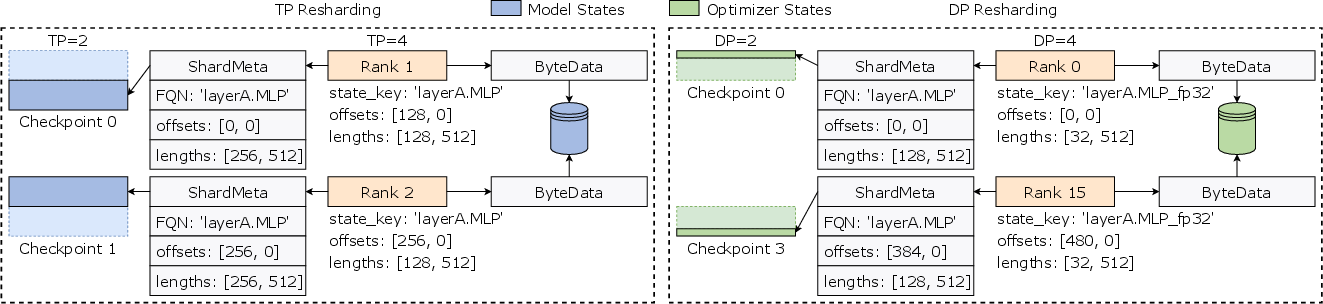
Figure 3: An illustration of automatic online resharding. Assume that each tensor shard is retained in its original shape before saving.
Addressing Irregular Tensor Sharding
ByteCheckpoint introduces asynchronous tensor merging techniques to handle cases where tensors are irregularly sharded, such as in certain optimizer states in Megatron-LM and veScale. This strategy reduces communication overhead and supports efficient parallelism remapping.

Figure 4: Irregular tensor sharding in the distributed optimizers of Megatron-LM.
Workflow and API Design
ByteCheckpoint distinguishes itself with a simplified API that abstracts the complexities of checkpoint management. Users interact with two main functions: bytecheckpoint.save() and bytecheckpoint.load(), which handle checkpointing details internally.
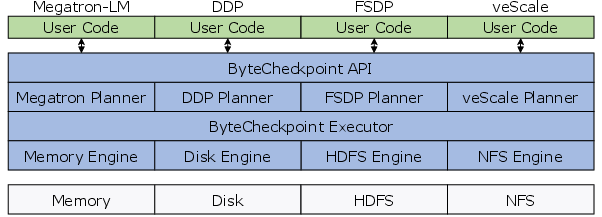
Figure 5: Workflow of ByteCheckpoint.
The paper details several optimization techniques to enhance checkpointing efficiency:
Experimental Results
Experiments demonstrate ByteCheckpoint's superiority over baseline systems in reducing checkpoint stalls by up to 529.22×, with loading times improved by up to 3.51×. These results underscore the system's efficiency and adaptability in real-world production environments.
Conclusion
ByteCheckpoint sets a new standard for checkpointing systems in LLM development by offering efficient, scalable solutions to the issues of saving and loading large distributed models. Its innovative architecture and optimization strategies pave the way for broader applications across diverse AI tasks, emphasizing its pivotal role in advancing LLM training practices.





