- The paper introduces a RL-guided unmasking strategy that jointly optimizes accuracy and efficiency in masked diffusion language models.
- It employs an adaptive planner head and Group Relative Policy Optimization to balance domain-specific, distillation, and efficiency rewards.
- Experimental results show a 4–9 point accuracy boost and 30–40% fewer denoising steps compared to prior heuristic and distillation methods.
dUltra: Ultra-Fast Diffusion LLMs via Reinforcement Learning
Motivation and Background
The emergence of masked diffusion LLMs (MDLMs) has established a competitive paradigm for generative language modeling, offering the potential for high-throughput, parallel generation. Despite their theoretical advantages over autoregressive (AR) transformers—such as robust error correction via denoising and flexible output infilling—MDLMs remain hampered by inefficient sampling; most open-source implementations decode only a small number of tokens per denoising step, and their practical throughput is comparable to optimized AR models with speculative decoding. The bottleneck arises from the conditional independence assumption required for parallel decoding: decoding dependent, ambiguous tokens in parallel introduces spurious modes and often yields incoherent sequences.
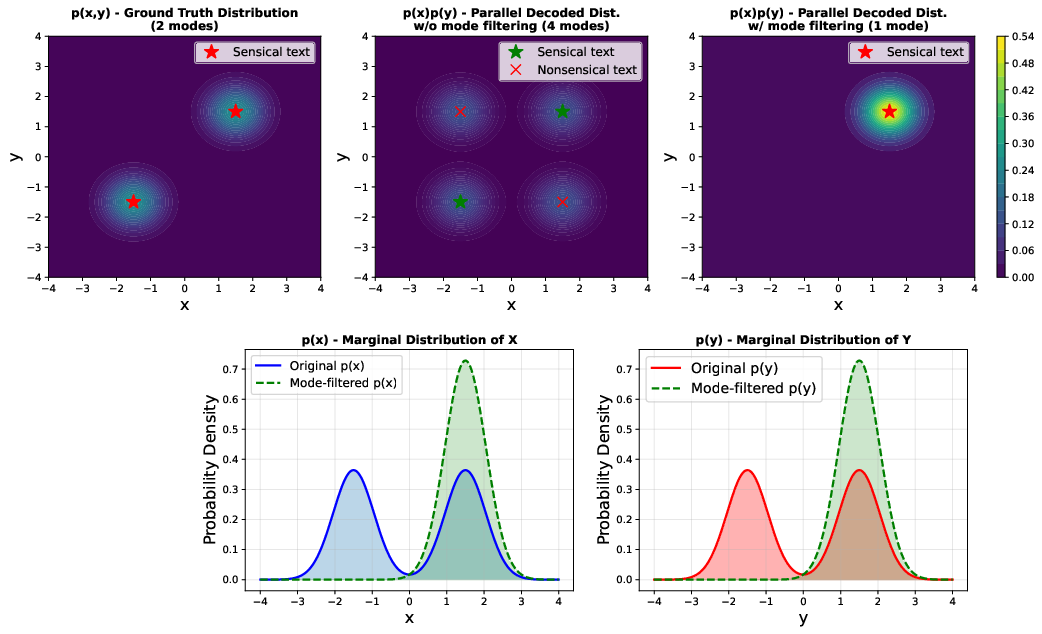
Figure 1: Parallel decoding of dependent ambiguous tokens can lead to unwanted modes.
This mode-mixing problem is exacerbated as one increases the degree of parallelism (number of tokens unmasked in each step), leading to failures in generation reliability, as illustrated in Figure 1. Existing heuristic and distillation-based samplers (e.g., dParallel, d3LLM) operate off-policy, imitating sampling trajectories generated by teacher models, which restricts exploration and limits distillation to the support of teacher policies. As a result, such methods cannot systematically surpass the performance and sample efficiency of the base models.
dUltra addresses these limitations by formulating unmasking order as a reinforcement learning (RL) problem. By learning adaptive unmasking policies online and integrating domain-verifiable and distillation-based rewards, dUltra achieves significantly improved accuracy-efficiency trade-offs. Notably, it brings open-source diffusion LLMs closer to the "diffusion supremacy" regime, outperforming prior MDLM acceleration strategies and moving towards the inference efficiency exhibited by recent commercial diffusion LMs.
Methodology
Adaptive Unmasking Planner via RL
dUltra introduces an explicit unmasking planner head, a lightweight module predicting per-token unmasking probabilities conditioned on the last-layer hidden states of the diffusion LM. At each denoising step, candidate masked tokens receive independent Bernoulli probabilities for unmasking, allowing the planner to flexibly orchestrate the unmasking trajectory. This independence is computationally efficient, yet the parameterization incorporates global sequence context via self-attention.

Figure 2: dUltra overview—accuracy versus NFE (left); architecture illustrating the base MDLM, parallel token decoding, and unmasking planner components (right).
The base model and planner are jointly trained using Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), an on-policy policy gradient method. The RL framework leverages a composite reward:
- Verifiable Task Reward: Domain-specific, e.g., mathematical correctness or passing functional tests for code.
- On-policy Distillation Reward: Sequence-level log-likelihood from a strong teacher AR model, incentivizing high-probability modes while preserving diversity and coherence.
- Efficiency Reward: Penalization based on the number of denoising steps, directly optimizing for reduced function evaluations (NFE).
The likelihood of each rollout is computed exactly via the modeled unmasking and token selection probabilities, supporting sound policy optimization.
Initialization and Training Stabilization
To ensure stable early exploration, the planner head is initially finetuned to mimic a heuristic logit-based sampler (e.g., Fast-dLLM). This is followed by GRPO finetuning to unlock superior unmasking strategies. To prevent degenerate collapse into over-conservative polices (never unmasking), advantage clipping is applied—advantages below a threshold are zeroed, restricting learning updates to trajectories with above-average returns.
Analysis of Conditional Independence
A fundamental observation is that random masking schedules decorrelate token dependencies, allowing the model to unmask more tokens per step without introducing mode collapse. Empirically, the quality of generation strongly degrades under AR masking at the sequence end (autoregressive masking), but is preserved under random masking—even at high mask rates.
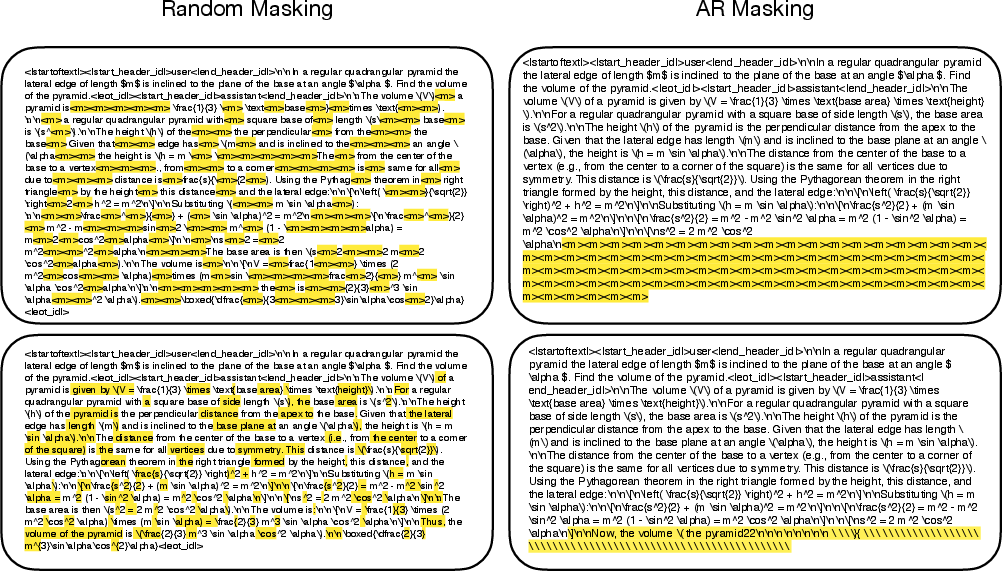
Figure 3: Case study comparing random vs. autoregressive masking; parallel recovery under random masking maintains quality, while AR masking yields subpar completions.
dUltra exploits this insight by learning unmasking policies that maximize parallelism in positions with high contextual independence, departing from rigid left-to-right decoding schedules and imitating a form of conditional independence-aware planning. In code generation tasks, for example, function signatures and control-flow keywords are unmasked early, while more interdependent sequences adhere to AR order.
Experimental Results
Training Dynamics and Convergence
The GRPO-based approach yields stable, monotonic improvement in correctness, efficiency, and distillation reward metrics throughout training on tasks such as GSM8K (math reasoning).

Figure 4: Training dynamics on GSM8K—correctness, efficiency, and distillation rewards evolve stably together.
Advantage clipping is critically important; without it, the policy degenerates and sampling slows indefinitely (NFE diverges, planner ceases to unmask).

Figure 5: Effect of advantage clipping; only with proper clipping (here, C=0) can stable, efficient policies be learned.
Main Results: Accuracy–Efficiency Trade-off
dUltra shows consistent improvements across mathematical and code generation tasks, outperforming Fast-dLLM, dParallel, and d3LLM in either accuracy or sample-efficiency (often both). For GSM8K, dUltra improves accuracy by 4–9 points relative to distillation baselines, while requiring 30–40% fewer denoising steps. The efficiency–accuracy trade-off can be modulated at inference time by scaling the planner’s unmasking probabilities.
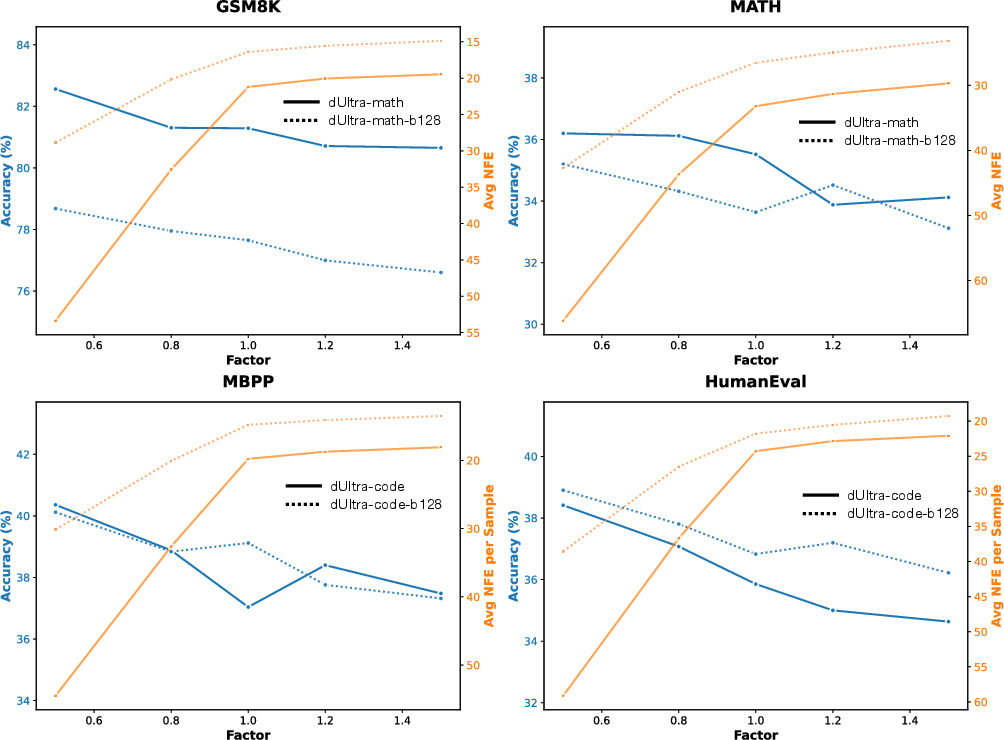
Figure 6: Pareto frontier of accuracy vs. NFE across multiple tasks with variable unmasking probability scaling.
Increasing block size further accelerates sampling: with block size 128, dUltra achieves $16.38$ NFE on GSM8K with minimal accuracy degradation. On code generation (HumanEval, MBPP), the learned planner achieves order-of-magnitude lower NFE and up to 17–18 percentage points accuracy advantage over non-planner baseline sampling.
Unmasking Policy Visualization
Visualization of unmasking order shows that the learned strategies largely follow autoregressive left-to-right progression but include notable deviations that exploit conditional independence.

Figure 7: GSM8K unmasking pattern. Mostly AR with small conditional independence-exploiting deviations.
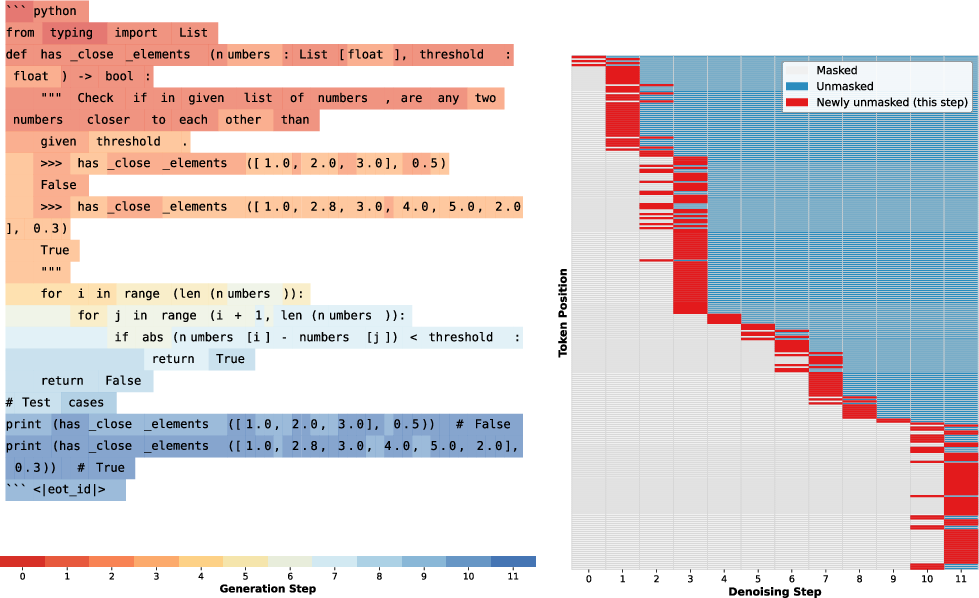
Figure 8: HumanEval code unmasking. More non-AR behavior—early unmasking of functional and structural code elements.
Unmasking policies in code are less sequential, with jumps to earlier generation of structural components, indicating flexibility and a higher degree of parallelism available in non-strictly sequential tasks.
Theoretical and Practical Implications
dUltra demonstrates that RL-guided unmasking policies can overcome the inefficiency and mode-selection limitations of prior off-policy, distillation-guided methods. The approach establishes a tractable framework for policy optimization on MDLMs by providing exact rollout likelihoods and balancing domain correctness, sample diversity, and computational efficiency.
Strong claims in the paper include:
- Joint optimization of the base diffusion model and the learnable unmasking order leads to simultaneous improvements in both accuracy and sample efficiency over SOTA distillation and heuristic acceleration baselines.
- On-policy training is essential for discovering superior unmasking strategies and for mode filtering without being limited by off-policy trajectories.
- The method brings open-source MDLMs significantly closer to the high throughput of proprietary diffusion LMs, making "diffusion supremacy" practical on community-accessible models.
Practically, this work suggests that diffusion-based LLMs can be deployed in real-time, high-throughput generative tasks traditionally dominated by AR LMs. Theoretically, conditional independence-driven scheduling and joint RL optimization are poised to become standard in the next generation of high-speed, high-accuracy MDLMs.
Open questions remain regarding full exploitation of non-AR generation order, further adaptation for general reasoning tasks, the limits of parallel decoding, and robustness of policies under different domains and input distributions.
Conclusion
dUltra delivers a principled acceleration strategy for masked diffusion LLMs by learning optimal unmasking strategies through reinforcement learning. The joint RL optimization of the base model and planner, together with on-policy distillation and efficiency rewards, systematically improves both sample efficiency and accuracy, outperforming leading off-policy distillation and heuristic approaches. The architecture and training pipeline of dUltra mark a substantial advance in making high-throughput, robust generative text models feasible in both open-source and production settings. The prospective theoretical and practical impact is profound, and future developments are expected to investigate even more expressive, context-adaptive planning strategies, non-autoregressive reasoning, and memory-efficient large-context generation.











