- The paper’s main contribution is the development of behaviorally calibrated RL methods that enable models to adaptively abstain under uncertainty, reducing hallucination.
- It introduces explicit risk thresholding, verbalized confidence, and critic value strategies to refine model predictions and control epistemic risks.
- Empirical results show improved calibration metrics, including higher Confidence AUC, enhanced SNR Gain, and reduced smoothing calibration error on diverse tasks.
Mitigating Hallucination in LLMs via Behaviorally Calibrated Reinforcement Learning
Hallucination in LLMs—the tendency to produce plausible but factually incorrect outputs—remains a critical impediment in deploying these systems for high-stakes applications. The paper "Mitigating LLM Hallucination via Behaviorally Calibrated Reinforcement Learning" (2512.19920) formalizes hallucination as a logical consequence of misaligned training objectives, particularly those that prioritize maximum accuracy without a principled approach to epistemic uncertainty. Standard RLVR protocols using binary rewards for correctness induce models to behave as optimal test-takers, always responding if there is nonzero expected utility, even in regions of low confidence, thereby inflating the rate of confident errors.
Building on theoretical findings that equate hallucination with reward misalignment (Kalai et al., 4 Sep 2025), this work advances behavioral calibration—a paradigm that requires models to adaptively abstain or signal uncertainty in accordance with user-specified risk tolerances. The approach aims to decouple the meta-cognitive skill of uncertainty quantification from raw predictive accuracy, thereby enabling models to more robustly self-limit in unfamiliar or dubious contexts.
Proposed Methodologies
Three primary interventions for behavioral calibration are proposed and empirically contrasted:
- Explicit Risk Thresholding: Conditioning model outputs on a stochastic, user-prompted risk threshold t, with a reward function that sharply penalizes incorrect answers in high-risk settings, neutral on abstention, and maximally rewarding on correct predictions.
- Verbalized Confidence: Training the model to output a quantitative confidence value for its endorsements, then post-hoc calibrating abstention and answer policies via strictly proper scoring rules derived by integrating over plausible risk tolerance priors (Uniform, Beta). This shifts optimization from discrete refusal events to calibration of stated confidence distributions.
- Critic Value: Utilizing the value prediction from the PPO critic network as an implicit estimator for epistemic certainty, exploiting its natural convergence to the success probability via Brier score minimization.
Each mechanism is extended to both response- and claim-level abstention policies, supporting fine-grained epistemic transparency.






Figure 1: Accuracy, hallucination, and abstention rates across Explicit Risk Thresholding training, showing convergence challenges in dynamic risk conditioning.
Empirical Evaluation
Response- and Claim-Level Calibration
Models are trained on mathematical reasoning tasks using Qwen3-4B-Instruct as the base, with reward design incorporating proper scoring rules spanning the risk spectrum. Claim-level calibration is achieved by prompting explicit confidence statements for each solution step, utilizing weak supervision aggregated at the final outcome.

Figure 2: Sample interface for stepwise verbalized confidence via Qwen3-4B-Instruct-confidence-min.
Strong improvements are demonstrated in both discrimination metrics (Confidence AUC, SNR Gain) and calibration error (smoothed ECE), with the behavior-calibrated models outperforming frontier models in meta-cognitive metrics independent of their absolute accuracy.


Figure 3: Calibration diagrams for response-level stated confidence, showing strong monotonicity between accuracy and reported confidence in calibrated models.
Critic Value Analysis
The PPO critic's value output dynamically tracks progress and detected contradictions in reasoning chains, visualized in stepwise token gradients. While value prediction decreases sharply at contradiction events, it lacks fine localization to precise error sources due to its optimization for terminal outcomes.


Figure 4: Critic Value confidence visualization, illustrating rapid decreases at contradiction steps in mathematical reasoning.
Hallucination Mitigation and Calibration Criteria
SNR analysis and True Positive/False Negative curves confirm that risk-adaptive policies rapidly reduce hallucination under increasing risk tolerance thresholds. Concave abstention curves differentiate calibrated models from standard PPO and frontier models, where convexity reflects poor adaptivity.

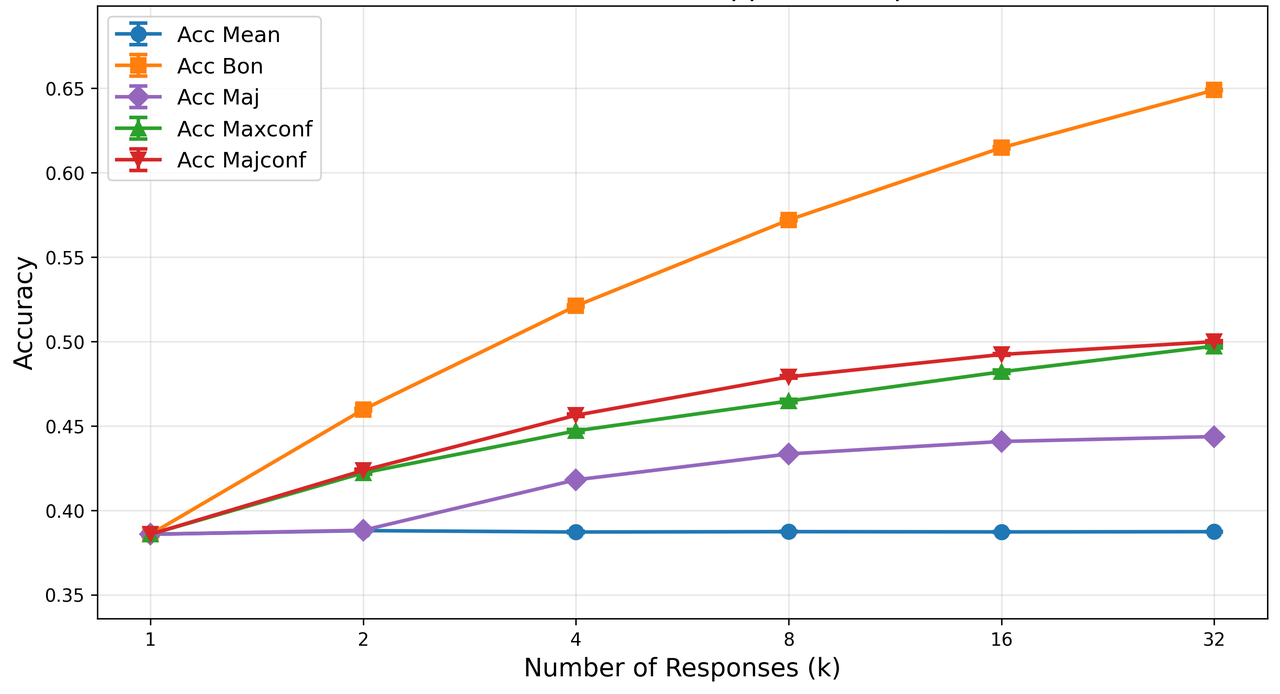

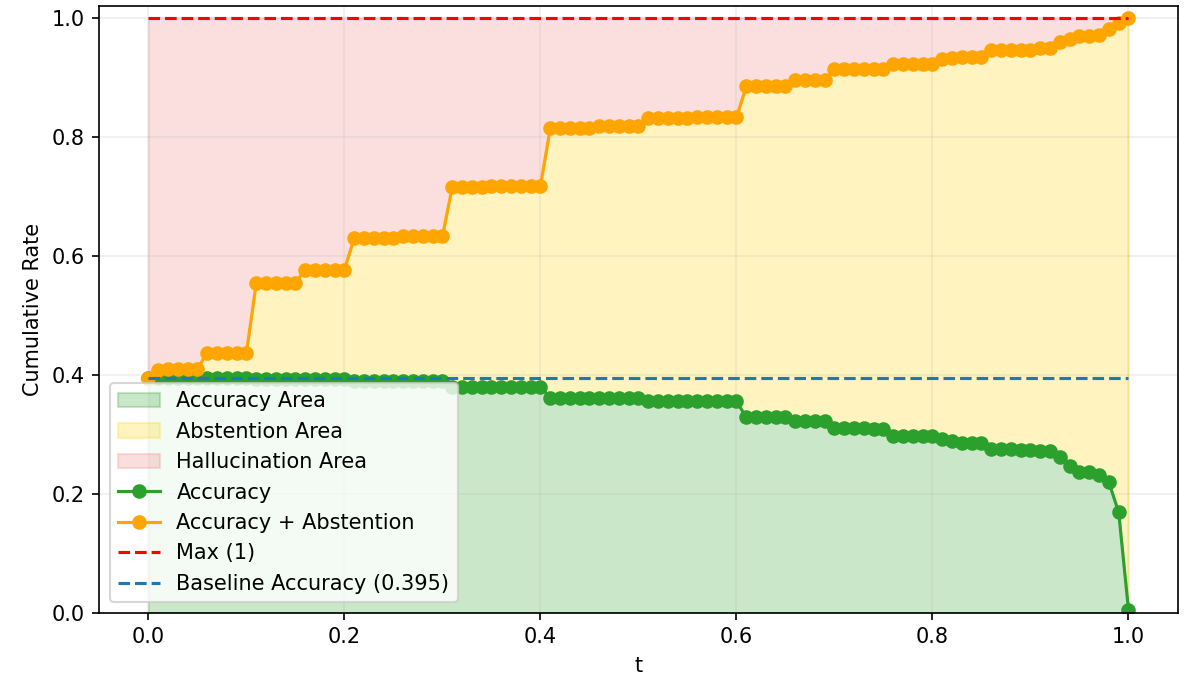

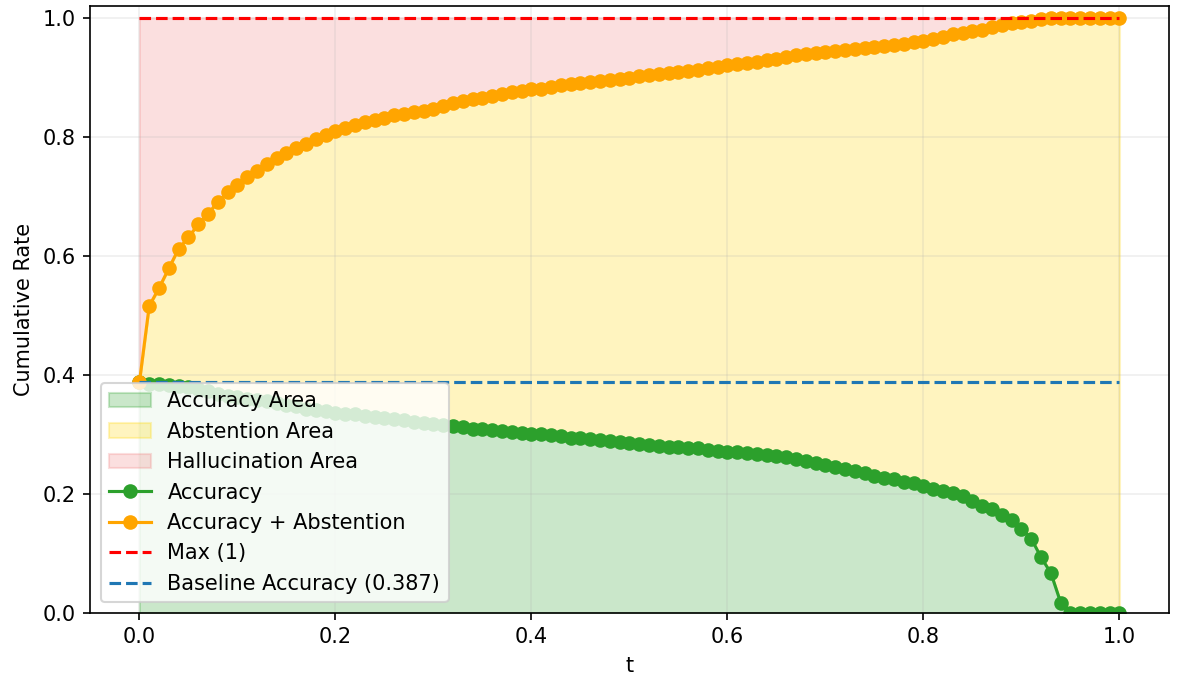

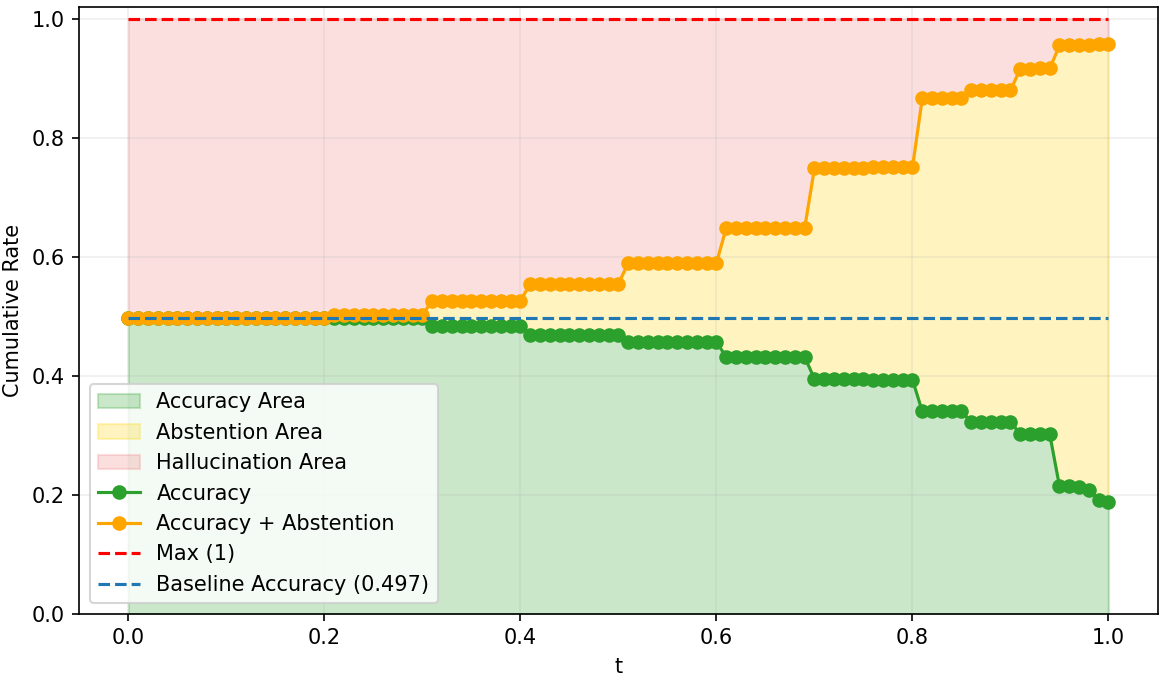

Figure 5: PPO baseline response-level abstention curves, with suboptimal SNR and calibration under increasing risk.

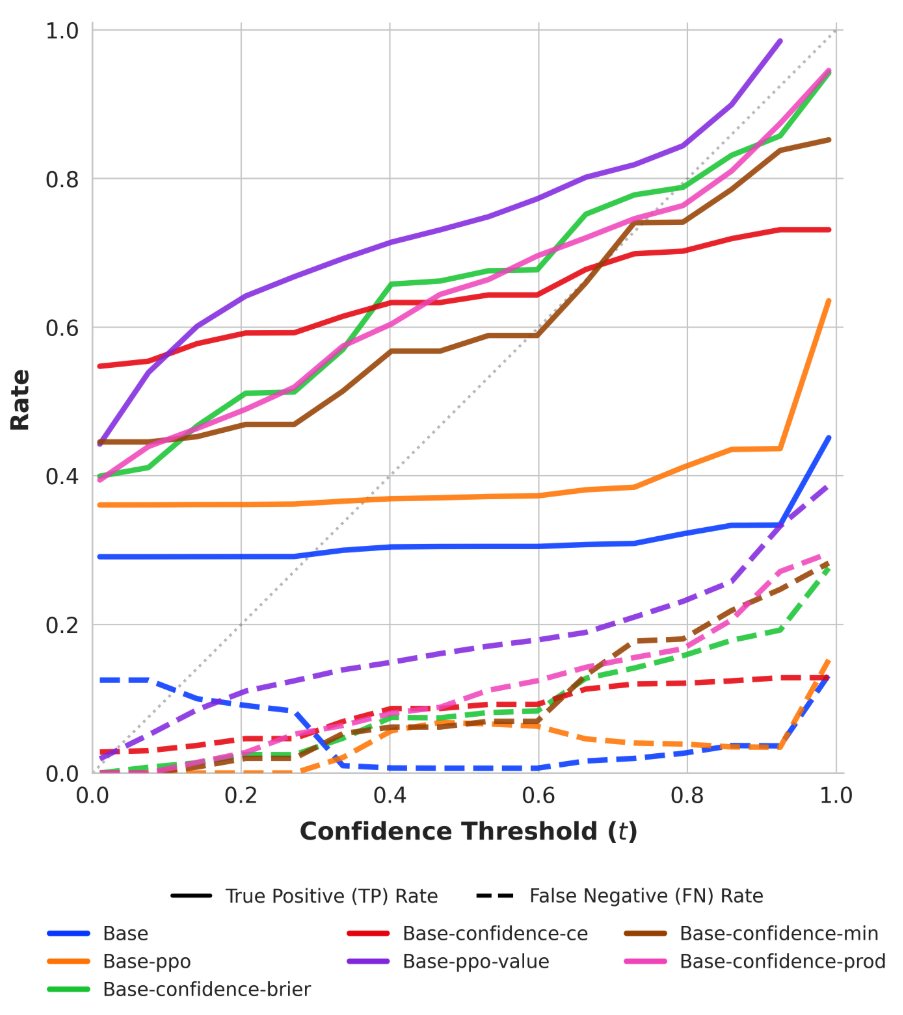

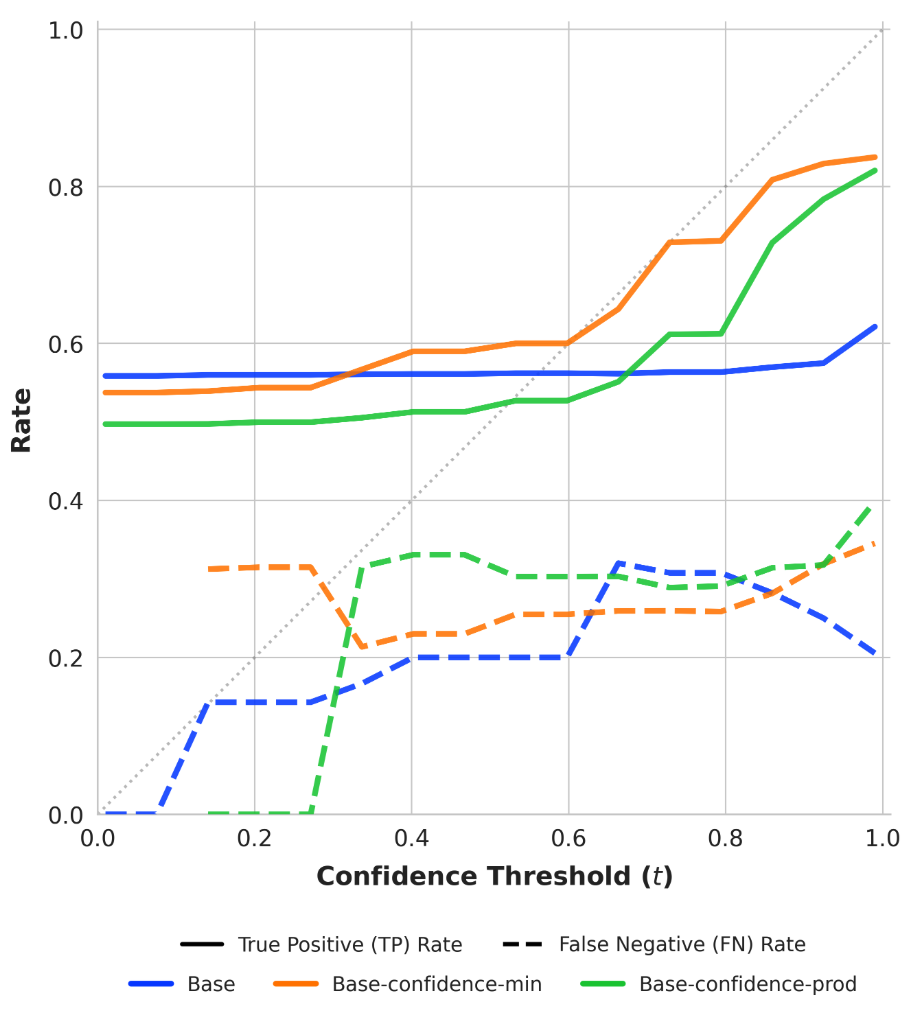
Figure 6: Behavioral calibration diagrams for response-level outputs, showing true positive and false negative regimes across risk thresholds.
Transferability and Generalization
Meta-cognitive skill transfer is validated on SimpleQA, a factual QA benchmark outside the mathematics training domain. Despite low direct accuracy, behaviorally calibrated models rival or exceed frontier models in SNR Gain and Confidence AUC, demonstrating the orthogonality of calibration to underlying domain performance.
Test-Time Implications
Confidence estimates from behaviorally calibrated models serve effectively as reward proxies for test-time scaling—increasing ensemble accuracy with confidence-weighted voting and selection over simple majority approaches. This underlines the practical utility of calibrated confidence in downstream deployment.
Theoretical and Practical Implications
The findings substantiate that:
- Hallucination is an inherent byproduct of utility-maximizing optimization under binary correctness rewards.
- Calibration can be acquired as a distinct meta-cognitive capability, largely independent of parameter scale or base task proficiency.
- Proper scoring-rule-based RL induces models that dynamically control response refusal in accordance with external risk specifications, satisfying rigorous behavioral calibration objectives.
- Small models, when appropriately trained, can match or exceed large models in self-limitation and uncertainty signaling, confirming meta-calibration's transferability and its independence from native domain knowledge.
Conclusion
This paper rigorously demonstrates that hallucination in LLMs can be quantitatively mitigated by enforcing behaviorally calibrated reinforcement learning objectives, whereby models internalize principled abstention and uncertainty signaling policies. The decoupling of calibration from accuracy enables broad generalization and scalable epistemic control, suggesting that future advancements in LLM safety should prioritize behavioral calibration alongside traditional accuracy and reasoning metrics. The methodologies presented are robust to model scale and domain specificity, positioning behavioral calibration as an essential axis for safe, deployable AI systems.























