- The paper demonstrates a two-step framework using local LLMs and RAG to classify and generate network commands from natural language inputs.
- It implements a 4-bit quantized LLaMA-3 on NVIDIA 3060 GPUs, ensuring data privacy and lowering deployment costs.
- Results show an 18% improvement in precision and a 25% increase in accuracy, highlighting the potential for secure and efficient 5G automation.
5G Network Automation Using Local LLMs and Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Introduction
The paper, "5G Network Automation Using Local LLMs and Retrieval-Augmented Generation" (2511.21084), presents a demonstration of integrating localized LLMs with RAG to automate 5G network management operations. The transition from 4G to 5G technology demands sophisticated configurations often requiring specialized skills, which this research aims to simplify. By leveraging LLMs and RAG, the proposed system automates the configuration and management tasks of private networks while maintaining privacy and reducing costs. This paper contributes significant advancements in developing secure, efficient, and adaptable 5G network solutions.
Methodology
The proposed methodology utilizes a two-step framework for generating network commands from natural language input, leveraging a locally deployed LLM augmented by a RAG system.
Step 1: Command Classification — Initially, the LLM classifies the input into one of 11 predefined command categories using the prompt appended with examples from a dedicated corpus. A sample retrieval mechanism facilitates this process by providing relevant examples, aiding the LLM in accurate classification.
Step 2: Command Generation — Upon classifying the command, the system employs a tailored prompt containing task descriptions and relevant samples to generate the precise command. The generated output is subsequently filtered to extract only the essential command components.
This localized deployment, coupled with retrieval augmentation, enhances the model's predictive capabilities while ensuring data privacy by preventing sensitive information from leaving the local environment.
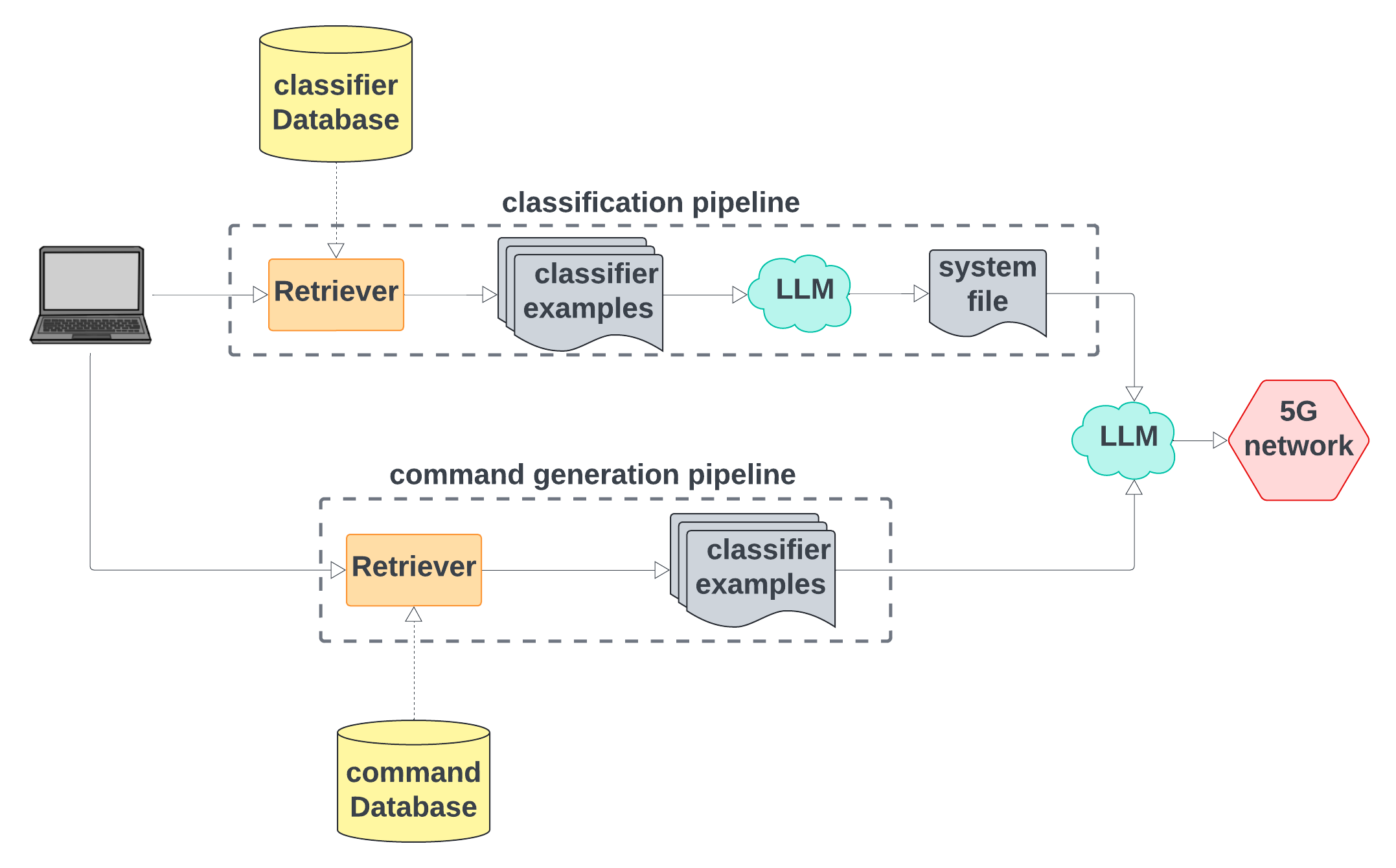
Figure 1: System overview demonstrating data flow through two parallel pipelines ending in LLM-generated commands.
Model Implementation
The implementation is based on a 4-bit quantized LLaMA-3 with 8 billion parameters. This model is deployed using the Ollama library, allowing it to operate efficiently on commonly available hardware such as NVIDIA 3060 GPUs. By ensuring low resource consumption and local processing, the implementation highlights advancements in making LLMs accessible without significant infrastructure investments.
Results
The performance metrics for the proposed system focused on accuracy and uni-gram precision. The results demonstrated a uni-gram precision of 68% and an accuracy of 46% for the RAG-enabled Llama-3 model, marking an 18% improvement in precision and a 25% elevation in accuracy compared to its non-RAG counterpart. These enhancements illustrate the effectiveness of integrating RAG within LLM frameworks for contextual command generation in 5G networks.
Conclusion
This research offers a viable framework for automating 5G network management through localized LLMs and RAG, ensuring secure and cost-effective solutions. The demonstrated increase in uni-gram precision underscores the potential of these technologies in refining LLM outputs. Future directions include fine-tuning using methods such as LoRA to enhance model capabilities further. The paper marks a step towards reducing the technical barrier in private network configuration, potentially accelerating the adoption of 5G technologies across varied user demographics.


