- The paper introduces a modular genetic search framework that explores 46,080 RAG configurations to enhance inter-component synergy.
- Robust module components like vector retrieval and post-generation reflection deliver consistent gains across varied domains.
- Domain-specific insights reveal that tailoring module selection to dataset characteristics can boost performance by up to +6.9% over baselines.
RAGSmith: A Comprehensive Framework for RAG Optimization Across Domains
Introduction
The paper on "RAGSmith: A Framework for Finding the Optimal Composition of Retrieval-Augmented Generation Methods Across Datasets" introduces a modular framework designed to optimize Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. The RAGSmith framework utilizes a genetic search algorithm to identify optimal configurations across various datasets, addressing limitations in current RAG approaches which often optimize modules in isolation rather than as a cohesive pipeline. The framework systematically explores combinations of RAG techniques, making it feasible to optimize configurations effectively across different domains without exhaustive manual tuning.
Modular Framework and Techniques
RAGSmith defines a nine-step modular pipeline for RAG systems, encompassing multiple stages: Pre-Embedding, Query Expansion, Retrieval, Reranking, Passage Filtering, Passage Augmentation, Passage Compression, Prompt Making, and Post-Generation. Each stage offers a selection of techniques, leading to a total of 46,080 possible configurations that the genetic algorithm explores.
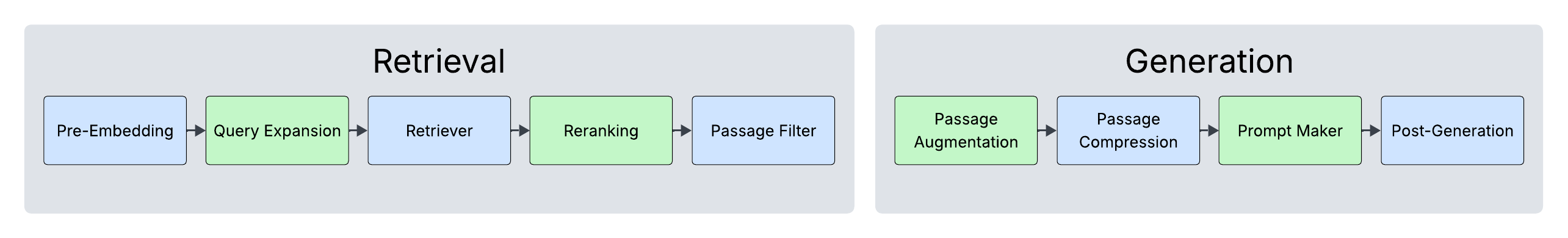
Figure 1: RAG Technique Categories.

Figure 2: All RAG Techniques used in RAGSmith.
Search and Evaluation Methodology
The framework employs a genetic search algorithm that evaluates about 0.2% of the configuration space to discover high-performing RAG pipelines efficiently. Candidates are scored on a scalar objective combining retrieval metrics (e.g., recall, nDCG) and generation metrics (e.g., semantic similarity, LLM-Judge). This approach surpasses traditional greedy optimization by considering inter-component synergies and conflicts, enabling holistic configuration discovery.
The study evaluates RAGSmith across six domains: Mathematics, Law, Finance, Medicine, Defense Industry, and Computer Science, each presented with 100 questions spanning factual, interpretation, and long-answer types. Overall performance improvements range from +1.2% to +6.9% over a naive RAG baseline, demonstrating consistent gains across domains.
Key Findings and Insights
Robust Components: Vector retrieval and post-generation reflection/revision consistently yield strong performance, constituting a robust backbone for RAG pipelines across domains. These components provide foundational capabilities that generalize well despite domain specificity.
Domain-Specific Optimization: The framework identifies effective module combinations tailored to dataset characteristics—high chunk density influences reranker selection, while hierarchical content informs augmentation strategy. These insights guide scalable deployment across diverse knowledge domains.
Question Type Sensitivity: Dataset question-type distribution significantly influences improvement potential, with larger gains observed on factual/long-answer mixes than interpretation-heavy sets, highlighting a gap in current RAG techniques for enhancing inferential reasoning.


Figure 3: Retrieval performance comparison.


Figure 4: Overall performance comparison.
Conclusion
RAGSmith advances RAG system design by treating configuration as a holistic optimization problem rather than independent module selection. Its genetic search methodology efficiently navigates a vast design space, uncovering configurations that outperform naive setups. The framework's adaptive approach, informed by dataset-specific insights, extends RAGSmith's utility across varied domains and question constructs, providing a scalable, data-driven solution for optimizing RAG pipelines tailored to specific requirements. The study underscores the importance of considering inter-component dynamics, offering a methodologically robust tool for enhancing RAG systems in practical deployments.







