- The paper introduces DySQL-Bench, a benchmark that evaluates multi-turn, dynamic SQL interactions for improved database query handling.
- It employs an automated two-stage task synthesis pipeline that guarantees task correctness and supports diverse CRUD operations.
- Experimental results reveal significant challenges, including performance degradation and hallucination issues, emphasizing the need for better contextual reasoning.
Rethinking Text-to-SQL: Dynamic Multi-turn SQL Interaction for Real-world Database Exploration
Abstract
The paper "Rethinking Text-to-SQL: Dynamic Multi-turn SQL Interaction for Real-world Database Exploration" (2510.26495) addresses a critical gap in Text-to-SQL research: the inadequacy of static, single-turn models in handling dynamic, real-world applications where user queries evolve over multiple turns. To address this, the authors introduce DySQL-Bench, an innovative benchmark designed to evaluate models under dynamic user interactions. The benchmark employs an automated two-stage pipeline that synthesizes and verifies tasks, transforming raw database tables into structured trees for LLMs to generate diverse evaluation tasks. Furthermore, the paper proposes a multi-turn dynamic evaluation framework involving interaction among a simulated user, the model, and an executable database system.
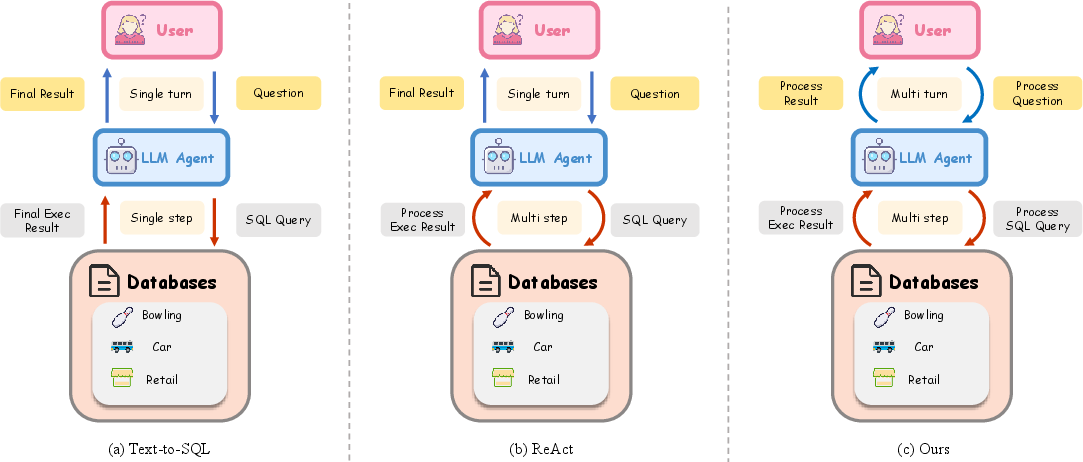
Figure 1: Overview of interaction types between user, LLM agent, and database. From left to right: (a) direct Text-to-SQL execution, (b) iterative reasoning within a single query (ReAct), and (c) our approach enabling multi-step, multi-turn contextual execution.
Introduction
SQL is fundamental in data-driven domains like customer service and financial analytics, where user interactions unfold as multi-turn dialogues due to incomplete objectives or evolving requirements. Existing benchmarks like Spider and BIRD focus on single-turn tasks, neglecting the dynamic nature of real-world interaction. DySQL-Bench addresses these gaps by integrating databases from diverse domains, employing automated synthesis and expert verification to ensure correctness and relevance.
DySQL-Bench's Contributions:
- Dynamic Multi-turn Interaction: Evaluates models in evolving scenarios necessitating multi-turn reasoning.
- Two-Stage Task Synthesis: Automates task creation, ensuring 100% correctness through rigorous validation.
- Comprehensive CRUD Operations: Covers the full spectrum of Create, Read, Update, Delete operations, reflecting real-world demands.
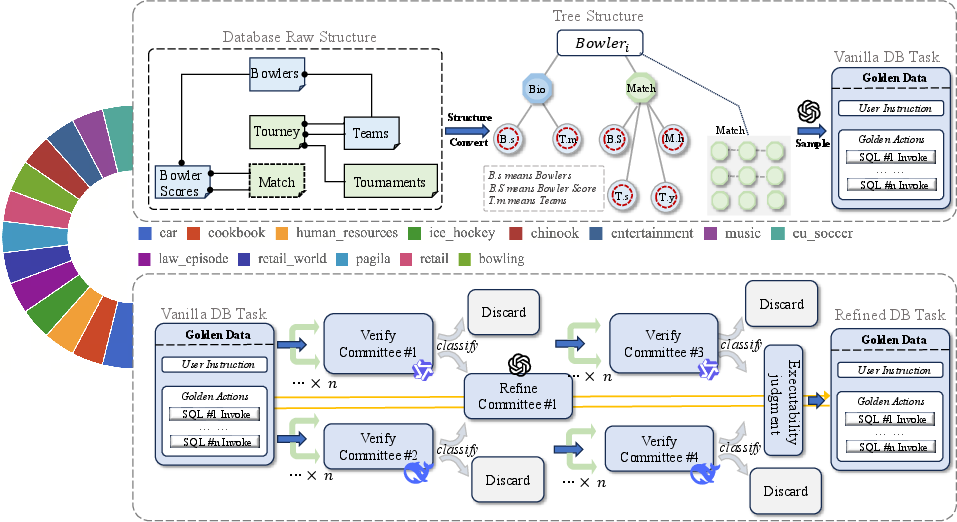
Figure 2: Task Generation Pipeline. Based on 13 databases from Spider 2 and BIRD, we designed a two-stage DynSQL-Bench task synthesis method. In the first stage, an LLM generates initial tasks. In the second stage, a filtering mechanism selects high-quality tasks.
Methodology
Task Definition
DySQL-Bench defines a multi-turn Text-to-SQL task where an LLM-simulated user interacts with a SQL model, generating actions that manipulate the database state. Task success is determined by matching the model-generated states with expert-verified golden states using a consistent hashing mechanism.
Multi-turn DB Tasks Generation
The benchmark employs databases from BIRD and Spider2, transforming relational schemas into hierarchical JSON structures for efficient task generation. The tasks cover varied domains, emphasizing complex CRUD operations beyond static SELECT queries. A multi-stage pipeline ensures high-quality task generation, employing validation committees and human oversight for robust data quality.
Evaluation Framework
DySQL-Bench's evaluation framework simulates real-world interactions, assessing models on task reformulation, adaptability, and error recovery in dynamic settings. Models are evaluated using metrics like Passk, reflecting multi-turn interaction stability and efficacy in maintaining consistent dialogue state over trials.
Experimental Results
Evaluations reveal that existing models exhibit significant performance degradation with increased trials, emphasizing the need for stability in dynamic interactions. Even advanced models like GPT-4o achieve only 58.34% accuracy and 23.81% on the Pass5 metric, highlighting challenges in multi-turn SQL reasoning.
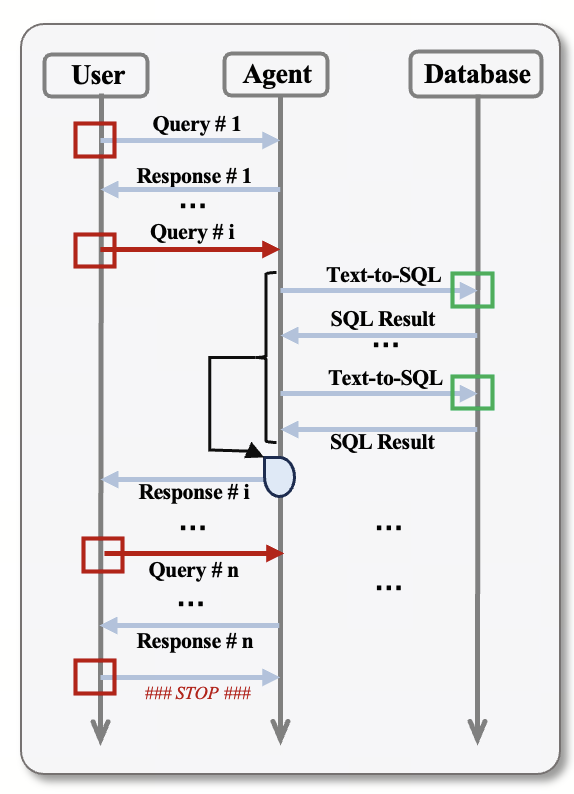
Figure 3: Schematic diagram of dynamic multi-turn interactions among the three roles of User, Agent, and Database.
Hallucination Challenge
Hallucinations remain a critical issue, where models fabricate results post-SQL execution, leading to inaccuracies. DeepSeek-V3 and OmniSQL-32B display the highest hallucination rates, attributed to procedural reasoning patterns, necessitating improved contextual understanding and execution accuracy.
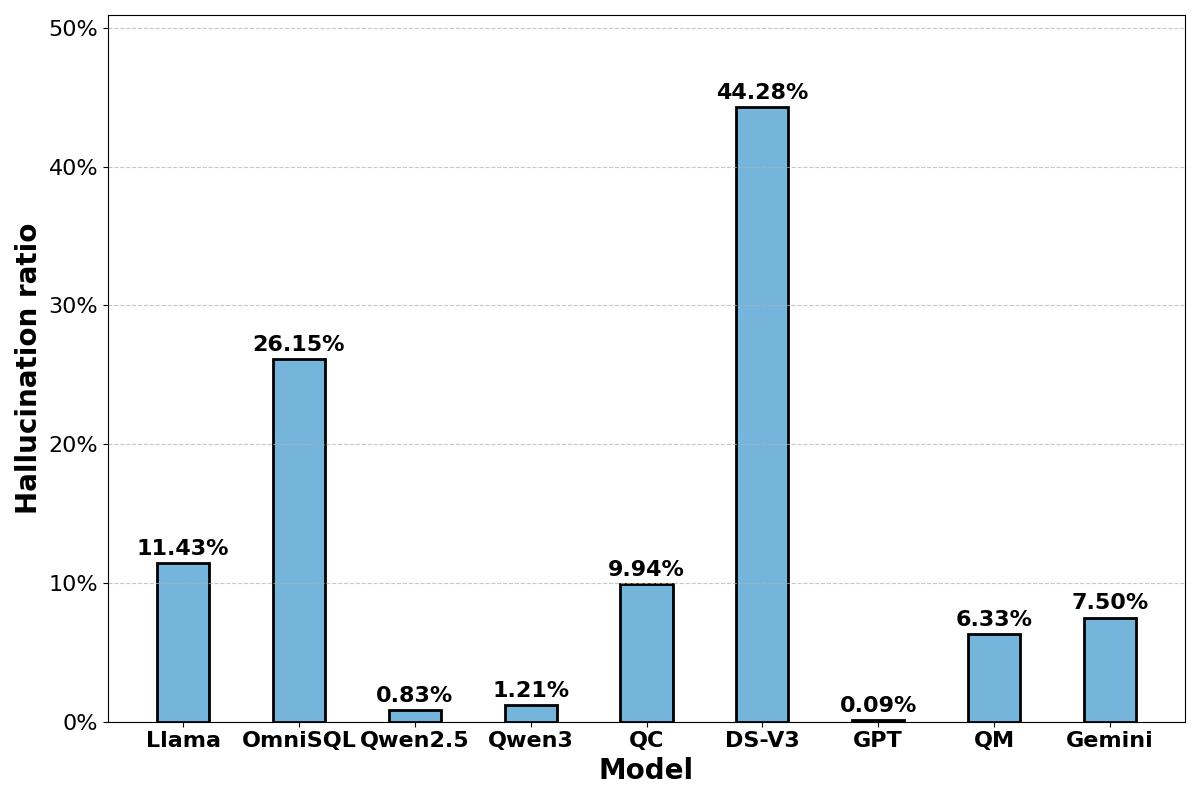
Figure 4: Comparison of hallucination rates across different models.
Conclusion
DySQL-Bench establishes a new standard for evaluating interactive database query systems, aligning benchmark design with real-world dynamic interaction demands. By facilitating detailed assessment of LLMs in complex, evolving scenarios, DySQL-Bench offers a robust foundation for advancing multi-turn conversational intelligence in database exploration.
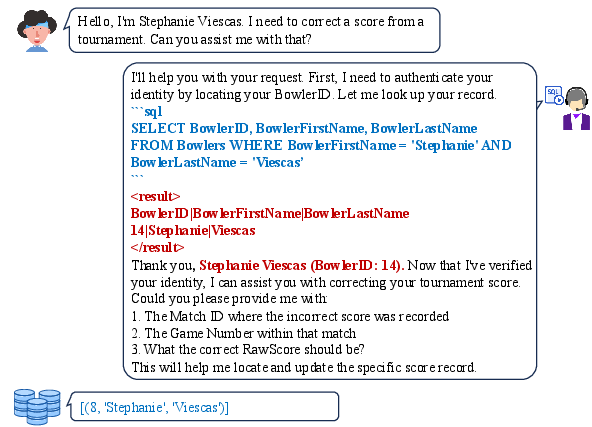
Figure 5: An example of a hallucination produced by the DeepSeek-V3 model. The model fabricated a BowlerID of 14, whereas the actual BowlerID should be 8, demonstrating a hallucination case.






