- The paper introduces SimpleQA Verified, a refined benchmark that improves upon existing datasets by eliminating redundancy and bias for accurate LLM factual recall.
- It employs a multi-stage curation process including deduplication, semantic filtering, and balanced resampling to ensure diverse and challenging questions.
- Benchmark results reveal the state-of-the-art performance of Gemini 2.5 Pro, highlighting the utility of tool-free, pure parametric evaluation.
SimpleQA Verified: A High-Fidelity Benchmark for LLM Parametric Factuality
Motivation and Background
Factual accuracy is a core performance axis for LLMs deployed in both consumer-facing and enterprise use cases. Existing benchmarks, particularly older QA datasets such as TriviaQA, Natural Questions, and TruthfulQA, have been saturated by advances in LLMs and thus insufficient to differentiate amongst contemporary systems on factual recall. More recently, OpenAI SimpleQA was introduced to address this gap, focusing specifically on parametric knowledge recall—measurement of the factual content retrievable from a model's parameters, independent of retrieval or grounding. However, SimpleQA exhibits significant limitations, including label inaccuracies, topical and answer type biases, and extensive redundancy among questions. These methodological weaknesses confound the interpretability of model scores and incentivize overfitting to idiosyncratic data artifacts rather than genuine factual competence.
Data Curation Methodology
SimpleQA Verified systematically addresses the flaws of SimpleQA via a comprehensive, multi-stage data refinement pipeline:
- Deduplication by Source: Any pair of questions sharing a reference URL was filtered, ensuring topic diversity and minimizing rater-induced topical sampling biases.
- Semantic and TF-IDF-Based Redundancy Removal: Embedding-based de-duplication (Gemini Embeddings, cosine similarity threshold 0.77) followed by TF-IDF vector matching (cosine similarity > 0.4) identified and eliminated semantically similar or trivially rephrased questions.
- Respect for Web Publisher Preferences: Questions referencing URLs from publishers with explicit model/crawl disallowances (robots.txt) for major LLM providers were excised.
- Answer-Type and Topical Re-Balancing: Datasets were re-sampled to mitigate overrepresentation of dates, persons, or specific domains, targeting balanced distributions across both axes.
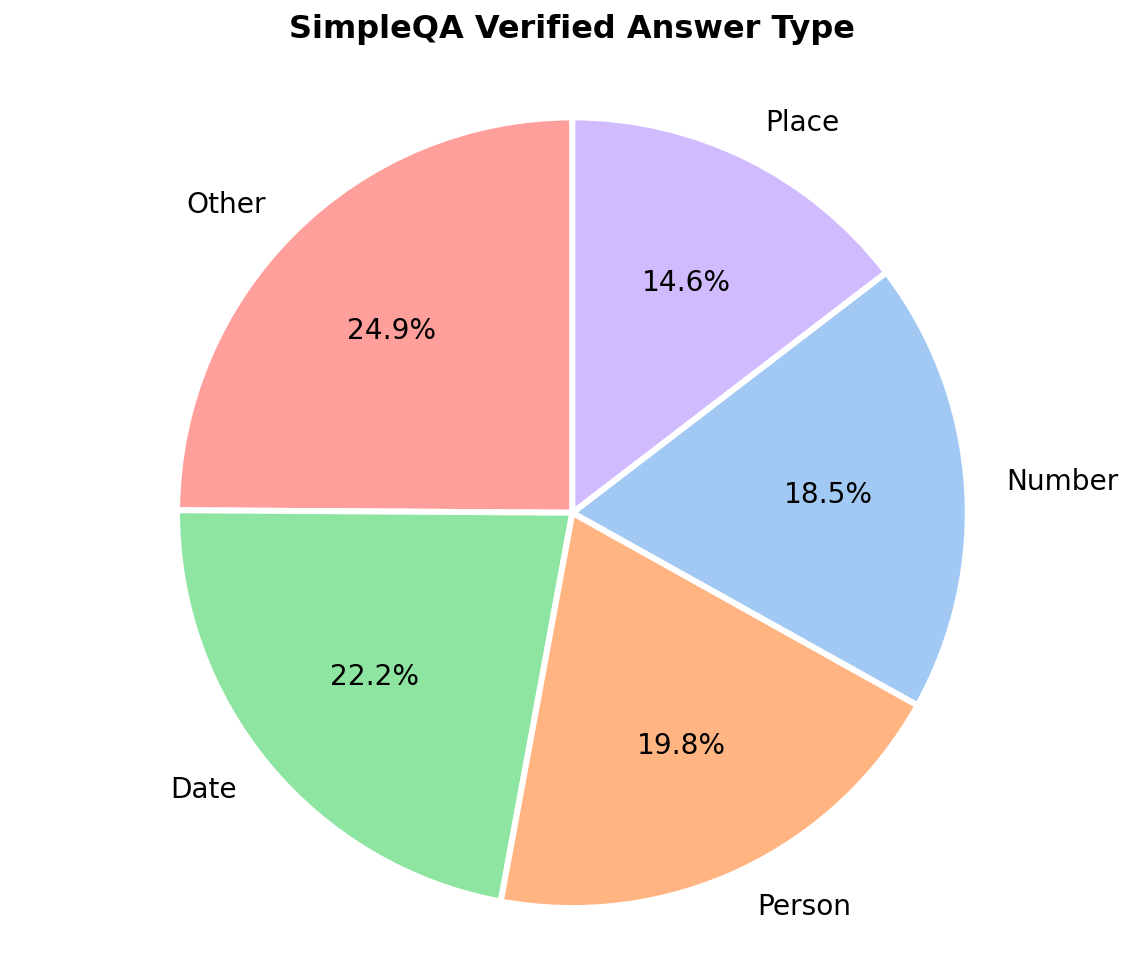
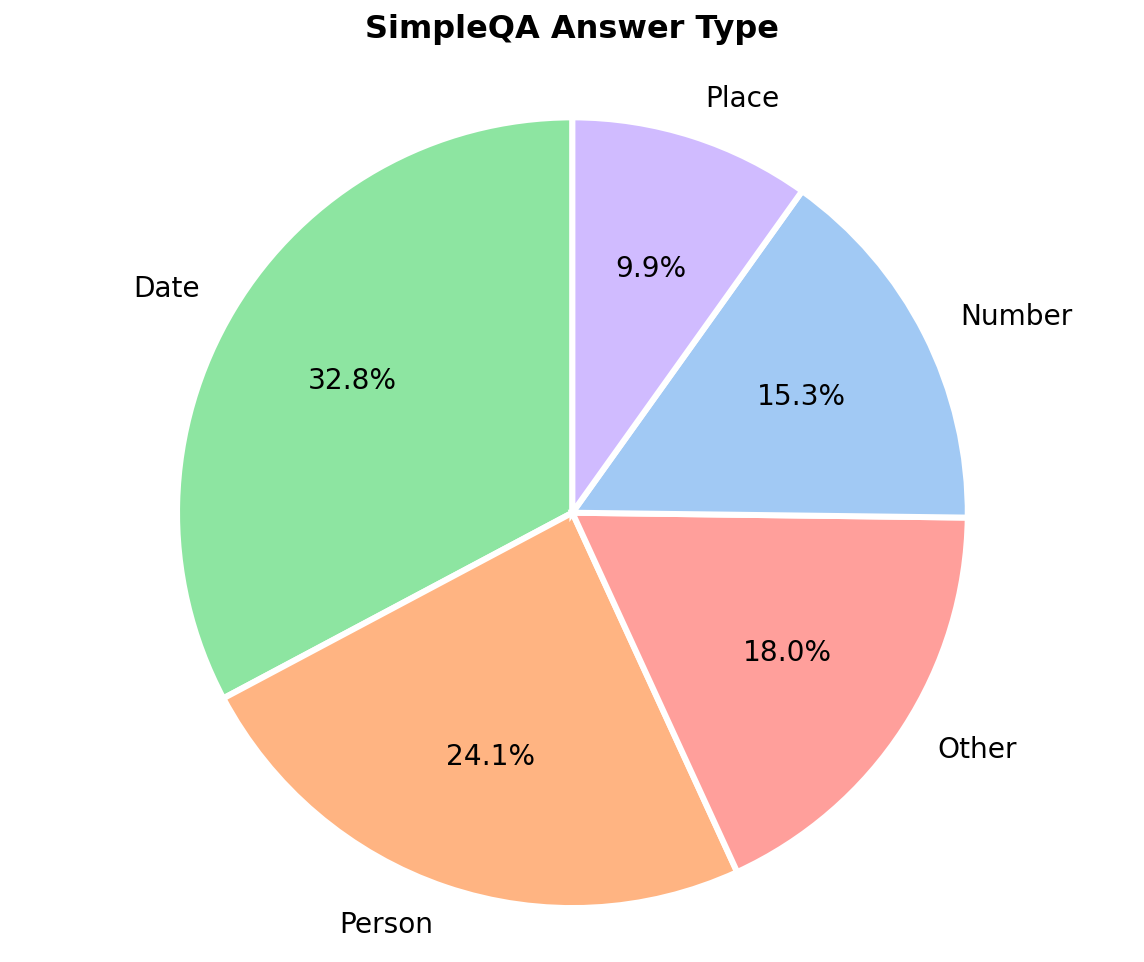
Figure 1: SimpleQA Verified achieves a more uniform distribution of answer types compared to the original SimpleQA, addressing predominant bias toward dates and named entities.

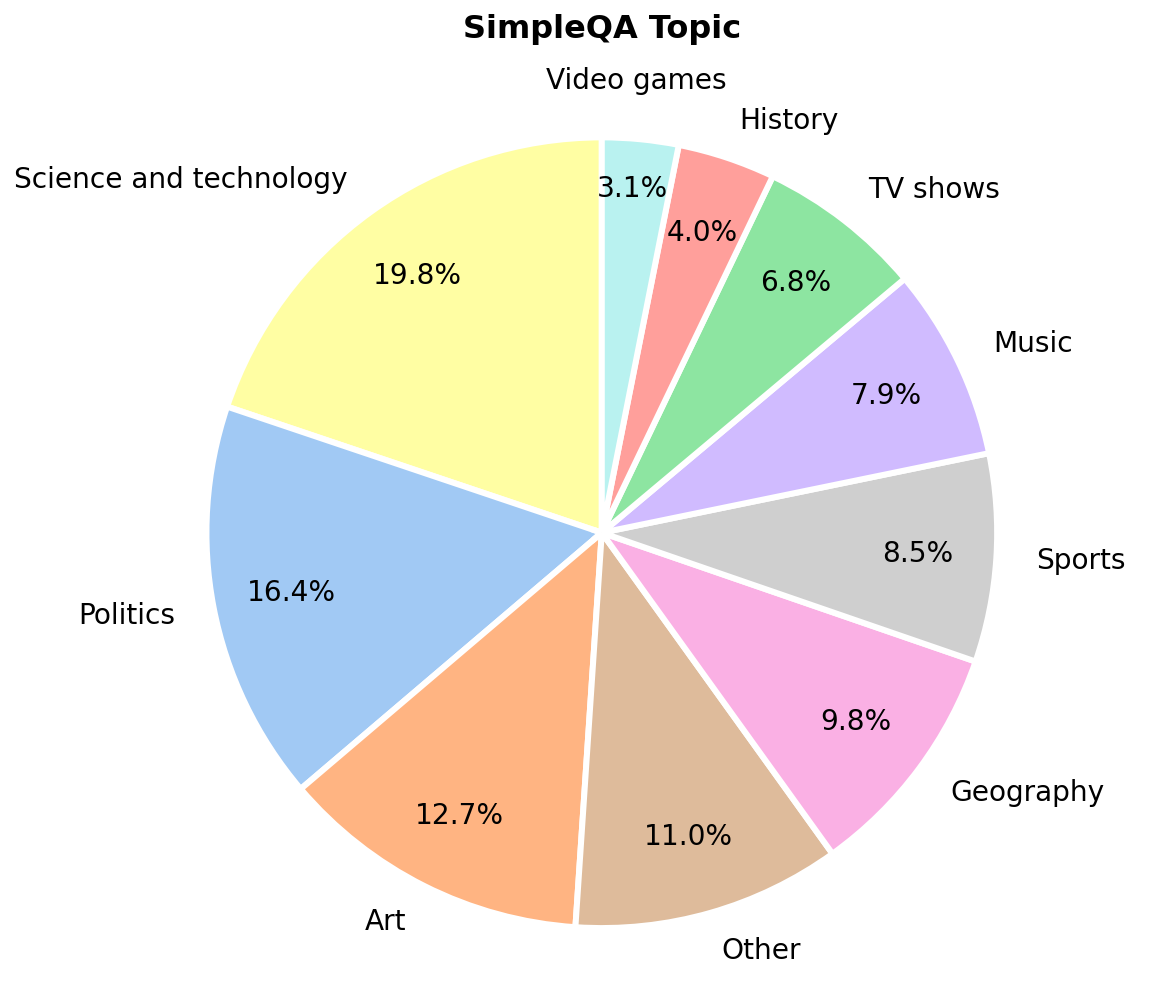
Figure 2: Topical coverage in SimpleQA Verified is rebalanced, countering the science-and-technology skew in SimpleQA.
- Source Reconciliation: For all ambiguous or conflicting sources—particularly acute in numeric questions—outlier ground truths were resolved. Numeric questions were retained only if a 5% margin of consensus between independent sources was achieved.
- Headroom Preservation: To retain benchmark difficulty, only questions unsolved by all top-tier models (Gemini 2.0 Flash, GPT-4o, Claude 3.7 Sonnet) were retained at each stage.
- Manual QA, Source Cleaning, and Metadata: Remaining questions underwent manual reference validation and adjustment of answer ranges. Additional annotation for reasoning requirement and multi-step inference was included.
The finalized dataset comprises 1,000 diverse, challenging, and unambiguous parametric QA prompts, representing a substantial methodological advance in data curation for LLM factuality assessment.
Improvements to Automated Grading
The benchmark's reliability is amplified by refinements to the autorater (automatic grading procedure):
- Explicit Numeric Ranges: Ground-truth numeric answers are annotated with explicit margins of error, derived by answer class and scale. The autorater is instructed to use these criterion for grading, addressing prior over-stringency with floating point answers.
- Expanded Hedging and Non-Attempt Examples: Prompt exemplars are diversified to ensure consistent treatment of soft refusals, multiple-candidate hedges, and partial responses.
- Direct-Answer Focus: The autorater is instructed to grade only the directly relevant information when long or rambling responses are given, minimizing spurious penalization for correct content embedded in verbose outputs.
These authoring decisions increase cross-model consistency and improve both grading stability and alignment with human judgments, particularly for edge cases, approximate numerics, and refusal strategies.
Model Benchmarking Results
Thirteen leading LLMs were evaluated on SimpleQA Verified using the refined autorater prompt. Notably, Gemini 2.5 Pro achieves a new state-of-the-art, with an F1-score of 55.6, outperforming the closest competitor (GPT-5, F1 52.3) as well as high-profile models such as GPT-4.1 and Claude Opus 4. Several key observations emerge:
- Benchmark Headroom Is Maintained: Mean F1-scores on SimpleQA Verified are very similar to those on the original SimpleQA, confirming that rigorous cleaning is counterbalanced by adversarial selection of harder questions.
- Elimination of Spurious Successes: Statistically significant performance drops between SimpleQA Verified and SimpleQA for models such as GPT-4o and Claude Opus 4 indicate the removal of artifact-driven easy wins; remaining success better reflects parametric recall.
- Tools versus Parametric: All evaluated models exhibit near-perfect accuracy when tool augmentation is permitted. This further reinforces SimpleQA Verified's efficacy as a pure parametric recall measure.
Implications and Future Directions
SimpleQA Verified constitutes a significantly more robust yardstick for model factuality by rectifying topical imbalance, redundancy, and ground-truth inconsistencies present in its predecessor. From a practical perspective, this enables the clearer identification of meaningful improvements across LLM architectures and training paradigms, discourages overfitting to benchmark-specific artifacts, and fosters more scientifically valid cross-model comparisons.
Theoretically, rigorously controlled parametric factuality benchmarks are prerequisites for deeper studies into the mechanics of knowledge representation, retention, and retrieval in transformer models. Furthermore, robust baseline quantification of short-form factuality via a tool-free protocol is indispensable as new architectures increasingly deploy RAG, fine-tuning, or hybrid protocols that confound pure parametric capability comparisons.
Conclusion
SimpleQA Verified establishes a new standard for the evaluation of LLM parametric factuality. Through principled data engineering and autorater improvements, it ensures model scores reflect actual factual recall and discriminative capacity, rather than idiosyncrasies of data or metric. Empirical results currently position Gemini 2.5 Pro as the state-of-the-art. The open release of this benchmark, its evaluation code, and public leaderboard will play a central role in advancing trustworthy model development and facilitating accurate longitudinal tracking of progress in LLM factuality.



