- The paper identifies limitations in standard evaluation metrics and highlights the challenge of detecting nuanced hallucinations in LLM outputs.
- The paper demonstrates that retrieval-augmented generation and advanced prompting strategies effectively align outputs with verifiable evidence.
- The paper emphasizes the need for domain-specific datasets and fine-tuning to enhance model robustness in real-world fact-checking scenarios.
Hallucination to Truth: A Review of Fact-Checking and Factuality Evaluation in LLMs
Introduction
The paper "Hallucination to Truth: A Review of Fact-Checking and Factuality Evaluation in LLMs" presents an in-depth evaluation of the challenges and methodologies in verifying the factual accuracy of outputs from LLMs. LLMs, trained on diverse and extensive datasets, are prone to generating misinformation, commonly termed hallucinations, necessitating robust fact-checking frameworks.
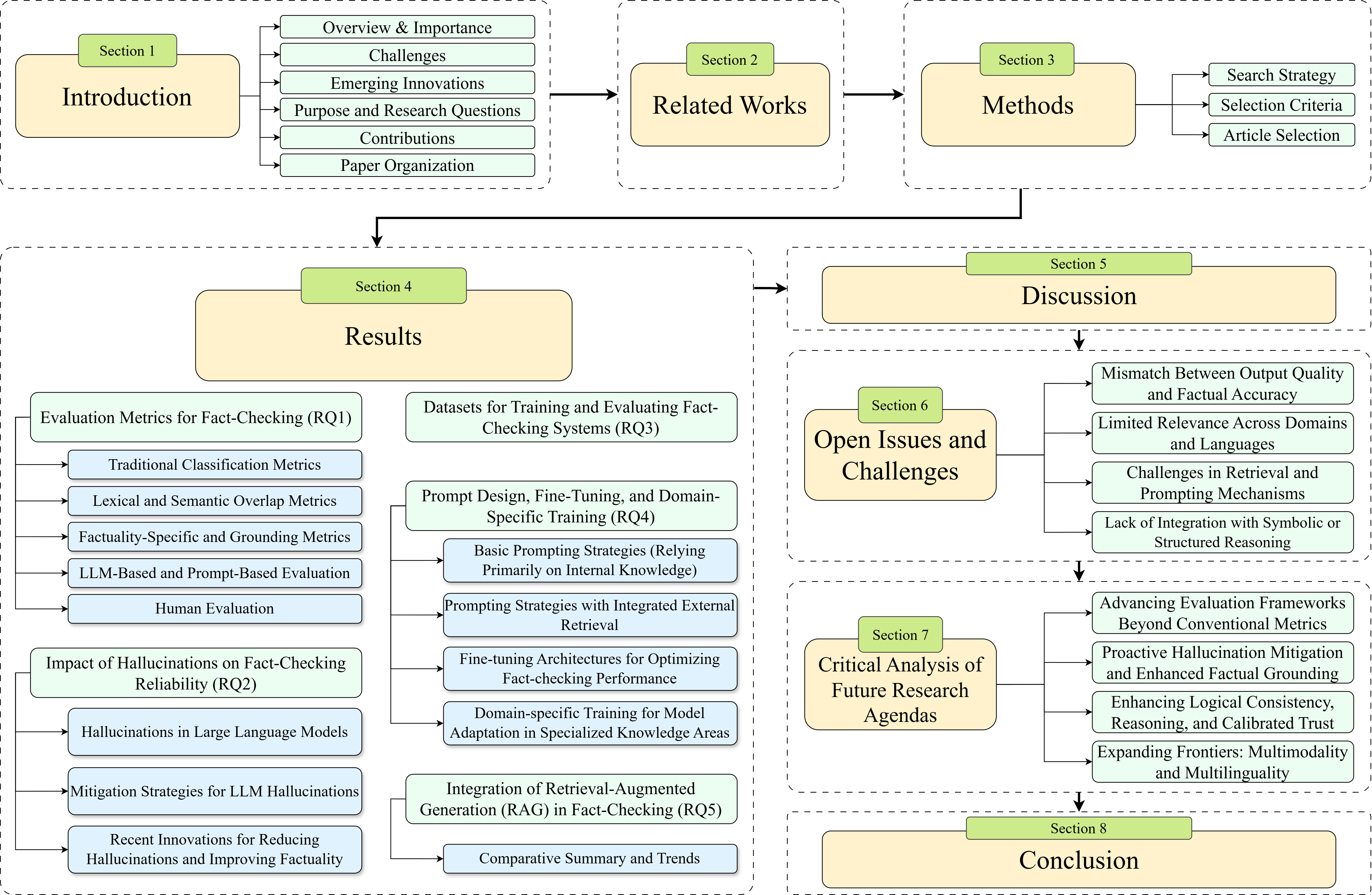
Figure 1: The fundamental content structure and categorization of this survey.
Challenges in Fact-Checking
Evaluation Metrics
The paper underscores the inadequacy of current evaluation metrics which focus more on surface-level similarity rather than factual consistency. Standard metrics like accuracy and F1-score are insufficient for detecting nuanced errors often present in LLM outputs.
Hallucinations
A critical issue with LLMs is their tendency to produce hallucinations: outputs that are linguistically correct but factually inaccurate. This can be attributed to inherent biases in training data and the limitations of existing LLMs in handling complex queries.

Figure 2: Intrinsic vs. extrinsic hallucinations in LLM outputs.
Innovations in Fact-Checking
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG methods have been highlighted as a promising technique to enhance factual accuracy. By integrating external evidence during the generation process, RAG helps align LLM outputs with verifiable sources. However, the implementation of RAG is not without challenges, such as efficiently retrieving and utilizing relevant data from extensive databases.
Advanced Prompting and Fine-Tuning
The paper discusses advanced prompting strategies and domain-specific fine-tuning as crucial techniques to improve LLM performance in fact-checking. Instruction tuning and multi-agent systems are also explored to enhance the reliability of LLMs by incorporating structured external knowledge sources.
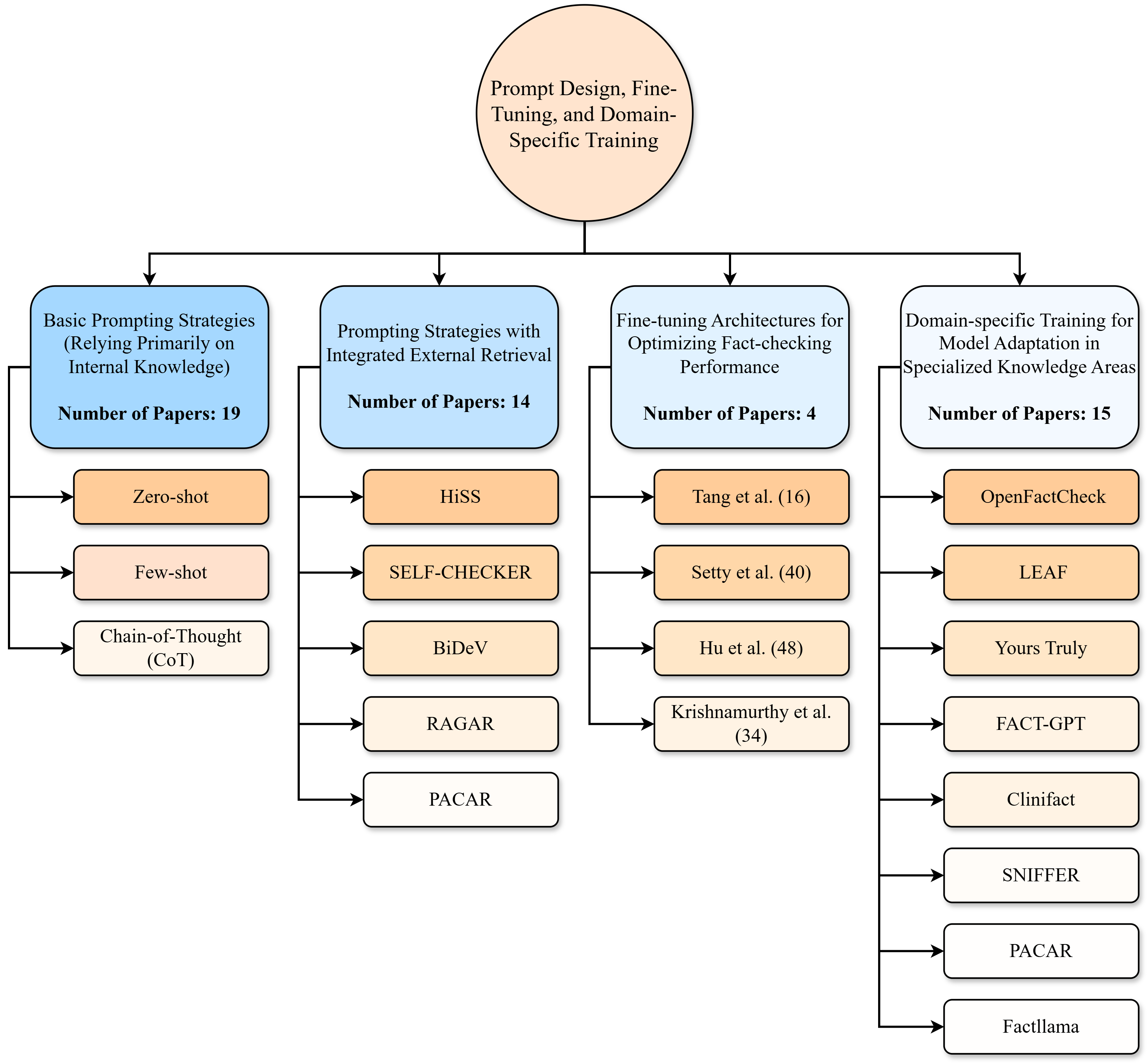
Figure 3: Breakdown of approaches in prompt design, fine-tuning, and domain-specific training for fact-checking with LLMs.
Dataset Limitations
The quality of datasets is a pivotal factor in the efficacy of fact-checking systems. Many benchmarks lack the complexity of real-world claims, limiting the generalizability of trained models. Domain-specific datasets are identified as essential for improving model robustness across diverse topics.
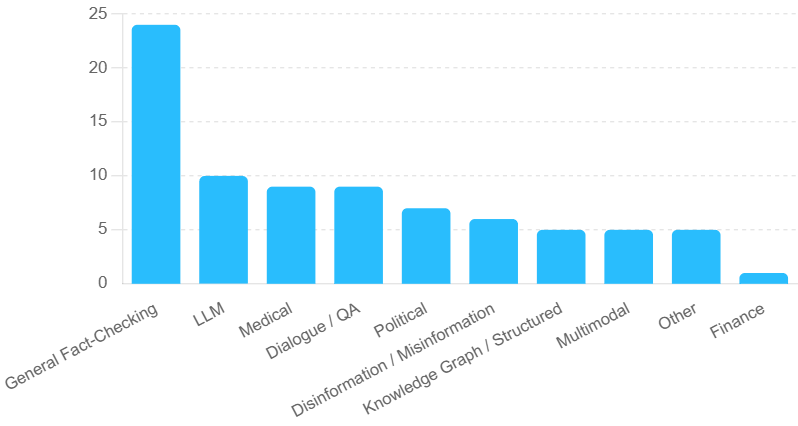
Figure 4: Illustration of major dataset types and domains.
Conclusion
The review concludes by emphasizing the need for robust and adaptive fact-checking systems that integrate advances in RAG, prompting strategies, and domain-specific training. These systems should aim to improve the factual precision of LLM outputs, thereby enhancing the trust in models used for critical applications such as news and policy making.
While significant progress has been made, the paper highlights ongoing challenges, such as the rapid development of misinformation and the evolving nature of factual databases, which require continuous adaptation and innovation in LLM-based fact-checking systems.





