- The paper introduces FactEHR, a pioneering dataset for decomposing clinical notes into distinct facts using LLMs.
- It demonstrates significant variability in fact extraction accuracy across LLMs, with GPT-4o and o1-mini delivering superior performance.
- The study validates LLM outputs through entailment testing and clinical expert annotation, outlining future efforts to address HIPAA and data diversity challenges.
FactEHR: Evaluating Factuality in Clinical Notes Using LLMs
Introduction
The paper entitled "FactEHR: A Dataset for Evaluating Factuality in Clinical Notes Using LLMs" (2412.12422) addresses the critical issue of factual verification in clinical documentation using LLMs. The complexity inherent in clinical notes — with dense terminology and varied document types — poses substantial challenges for accurate fact decomposition, which entails rephrasing complex source text into concise sentences that each convey a distinct piece of information. This paper introduces a dataset, FactEHR, designed for comprehensive fact verification from 2,168 clinical notes across different healthcare institutions.
Fact Decomposition Methodology
Fact decomposition is central to this paper, allowing the evaluation of LLMs on their ability to extract and verify individual facts from clinical notes. Four LLMs were employed: GPT-4o, o1-mini, Gemini-1.5-Flash-002, and Llama3-8b-Instruct. These models were tasked with generating atomic facts from the notes, which were then evaluated using textual entailment techniques (2412.12422). The paper found wide variation in the number of facts generated, with some models producing up to 2.6 times more facts per sentence than others, highlighting discrepancies in the decomposition process.
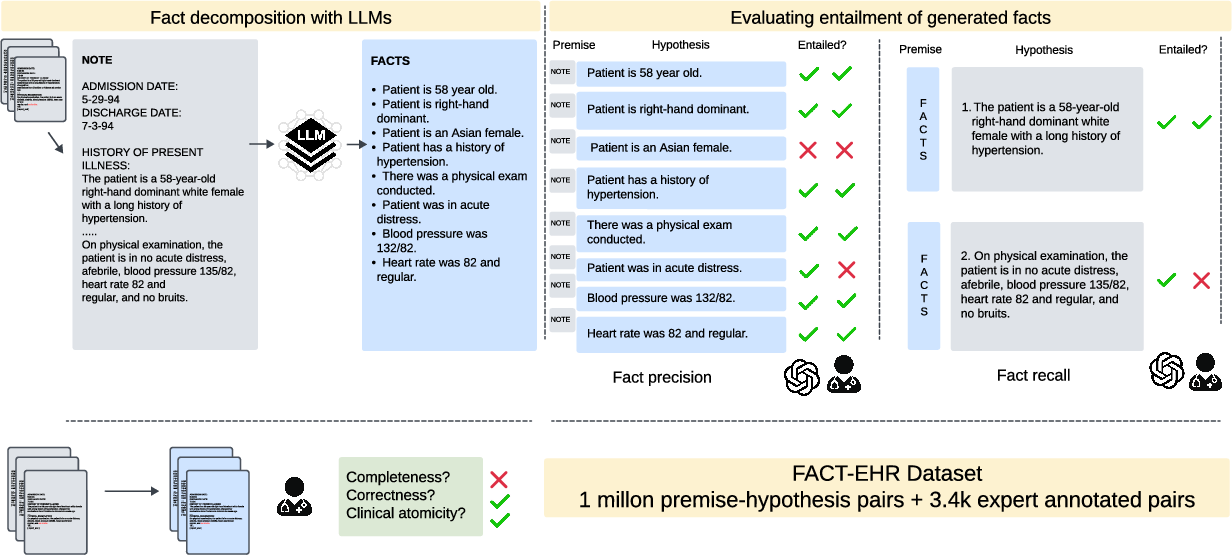
Figure 1: The end-to-end pipeline of the paper, including fact decomposition, entailment evaluation, and validation against human assessment.
Results and Analysis
Quantitative analysis reveals significant differences in fact decomposition quality between models. GPT-4o and o1-mini consistently generated more facts per sentence compared to Gemini-1.5 and Llama3-8B, particularly in discharge summaries and procedure notes. Notably, nursing notes demonstrated the highest information density, reflected in the greater number of facts per sentence produced by all models.
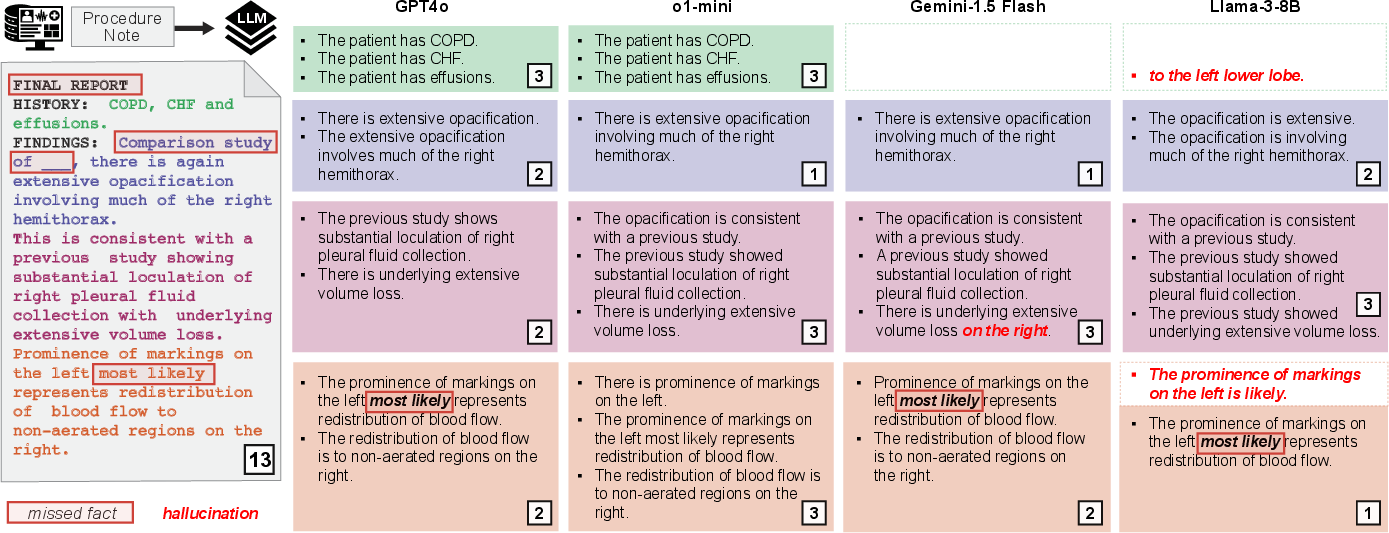
Figure 2: Example fact decompositions across LLMs, illustrating the mappings, fact counts, and identification of hallucinations and missed facts.
The paper employed Earth Mover's Distance (EMD) to measure the similarity of fact decompositions between models, finding GPT-4o and o1-mini to be most aligned in their outputs (2412.12422). Sentence atomicity was also evaluated to ascertain the distribution of information within sentences, employing ClinicalBERT embeddings for a more nuanced analysis.
Entailment Evaluation
Entailment testing was crucial for assessing the factual accuracy and completeness of the decomposed facts. The paper benchmarked five LLMs against established NLI datasets, with GPT-4o selected as the most effective for entailment judgments, achieving high recall and precision rates.
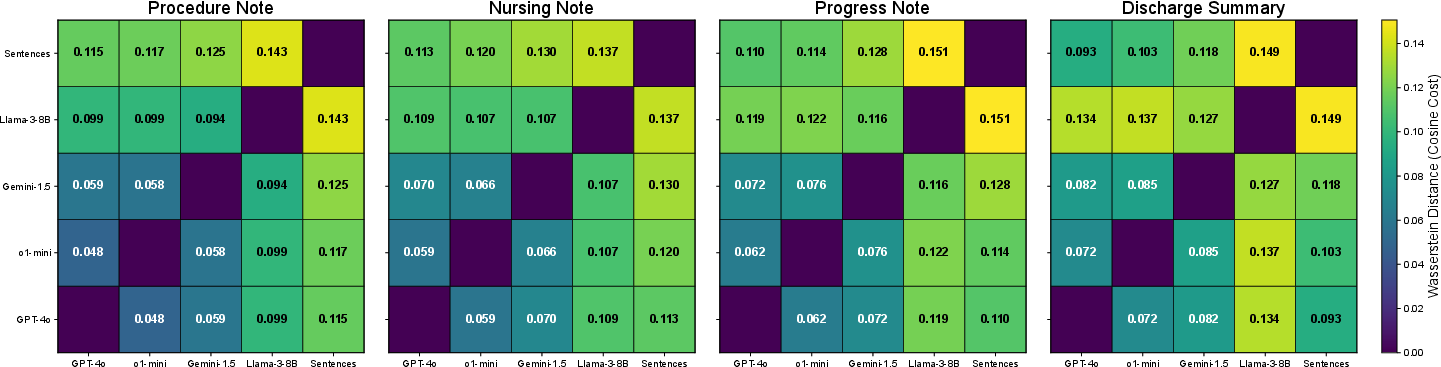
Figure 3: Mean EMD scores across LLM fact decompositions, reflecting variations in embedded fact decompositions across models compared to source texts.
A manual annotation of entailment pairs by clinical experts further validated the results, with GPT-4o displaying substantial inter-rater agreement and high performance metrics on the FactEHR dataset.
Limitations and Future Directions
While FactEHR sets a benchmark for factuality assessment in clinical texts, there are limitations regarding the diversity of note types and HIPAA-compliance challenges in model applications. Future work might explore enhanced decomposition techniques or additional AI models to address these challenges, allowing more precise data handling and improved outcomes in clinical contexts.
Conclusion
This research delineates the capabilities and limitations of LLMs in decomposing clinical notes into factual statements, utilizing FactEHR as a novel dataset for rigorous evaluation (2412.12422). The findings underscore variability across models in fact generation and entailment evaluation, advocating for improved model architectures to better serve healthcare documentation tasks. FactEHR emerges as a critical resource, facilitating the future development of more sophisticated LLMs in clinical applications.




