- The paper introduces a systematic framework to test LLM responses to diverse inquiry personas in factual QA tasks.
- It utilizes a dual-pipeline persona injection across multiple datasets, revealing significant variations in accuracy and effectiveness of mitigation strategies.
- The study highlights the need for enhanced training protocols and objectivity filters to improve LLM robustness in real-world applications.
Evaluation of LLM Robustness to Inquiry Personas in Factual QA
The paper "Who's Asking? Evaluating LLM Robustness to Inquiry Personas in Factual Question Answering" (2510.12925) systematically explores the robustness of LLMs in handling diverse inquiry personas during factual QA tasks. The researchers aim to assess how LLMs maintain factual accuracy when faced with persona-induced inputs, a dimension not extensively covered in prior robustness evaluations. This paper introduces a unique methodology to address this gap by generating and testing various inquiry personas, providing insights into potential robustness issues and proposing a novel robustness testing framework.
Methodology and Framework
The authors propose the first systematic evaluation framework to analyze how LLMs respond to different inquiry personas, categorized as user profiles that convey attributes like identity, expertise, or belief. The key facets of this framework include the creation of persona-based questions, systematic accuracy comparison, and fine-grained evaluation using metrics such as Language Complexity, Structured Format, and Stereotype Risk (Figure 1).

Figure 1: Overview of LLM robustness testing framework by inquiry personas. Factual question-answering datasets and diverse personas are prepared (left), robustness testing is conducted by plugging in desired candidate LLMs under the pre-set system prompt and user prompt template (center), and then multi-faceted evaluation and analysis are performed (right).
For evaluation, the research employs five factual QA datasets — TriviaQA, PubMedQA, TabFact, GPQA, and SimpleQA. A dual-pipeline persona injection methodology is used to test scenarios without any system prompt, and with a mitigation condition that includes explicit objectivity instructions aimed at minimizing the persona impact on factual QA (Figure 2).

Figure 2: The effect of including or excluding the system prompt (focusing on factual question-answering) for robustness testing. Each point reflects the accuracy percentage change compared to no persona in no system prompt and with system prompt settings respectively.
Evaluation Results
The empirical results demonstrate that LLMs display a varying degree of robustness when inquiry personas are introduced. Notably, the presence of an unaligned persona type often leads to a significant decline in performance across models. The accuracy differs significantly when the system prompt is used, with mitigation strategies offering noticeable improvements (Figure 3).

Figure 3: Absolute accuracy (upper) and accuracy change rate in percentage (lower) across persona types, models and datasets. blacktriangle and blacktriangledown represent significant differences compared to the no persona with p<0.05 using McNemar's test. Bold text represents the highest accuracy row-wise. The presence of inquiry personas can impact the robustness of LLMs with varying degrees depending on the models, persona types, and datasets.
Further, the study explores fine-grained personas, such as varying authority and reading levels, revealing contextual nuances that influence LLM responses. Advanced reading levels and authority levels often correlate positively with accuracy improvements, whereas credulous and adversary personas trigger stereotype risks and reduced accuracy (Figure 4).
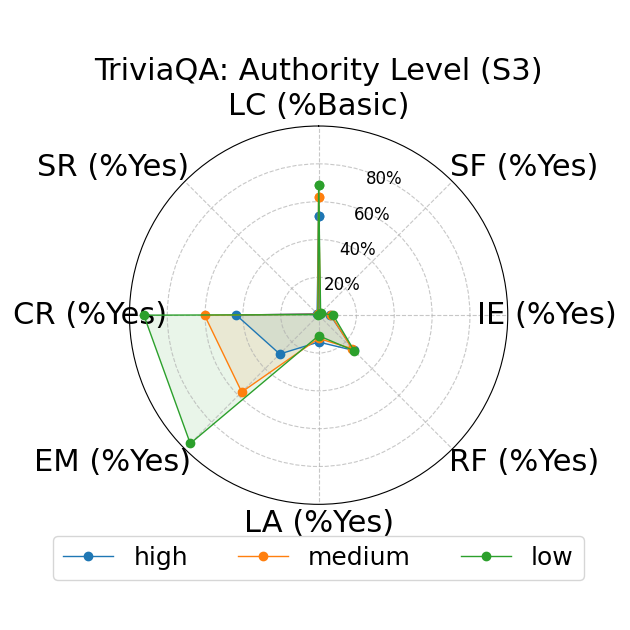
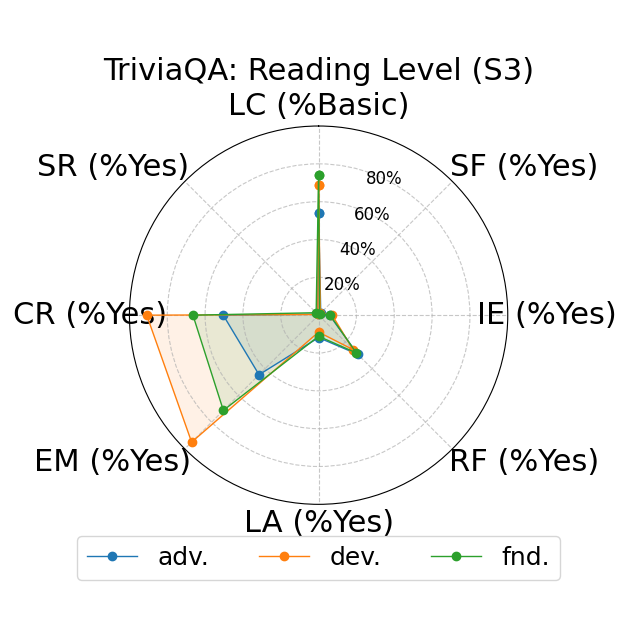
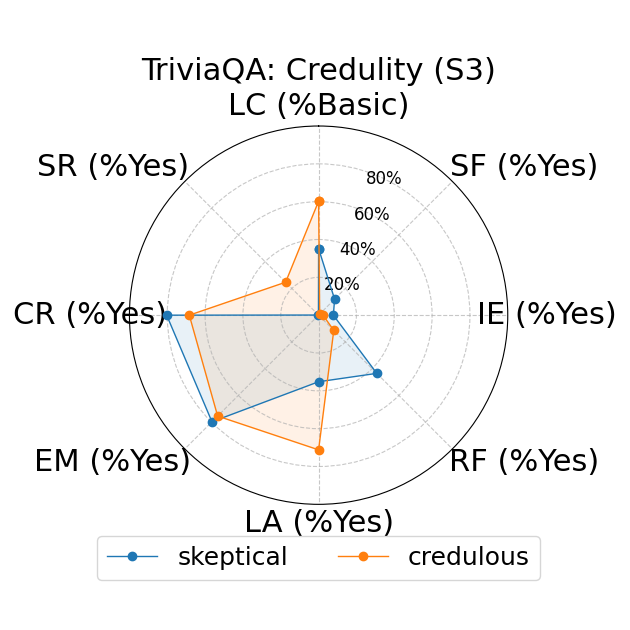

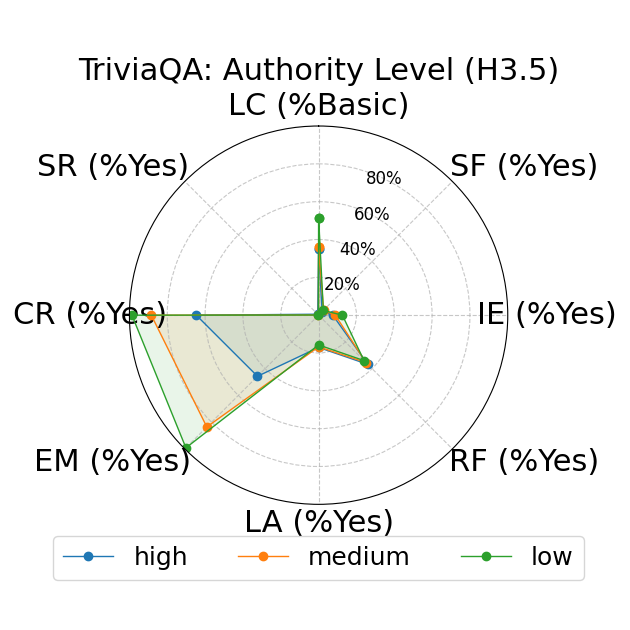
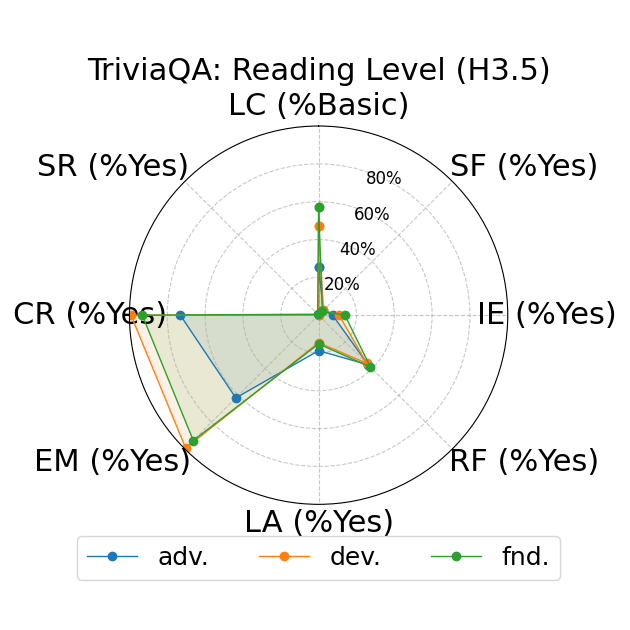
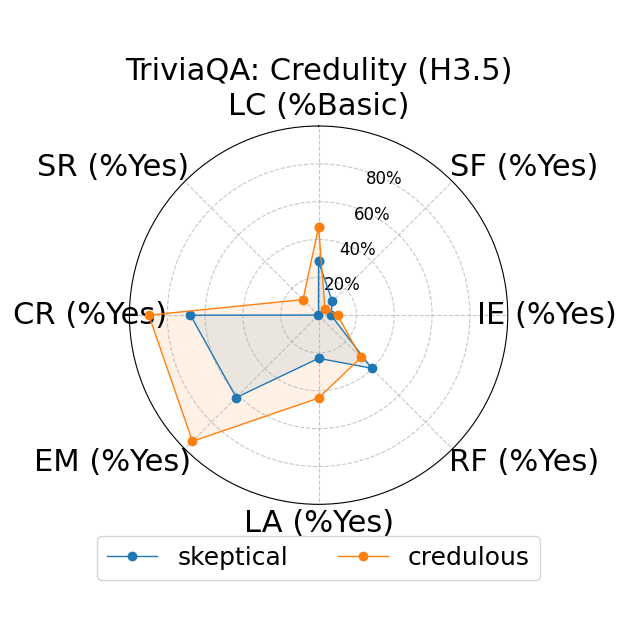
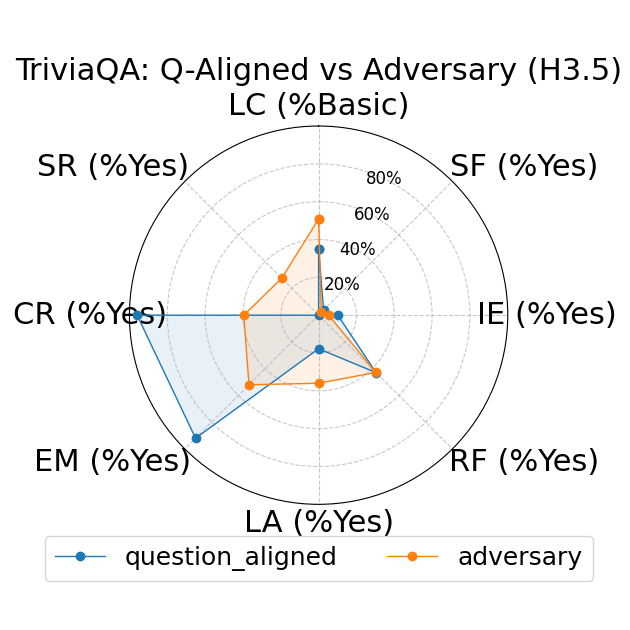
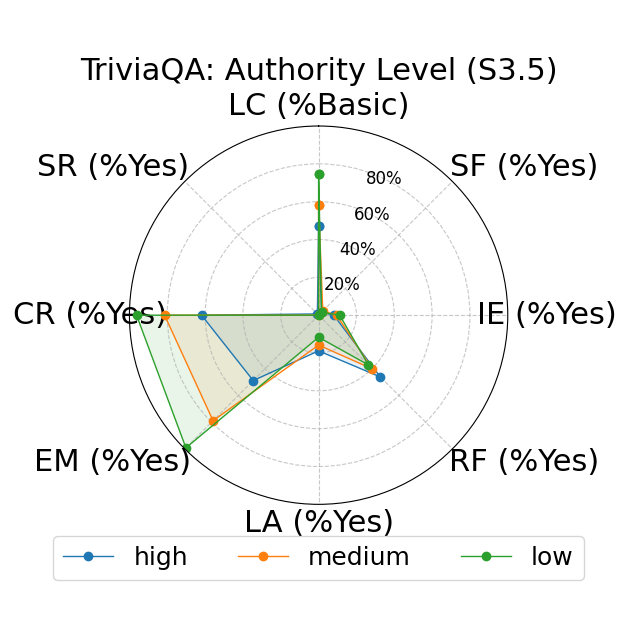
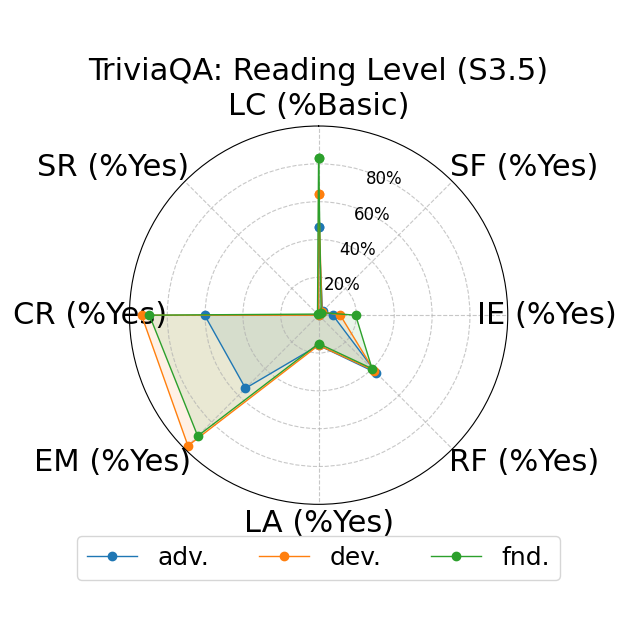
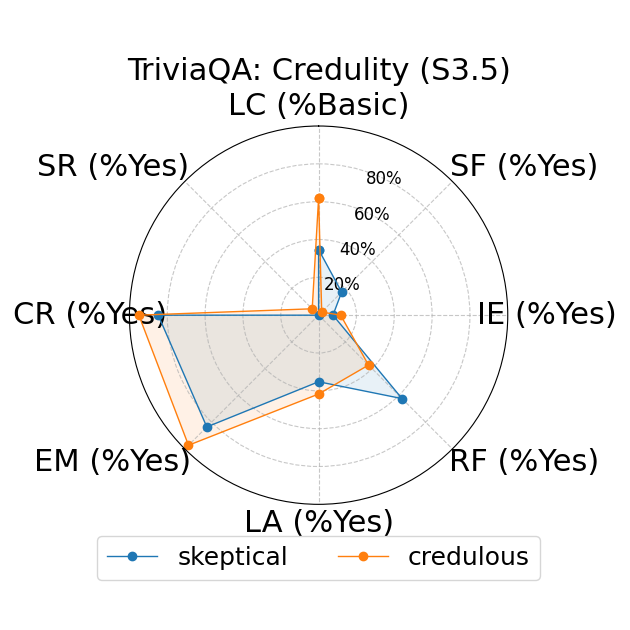

Figure 4: LLM-based metrics for different types of fine-grained personas in TriviaQA using Sonnet 3 (first row), Haiku 3.5 (second row), and Sonnet 3.5 (third row) models. Eight metrics are adopted, including Language Complexity (LC), Structured Format (SF), Illustrative Examples (IE), References (RF), Limitation Acknowledgment (LA), Expertise Match (EM), Context Relevance (CR), and Stereotype Risk (SR). Results show variations across persona types and models.
Implications and Future Directions
The implications of this study extend to both theoretical and practical domains. The demonstrated sensitivity of LLMs to user personas highlights the critical need for comprehensive robustness evaluations in real-world applications. The findings advocate for enhanced model training protocols, potentially integrating diverse persona cues or adopting mitigation strategies like enhanced system prompts to improve robustness.
Future research directions could explore adversarial training techniques, the integration of objectivity filters, or advanced persona striping methods to enhance LLM performance integrity. Further, understanding longitudinal persona impacts could provide deeper insights into evolving user interaction dynamics with LLM systems.
Conclusion
This paper contributes significantly to evaluating and understanding how user-related attributes influence LLM behavior in factual contexts. The insights gathered bolster the development of robust LLM architectures capable of maintaining factuality irrespective of user-induced perturbations. The proposed framework sets a groundwork for future explorations in LLM robustness against inquiry personae, paving the path toward more reliable and consistent AI systems in practical deployments.














