- The paper introduces a two-stage LLM annotation framework that processes 133 million paragraphs from PubMed Central to enhance training data quality.
- It demonstrates a methodological advancement by filtering based on educational quality and domain relevance, optimizing training efficiency.
- Results indicate that the BE-All variant reduces training tokens by about one-third while achieving superior zero-shot performance on benchmarks.
Biomed-Enriched: A Biomedical Dataset Enriched with LLMs
Introduction
The paper "Biomed-Enriched: A Biomedical Dataset Enriched with LLMs for Pretraining and Extracting Rare and Hidden Content" advances the capabilities of LLMs within specialized domains such as biomedical and clinical medicine, tapping into a precious corpus for enhanced LLM training. The Biomed-Enriched dataset provides a resource for clinical NLP applications, creatively circumventing the typical limitations imposed by privacy and accessibility of clinical data. The authors illustrate improvements with strategies exploiting domain-specific content and refined metadata to bolster the efficacy of LLMs in intricate biomedical reasoning.
Methodology
Data Collection and Preprocessing
The dataset construction began with extracting over 4.5 million full-text scientific articles from PubMed Central's Open Access Subset. The raw articles were meticulously processed, culminating in a collection of 133 million paragraphs meeting a minimum token count, ready for semantic annotation.
Two-Stage Annotation Framework
A two-stage annotation framework was employed: first, a robust LLM annotated 400,000 paragraphs across dimensions such as type, domain, and educational quality. Subsequently, these annotations were distilled into a smaller XLM-RoBERTa model designed to scale the annotation process efficiently across the entire corpus. The framework dynamically tailors content to highlight high-value segments that might be overlooked using conventional filtering methods.
Dataset Variants
Several dataset variants were curated, including BE-Base and BE-All, with strategic filtering for educational quality and domain upsampling. Across these, from replication of clinical content to metadata prefixing, these variants seek to optimize training efficiency while retaining the integrity of scientific article structures.
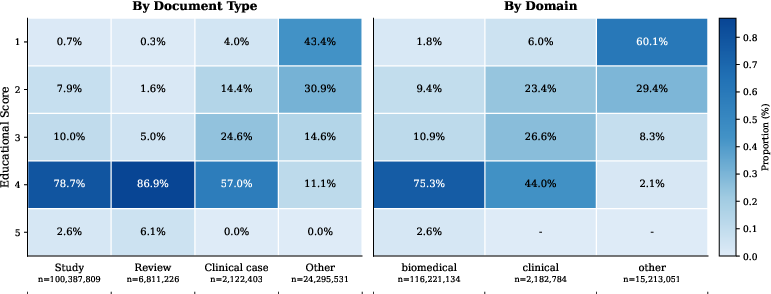
Figure 1: Distribution of educational quality scores by document type and domain. Reviews and studies show the highest proportion of high scores, while clinical texts display more variance.
Data Analysis
Score Distributions
Quantitative analyses on the dataset reveal a skew toward paragraphs with higher educational scores—especially reviews and studies—which underscore the feasibility of targeted training strategies. The metric of educational quality serves as a selection criterion to bolster learning outcomes in domain-specific tasks.
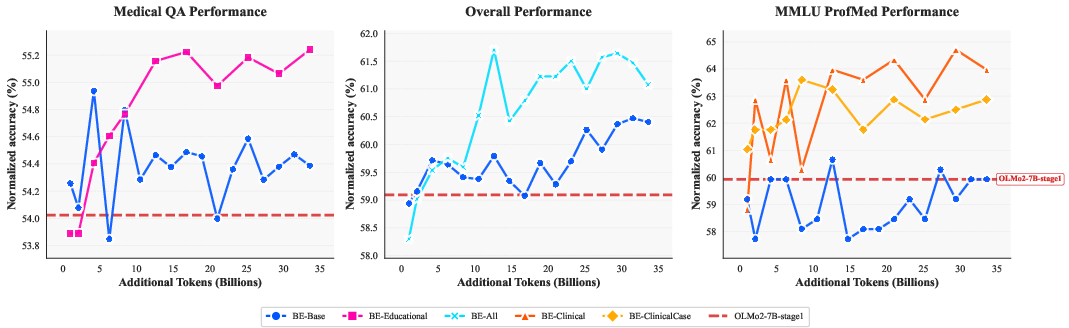
Figure 2: Performance comparison across dataset variants showing training progression. BE-All achieves target performance with approximately one-third of the training tokens required by BE-Base.
Continual Pretraining
The authors employed continual pretraining on OLMo2-7B-stage1, advancing the model while maintaining parameter constancy across experiments. This approach focused on elucidating the effects of curated datasets rather than pursuing state-of-the-art embeddings.
Evaluation and Results
Zero-shot evaluations on benchmarks, such as MMLU and MedQA, emphasize the quantitative improvements derived from Biomed-Enriched dataset variants over baseline models. Notably, BE-All showcases an effective amalgamation of enrichment techniques, achieving superior results with enhanced training efficiency—a reduction in training tokens by approximately one-third compared to the BE-Base variant.
Discussion
Biomed-Enriched's ability to extract niche biomedical narratives reflects the potential of strategically annotated data to bridge performance gaps in LLMs within specialized domains. The proposed enrichment strategies demonstrate significant improvements, underscoring the importance of aligning data strategies with task-specific requirements. Moreover, the non-English generalization potential highlights the flexibility of these enrichment approaches across linguistic domains.
Conclusion
"Biomed-Enriched: A Biomedical Dataset Enriched with LLMs" presents a refined approach to domain-specific LLM training, leveraging paragraph-level annotations and curated datasets to overcome typical privacy-constrained limitations. Its findings propel a shift toward modular, adaptable training strategies, offering a flexible foundation for specialized models that cater to diverse needs in biomedical NLP. The study advocates continued exploration of fine-grained data curation to support efficient pretraining configurations, ensuring future advancements in this critical area.

