- The paper introduces BIOMEDICA, a large-scale vision-language dataset with over 6 million articles and 24 million image-text pairs that enhances biomedical AI research.
- The paper details comprehensive annotations and an API for efficient filtering and retrieval, enabling targeted model training and integration.
- The paper demonstrates state-of-the-art performance improvements, including a 36.22% boost in guideline-based question answering tasks.
A Large-Scale Vision-Language Dataset Derived from Open Scientific Literature to Advance Biomedical Generalist AI
Dataset Overview
The paper presents "A Large-Scale Vision-Language Dataset Derived from Open Scientific Literature to Advance Biomedical Generalist AI", which introduces BIOMEDICA\ - an expansive, open-source vision-language dataset crafted from the PubMed Central Open Access repository. This dataset encompasses over 6 million articles and 24 million image-text pairs with 27 metadata fields, including expert annotations. Tools for targeted content retrieval and seamless integration with AI systems are discussed, enhancing accessibility without necessitating complete dataset downloads.
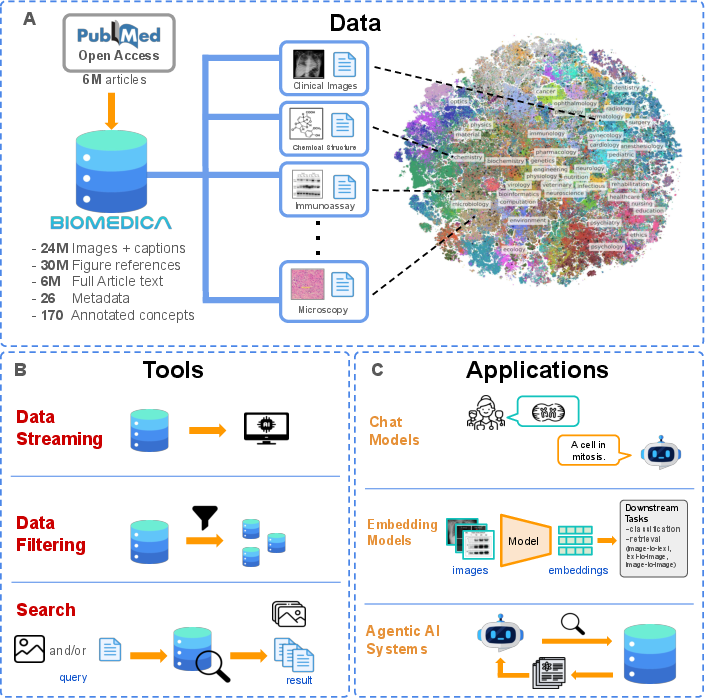
Figure 1: An overview of the BIOMEDICA\ dataset, tools for accessibility, and its applications.
BIOMEDICA\ aims to democratize access to scientific data across biomedical domains, facilitating the development of embedding models, chat-style models, and retrieval-augmented chat agents. These models have been shown to surpass prior open systems in accuracy and performance, emphasizing the critical significance of diverse, high-quality datasets in biomedical research.
Data Annotation and Accessibility
The BIOMEDICA\ dataset is thoroughly annotated, with each instance containing both article- and image-level metadata and human-derived annotations. This content includes bibliographic information, image classifications, panel-type annotations, and expert groupings, enabling effective concept balancing and personalized data filtering. The substantial scope of the dataset poses challenges in terms of resource management, which the authors address by hosting data artifacts on a web server and providing efficient access tools.
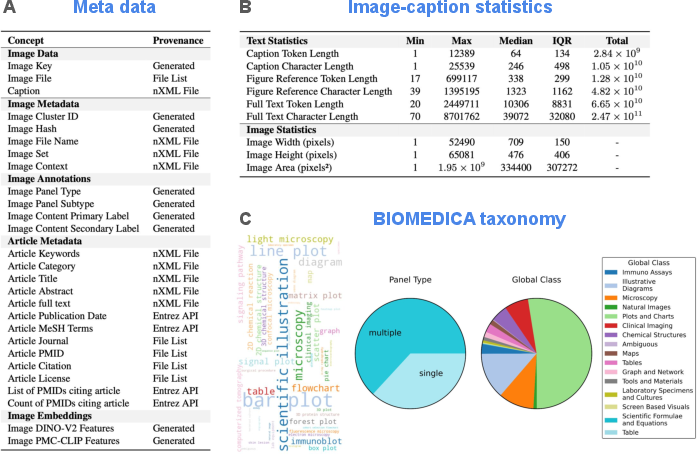
Figure 2: Overview of the BIOMEDICA\ dataset statistics and annotations.
By offering data streaming capabilities, users can train models without storing data locally, filtering the dataset to create domain-specific subsets for specialized models, thus ensuring user adaptability. For fast retrieval purposes, the authors release an application programming interface (API) that facilitates searching through articles, captions, and images with queries that incorporate text, images, or both.
BIOMEDICA\ models demonstrate impressive metrics on multimodal benchmarks. Multimodal embedding models, such as BMC-CLIP, obtained superior scores in biomedical image classification and retrieval tasks compared to previous models, including PMC-CLIP and BiomedCLIP.
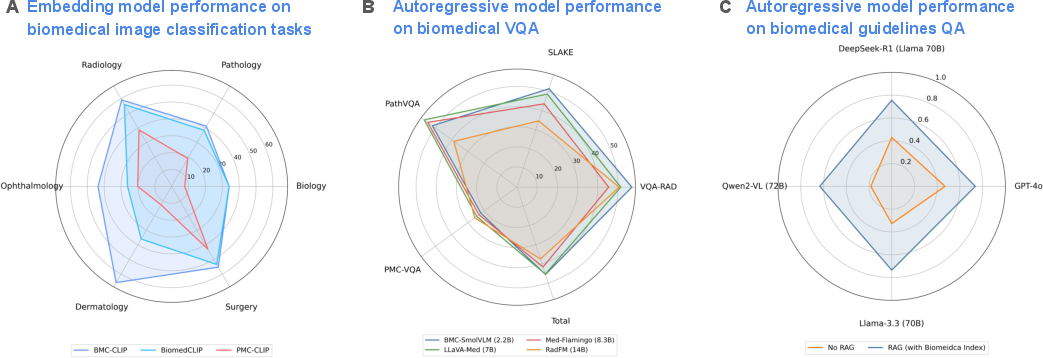
Figure 3: BIOMEDICA\ enables state-of-the-art performance across multiple applications.
Autoregressive models trained on BIOMEDICA\, such as BMC-SmolVLM, achieve competitive performance on vision question-answering tasks at reduced computational costs due to their efficient parameterization. The paper utilizes several vision question-answering datasets to validate these models' capability across numerous medical imaging tasks.
Furthermore, BIOMEDICA\ facilitates the first of its kind: an AI agent capable of multimodal query and retrieval across its vast index. The BIOMEDICA\ Index substantially boosts performance in retrieving relevant full-text articles for AI agentic systems, with evaluations confirming an average 36.22% improvement in guideline-based question answering tasks across various LLMs.
Implications and Future Directions
The introduction of BIOMEDICA\ represents an integral advancement in biomedical AI research, offering unparalleled access to multimodal scientific data for refining and developing generalist models. The authors' contributions to model accessibility and performance suggest that such datasets will play a crucial role in advancing precision medicine and driving scientific discoveries.
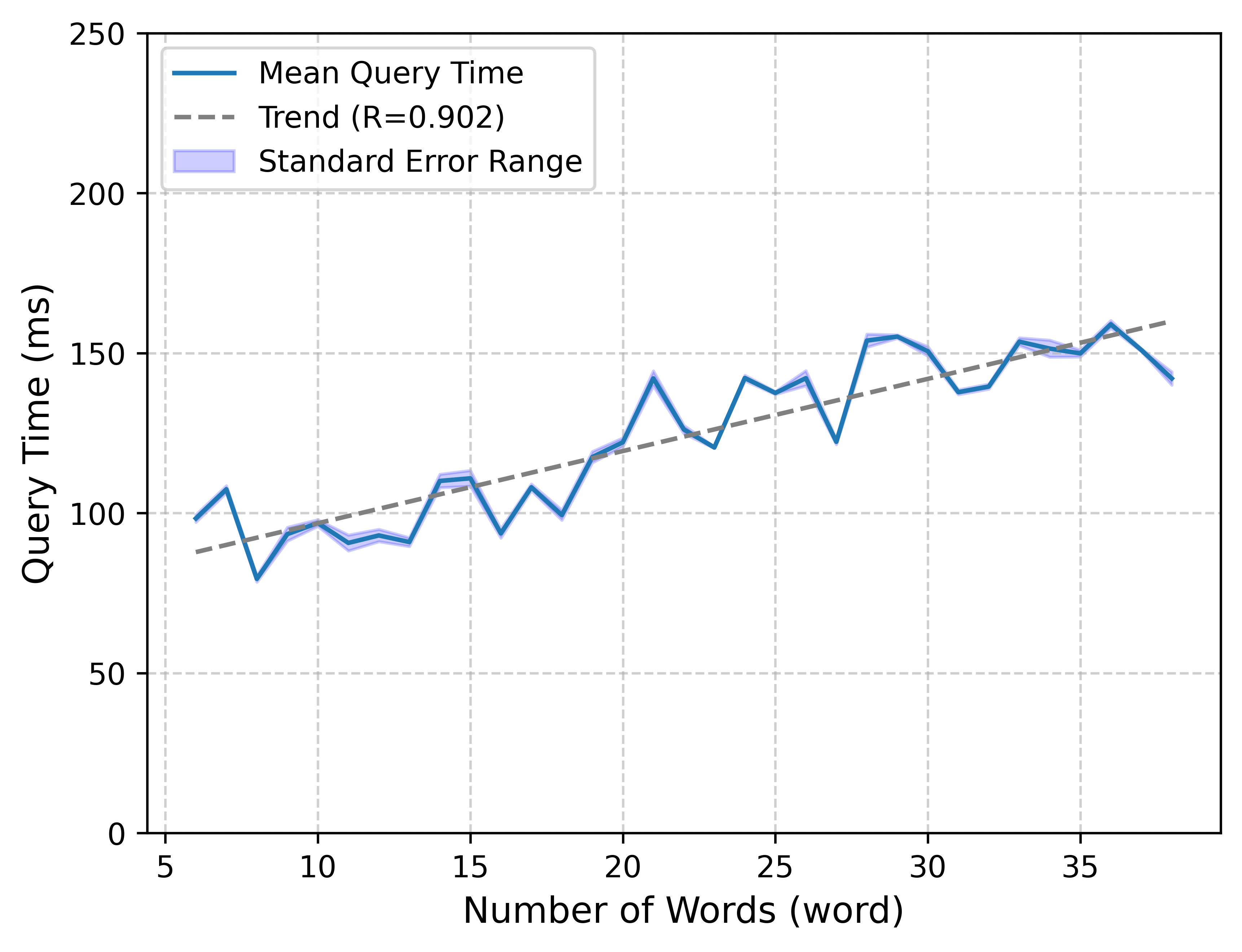
Figure 4: Query time as a function of words (tokens) in the BIOMEDICA\ index, indicating linear query time scalability.
Future developments will likely build upon these contributions by fostering greater integration of multimodal datasets into AI applications, especially as LLMs and FMs continue to evolve. This dataset's comprehensive nature positions it as a foundational asset for research, promising substantial impacts on personalized healthcare and scientific progress.
Conclusion
BIOMEDICA\ establishes itself as a significant asset in biomedical AI, promoting innovation by providing diversified, annotated, and large-scale multimodal data. The demonstrated capabilities of BIOMEDICA-driven models underscore the importance of accessible and comprehensive datasets in enhancing biomedical AI systems. This open-source contribution lays pivotal groundwork for the future of personalized healthcare and scientific advancement.





