- The paper presents a novel policy-as-prompt framework that embeds moderation policies directly into LLM prompts to enhance adaptability.
- It employs empirical testing to fine-tune prompt structures, revealing critical sensitivities in LLM outputs to minor text changes.
- The study emphasizes cross-disciplinary challenges, highlighting technical, sociotechnical, and governance issues in modern content moderation.
Policy-as-Prompt: Rethinking Content Moderation in the Age of LLMs
The paper "Policy-as-Prompt: Rethinking Content Moderation in the Age of LLMs" presents a novel framework that integrates content moderation policies directly into the prompts utilized by LLMs. This approach, termed "policy-as-prompt," is proposed as a transformative methodology to address burgeoning content volumes and dynamic moderation challenges. The paper explores both the promise and the multifaceted challenges posed by this paradigm shift.
Introduction and Motivation
Content moderation is an indispensable feature of maintaining secure and inclusive digital spaces. Traditional moderation pipelines often involve substantial human effort to translate abstract policy objectives into guidelines and datasets for machine learning models. Recent advances in LLMs afford the possibility to simplify these workflows by incorporating policies directly into the models as prompts, enabling more adaptable moderation with minimal manual input. However, this transition introduces several challenges across technical, sociotechnical, organizational, and governance domains.
Technical Challenges
Converting Policies to Prompts
The translation of human-readable policy guidelines into LLM-adapted prompts is complex, as LLMs require precise language with minimal ambiguity for optimal performance. Verifying prompt efficacy without an intermediary dataset poses additional challenges. Strategies like empirical testing are suggested to ensure model outputs align with policy intentions.
LLMs exhibit sensitivity to the structure and format of prompts, where minor adjustments can lead to significant variations in output. Empirical studies illustrate that even negligible changes in phrasing or punctuation can impact model decisions. This phenomenon challenges the robustness and reliability of LLM moderation systems.
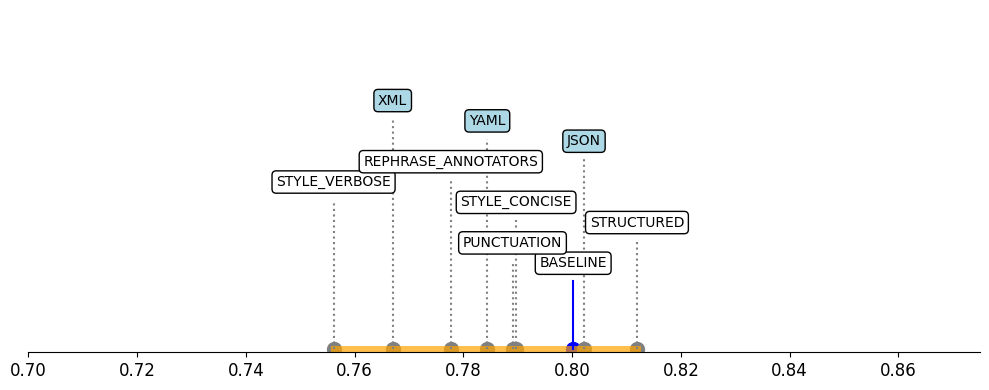
Figure 1: Performance spread (accuracy) for modifications in the format in which the policy is plugged into the prompt. Baseline refers to the plain text format.
Sociotechnical Implications
Technological Determinism
The adoption of LLMs raises concerns about technological determinism, where the technical capabilities of LLMs could unintentionally shape policy formulation. By prioritizing machine-friendly formats, nuanced human judgment might be undermined, potentially leading to homogenized enforcement that may not reflect diverse community standards or cultural nuances.
Organizational Dynamics
The seamless integration of LLMs necessitates a shift in the roles of policy authors and machine learning practitioners. Policy experts may need to expand their technical knowledge to effectively craft prompts, whereas machine learning experts may require deeper insights into policy implications. This cross-disciplinary collaboration is essential for the success of the policy-as-prompt approach.
Governance and Accountability
The policy-as-prompt paradigm challenges existing norms of transparency and accountability. The opaqueness of LLM decision-making hinders the attribution of outcomes to specific prompt configurations or policy elements. Establishing traceability for prompt modifications and ensuring regulatory compliance are critical concerns.
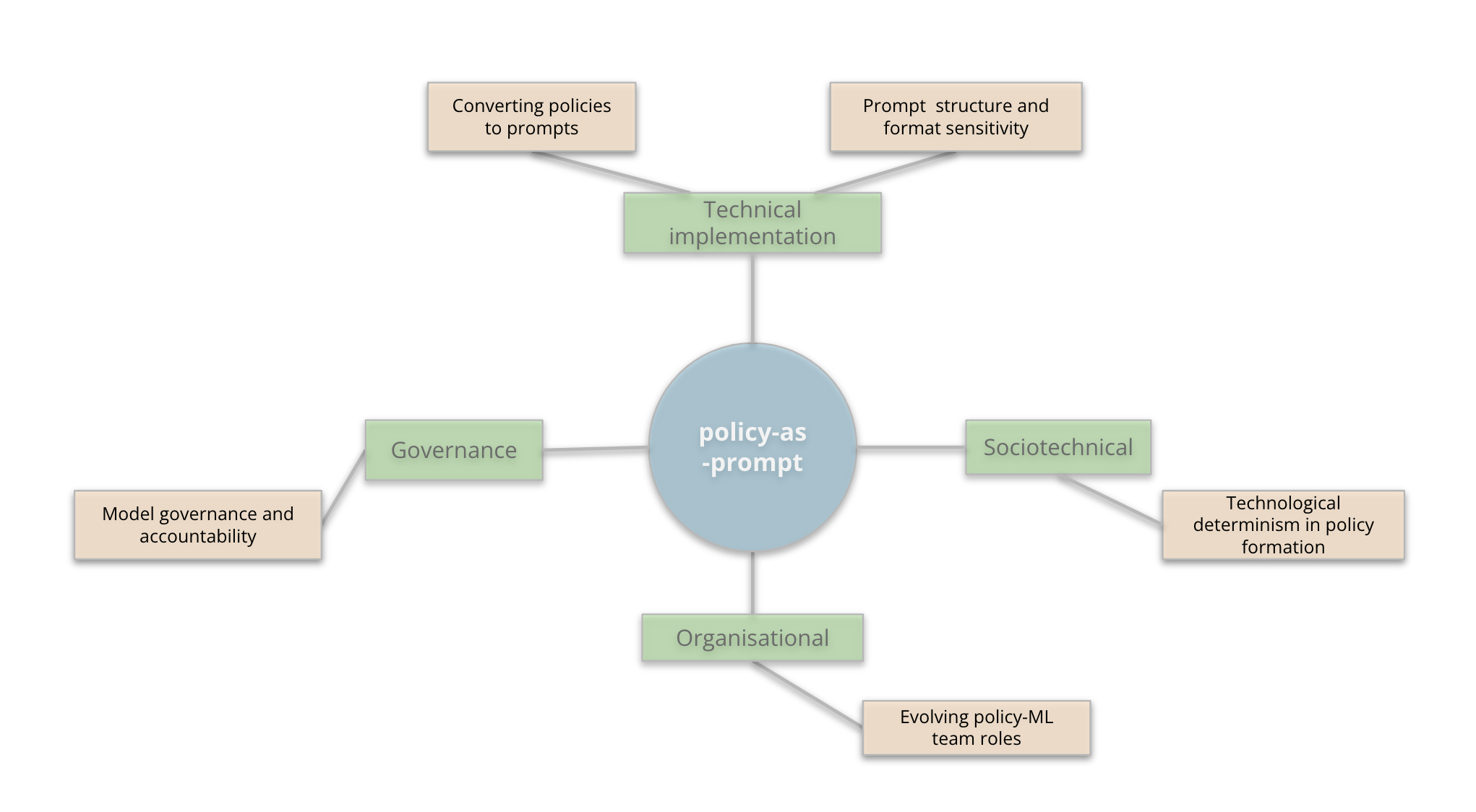
Figure 2: Challenges (light orange) across different areas (green) in policy-as-prompt implementation.
Recommendations and Mitigations
Enhanced Evaluation
Implementing rigorous evaluation frameworks that encompass sensitivity analyses can address prompt-related technical challenges. Continuous testing for performance robustness across various formats and structures is necessary.
Institutional Collaboration
Fostering deeper collaboration between policy and technical teams can mitigate organizational challenges. This can be achieved through shared documentation practices and regular interdisciplinary workshops focusing on developing a cohesive understanding and approach.
Governance Enhancements
Increasing transparency through detailed documentation of prompt changes and their impacts could alleviate governance concerns. Tools akin to version control systems for prompt modifications would support accountability and traceability needs.
Conclusion
The policy-as-prompt framework presents both significant opportunities and challenges in transforming content moderation processes. While initial experiments underscore the technical complexities and the need for multi-stakeholder collaboration, the potential benefits of adaptable and scalable content moderation are substantial. Ongoing research and refinement of this approach are imperative to fully realize its capabilities while addressing the associated challenges systematically.

