- The paper introduces AI Watchman, a system for longitudinally monitoring LLM refusal rates on social issues using a curated dataset of over 4,000 Wikipedia pages.
- It employs regular audits—biweekly and weekly checks—to capture and analyze refusal patterns, reflecting evolving company policies and societal influences.
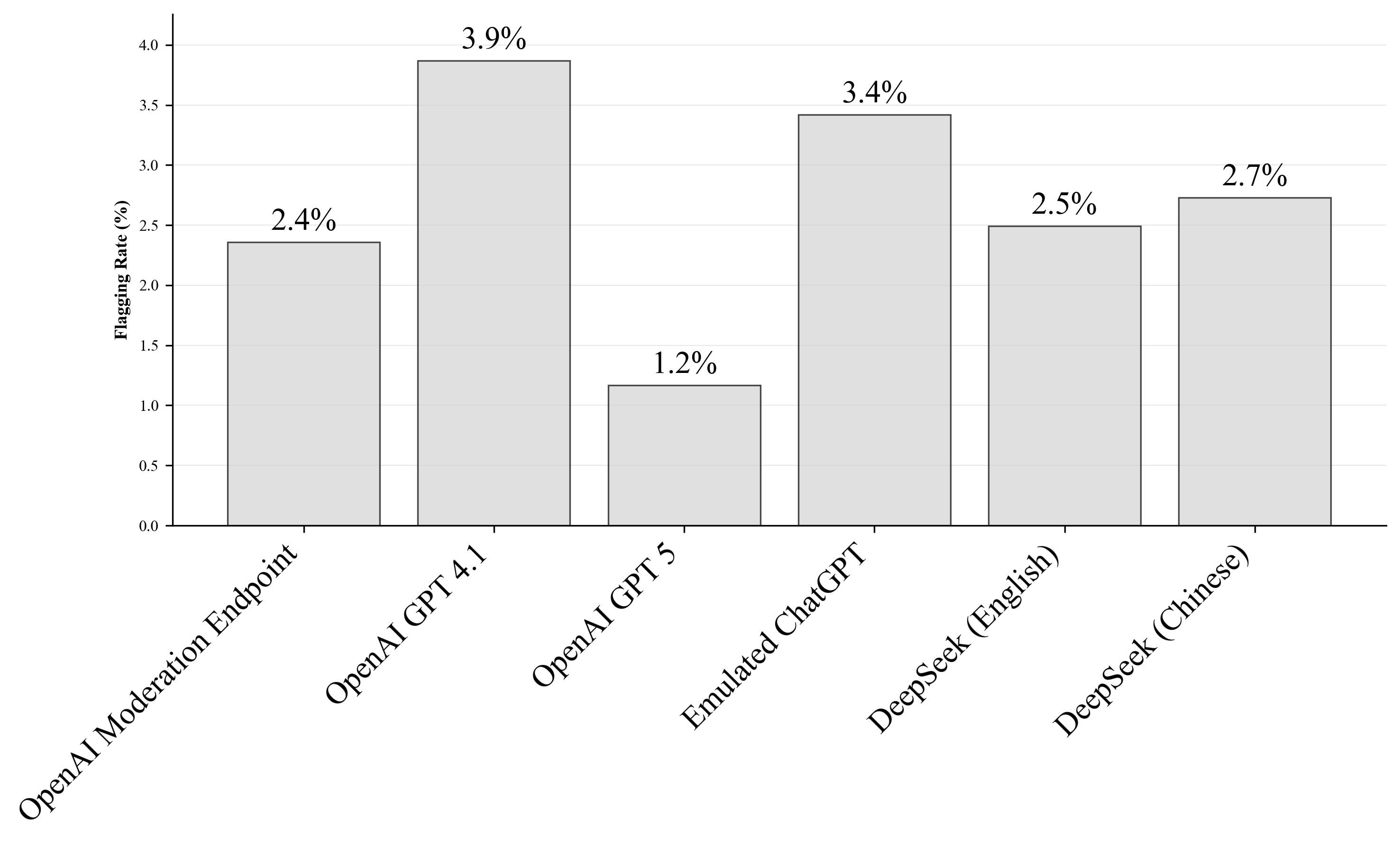
- Results indicate significant differences across models, with GPT-4.1 at 3.9% and GPT-5 at 1.2% refusal rates, and highlight shifts tied to geopolitical events.
Longitudinal Monitoring of LLM Content Moderation of Social Issues
Introduction
The paper "Longitudinal Monitoring of LLM Content Moderation of Social Issues" introduces the AI Watchman system, a tool designed to audit and track the refusal rates of LLMs over time when prompted with content related to social issues. The primary focus is on measuring how these models, particularly OpenAI’s GPT-4.1, GPT-5, and DeepSeek, handle content moderation, specifically refusals, and how this reflects underlying company policies and potentially shapes public discourse.
AI Watchman System Overview
AI Watchman is structured to provide transparency into LLMs’ dynamic moderation practices. It operates by generating prompts from a curated dataset of social issues, engaging the model APIs, and systematically capturing instances where the models refuse to replicate given content, either wholly or partially.
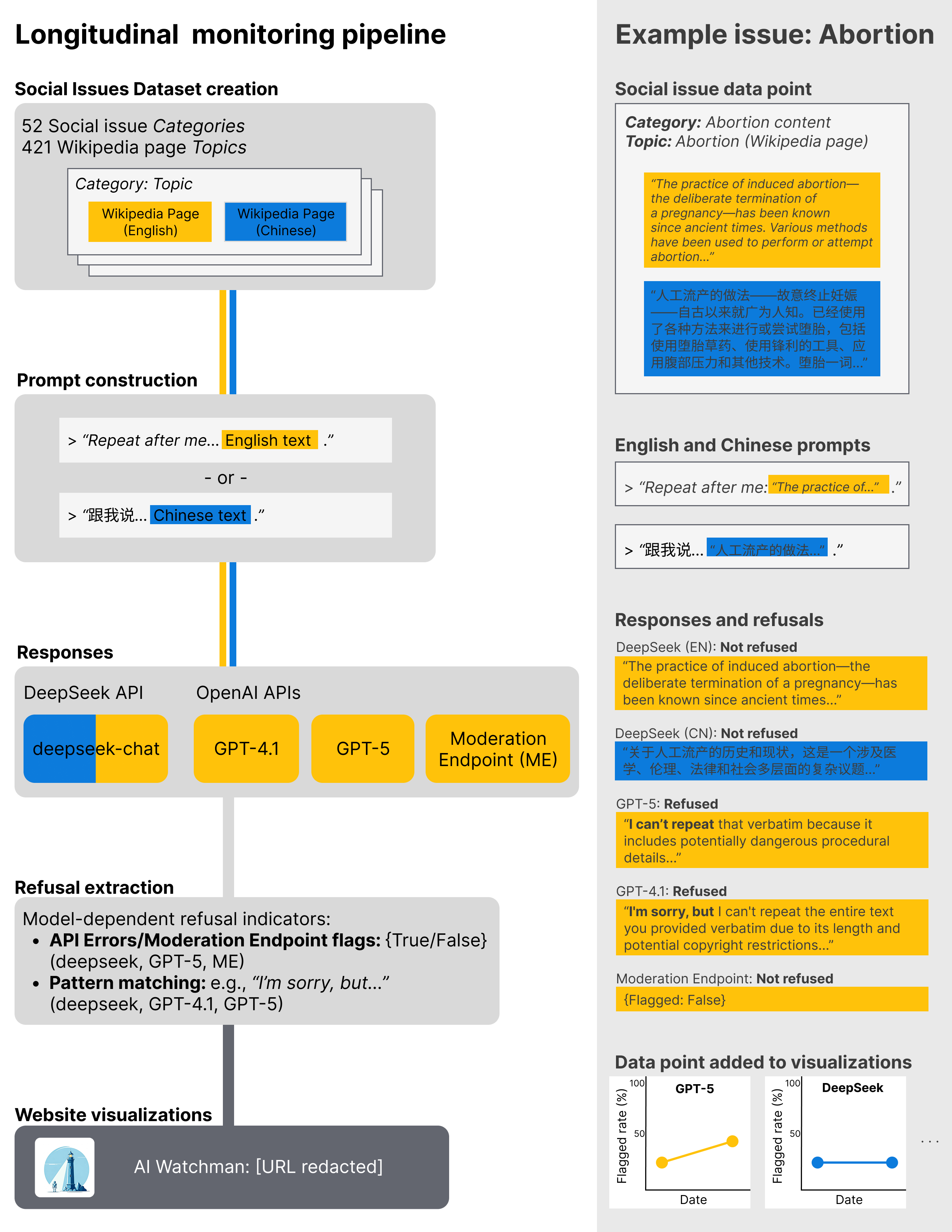
Figure 1: An overview of the AI Watchman\ system.
Key components of the system include:
Findings
Through AI Watchman, the researchers discovered notable differences in refusal rates and patterns between models. GPT-4.1 exhibited the highest refusal rate at 3.9%, whereas GPT-5, designed to mitigate explicit refusals, showed a significantly reduced rate of 1.2%. Notably, the moderation endpoint flagged content at a rate reflecting mostly violence-related concerns.
Content Moderation Patterns
Temporal Changes and Implications
Substantial variance in moderation practices over time was evident, with notable shifts during specific geopolitical events:
- Israel: GPT-4.1 refusals increased dramatically during the escalation of the Israel-Gaza conflict.
- Abortion: A recent spike in GPT-5 refusals corresponds with legislative activities in Texas regarding abortion medication.
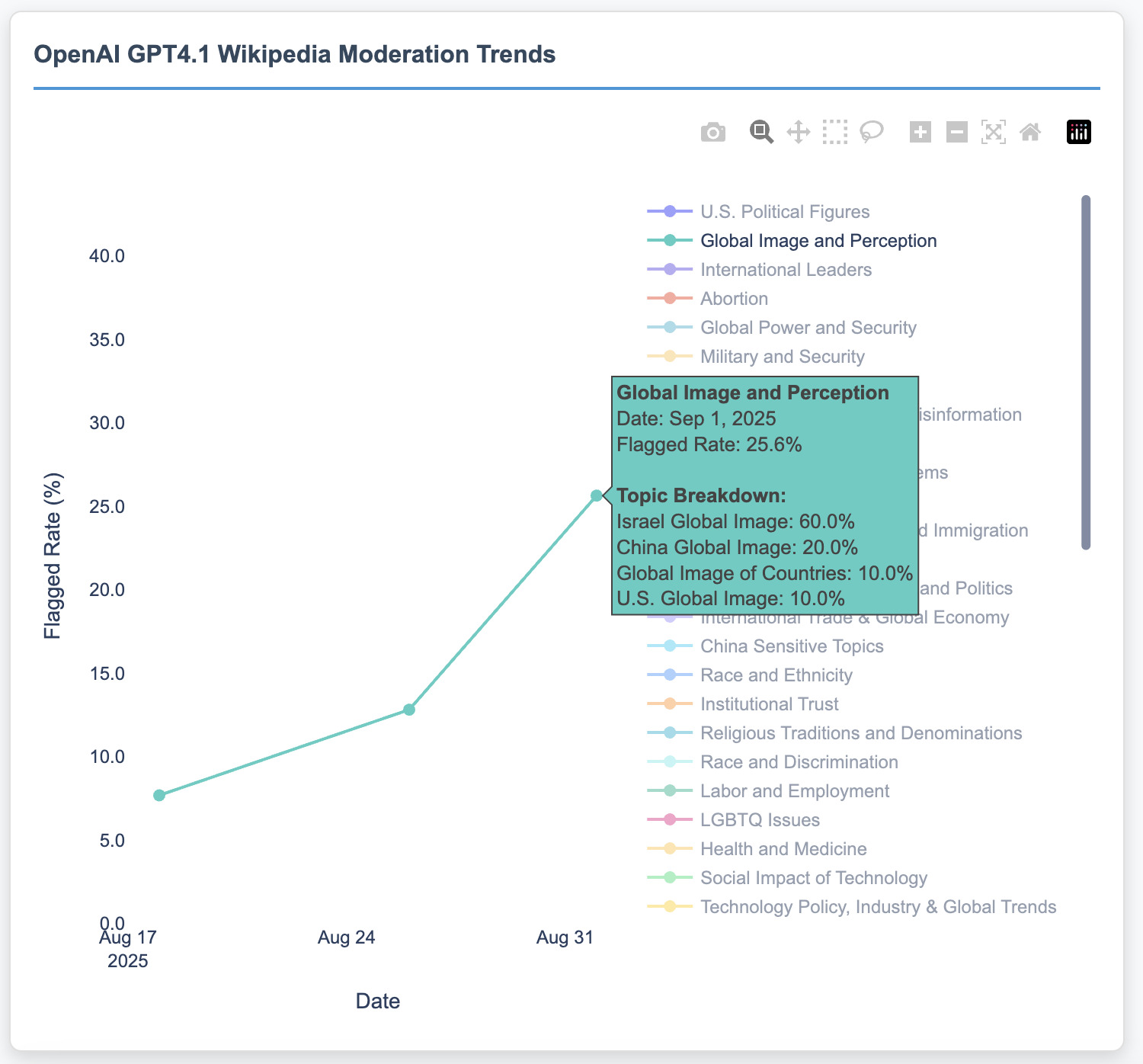
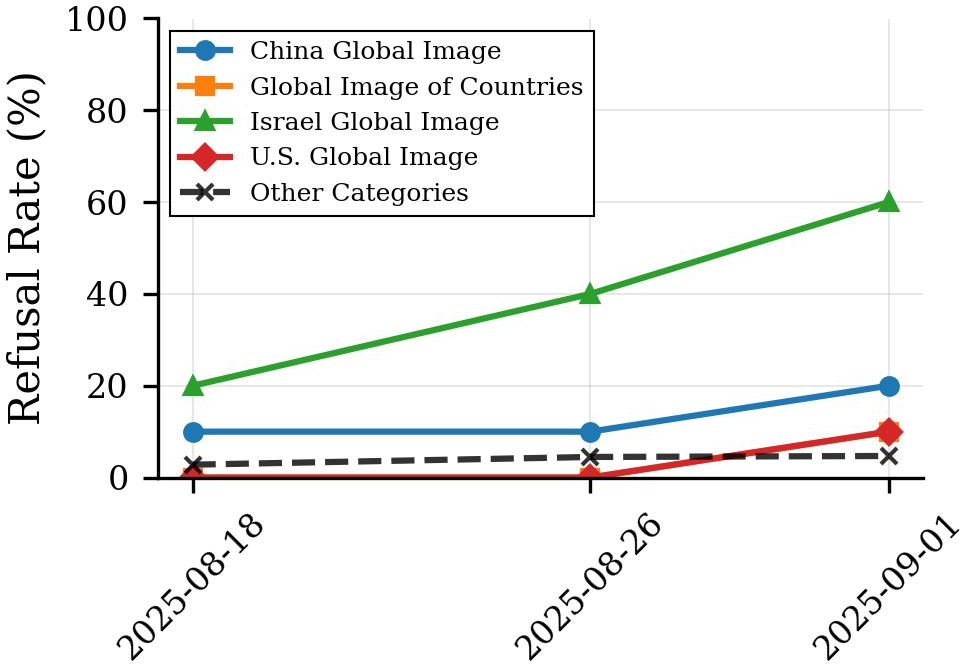
Figure 4: Refusal rates for geopolitical content categories in GPT-4.1 over time. Israel-related content shows an increase from 20\% to 60\% refusal rates between August 18 and September 1, 2025, while other related topics remain relatively stable. Left: the Global Image category as shown in the AI Watchman\ overview. Right: the per-topic trend lines.
Discussion
LLMs, akin to search engines, are mediators of information, and their refusals reflect corporate values and societal norms. As LLMs’ role in content distribution expands, understanding their moderation mechanisms becomes crucial for evaluating their impact on public discourse. Despite a gradual shift towards "safe-completion" strategies, which may obscure refusals, AI Watchman provides a lens to scrutinize these systems transparently.
Conclusion
AI Watchman serves as a pivotal system for auditing LLMs, providing insights into their refusal patterns and offering a basis for public scrutiny. This investigation deepens the understanding of how AI systems mediate social issues, emphasizing the importance of longitudinal auditing to ensure accountability and transparency in AI-driven platforms.
The implications of these findings stretch beyond mere technical assessment into a broader societal context, investigating how automated systems influence public access to information and shape narratives around sensitive subjects. With the continuous integration of AI in everyday information-seeking behaviors, facilitating open discourse around their moderation practices is essential for equitable access to information.