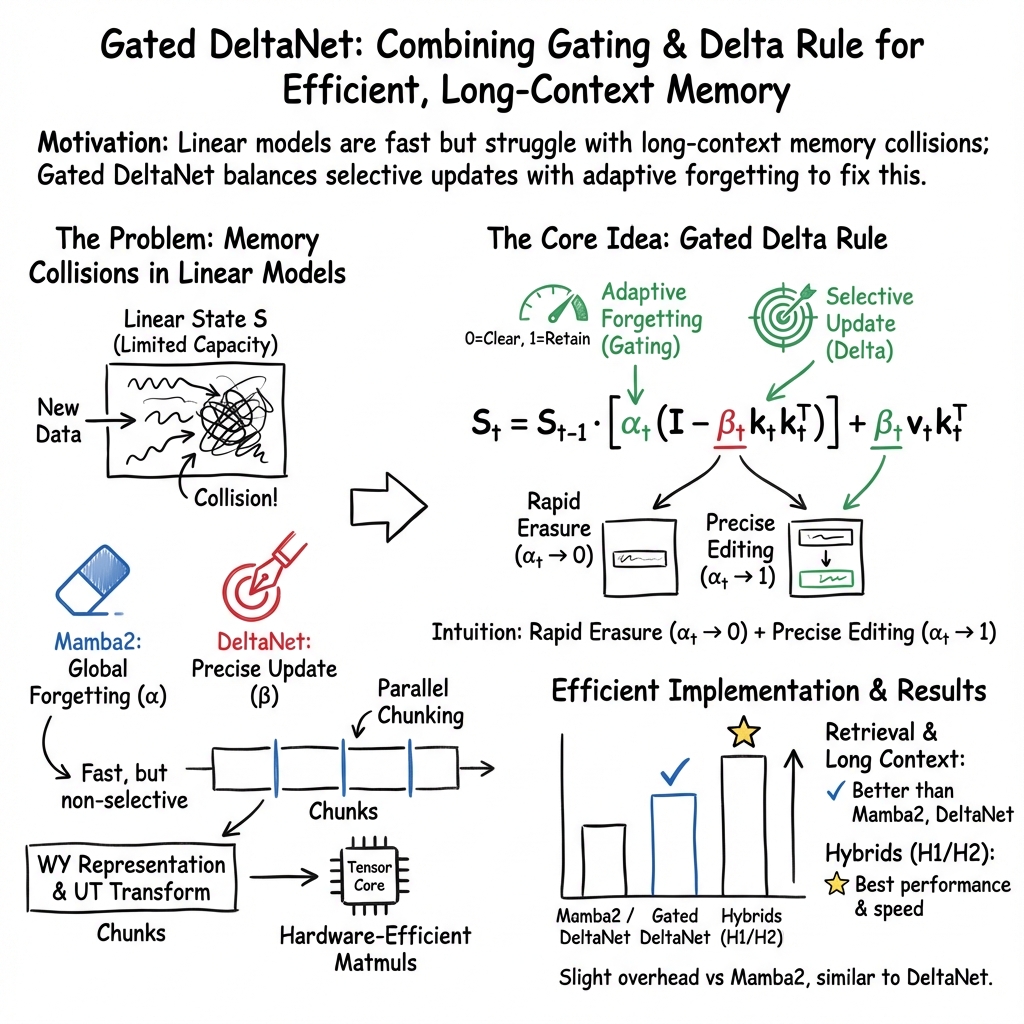
- The paper proposes a novel gated delta rule that merges adaptive gating with delta updates to precisely manage memory in linear Transformers.
- It demonstrates significant performance improvements over models such as Mamba2 across language modeling and long-context comprehension tasks.
- Empirical results show enhanced recall, commonsense reasoning, and training efficiency, highlighting the architecture’s potential for scalable sequence modeling.
Introduction
Gated Delta Networks build upon the foundational work of linear Transformers by integrating sophisticated memory management techniques crucial for long-context modeling tasks. The strategy specifically involves optimizing memory updates within Transformer architectures, facilitated through the synergistic integration of adaptive gating and delta update mechanisms. By focusing on complementary methods for managing sequence memory, this research addresses significant performance limitations present in prior models, such as Mamba2 and DeltaNet.
Theoretical Foundations and Innovations
The core innovation lies in merging the gating and delta update rule mechanisms. This combination enhances the precision of memory updates by offering selective flexibility: gating accomplishes rapid memory erasure while the delta rule allows seamless incorporation of new information. The architectural proposal, Gated DeltaNet, has been empirically tested to outperform existing alternatives like Mamba2, showing versatility across a variety of benchmarks including language modeling and long-context comprehension.
The "gated delta rule" leverages modern hardware capabilities through parallelized training algorithms. By incorporating an adaptive scaling factor, αt, which allows the model to dynamically emulate both full memory retention and specific instance forgetting, the architecture efficiently handles memory-related challenges without major computational overhead. The hardware-efficient nature arises from creating mappings that strategically involve tensor core accelerations.
Architectural Design
Gated DeltaNet extends the structural flexibility of linear RNN models through its sophisticated token mixer blocks. The architecture replaces simple self-attention modules with Gated DeltaNet layers incorporated with sliding window attention mechanisms. This hybrid structure not only enhances recall in contextual retrieval tasks but also benefits from the expressiveness of delta rules combined with the attention's ability to handle local context. Such design considerations contribute to state-of-the-art performance in both language modeling and recall-intensive applications.
Experimentation and Results
Gated DeltaNet demonstrates superior performance in both synthetic benchmarks and real-world applications. In contexts where precise memory control is necessary (e.g., needle-in-a-haystack tasks), Gated DeltaNet convincingly surpasses existing models. The empirical evaluation also highlights substantial improvements in commonsense reasoning tasks and knowledge retrieval, affirming the robustness of the proposed architecture in diverse operational scenarios.
The model's ability to extrapolate to longer sequences without a notable drop in performance is noteworthy. This capacity, coupled with consistent training throughput gains, illustrates the practicality of using Gated DeltaNet in environments requiring extensive computational efficiency and scalability.
Implications and Future Prospects
The introduction of Gated DeltaNet into the domain of linear Transformer models significantly enhances flexibility in sequence modeling. By addressing memory clearance and retrieval precision through the gated delta rule, the architecture sets new standards for handling long context dependency. Future developments could explore extensions that refine the gating mechanisms further or investigate the integration of emerging hardware efficiencies to broaden applicability.
Conclusion
Gated Delta Networks represent a crucial step forward in achieving balance between memory retention and update precision in sequence models. The architecture's strong empirical performance across varied benchmarks suggests substantial potential for its application in real-world tasks requiring complex reasoning over extensive sequences. The research highlights effective strategies for future explorations in expanding the model's adaptability and efficiency in increasingly demanding NLP tasks.