- The paper introduces ACC-Debate, an actor-critic framework that trains LLMs for debate-driven collaborative problem-solving.
- It integrates a novel partial trajectory reward to optimize debate accuracy and convergence across diverse benchmarks.
- Empirical results show significant performance gains on datasets like BoolQ, MMLU, and ARC, underscoring its robustness.
ACC-Collab: An Actor-Critic Approach to Multi-Agent LLM Collaboration
The paper introduces ACC-Debate, an Actor-Critic-based learning framework designed to enhance the collaborative capabilities of LLMs through a multi-agent debate approach. It presents a structured methodology for training LLMs in debate scenarios, focusing on collaborative problem-solving through an iterative, dialogue-based process.
Introduction
The ACC-Debate framework addresses the need to enhance LLMs' ability to reason and collaborate effectively by training them explicitly for these tasks, rather than relying on emergent behaviors. It builds upon existing multi-agent debate methodologies by integrating an actor-critic model that iteratively refines answers through structured debates. This approach facilitates the development of specialized collaborative skills in LLMs, as opposed to relying solely on their few-shot or zero-shot capabilities.
Methodology
Actor-Critic Debate Framework
The ACC-Debate employs a two-agent system comprising an actor and a critic. The actor proposes answers during the debate, while the critic provides feedback to guide the actor towards more accurate responses. This framework is optimized for maximizing the actor's accuracy at convergence, structured as a bi-level optimization problem.
Partial Trajectory Reward
A novel concept introduced is the "Partial Trajectory Reward," which evaluates the potential accuracy of a debate based on the dialogue state at any given point. This prediction helps in reinforcing beneficial pathways within the debate trajectory, thereby improving overall accuracy and convergence rates.
Off-Policy Trajectory Generation
The ACC-Debate framework uses an off-policy data generation strategy known as "guided-debate" to efficiently create high-quality training data. This process involves generating potential debate paths that either support or contest the current hypothesis, allowing for effective actor-critic training through preference optimization.
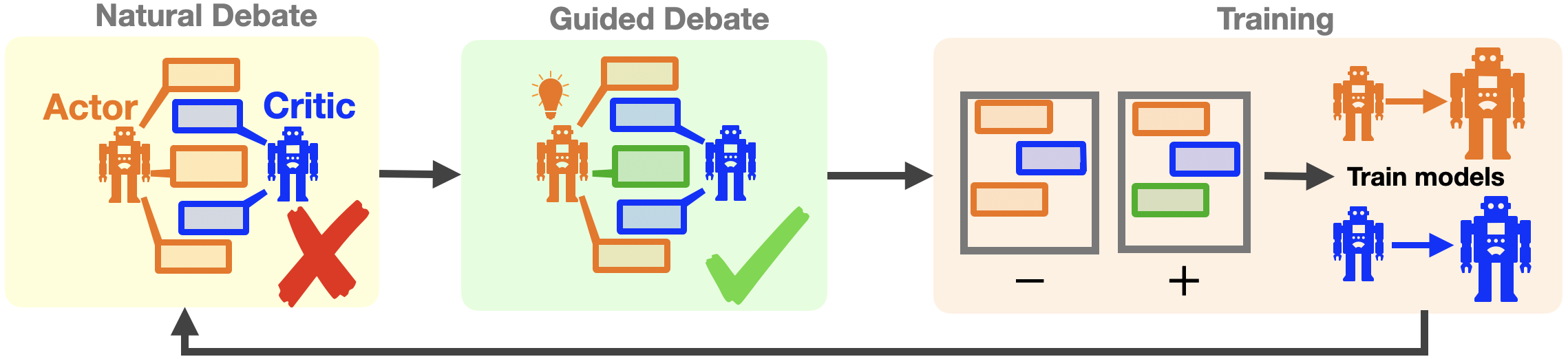
Figure 1: ACC-Debate training pipeline.
Experiments and Results
The paper reports that ACC-Debate outperforms state-of-the-art debate techniques across diverse benchmarks, including BoolQ, MMLU, BBH, SCIQ, and ARC. The experimental outcomes demonstrate that group-based debate among trained LLMs significantly enhances performance compared to traditional approaches.
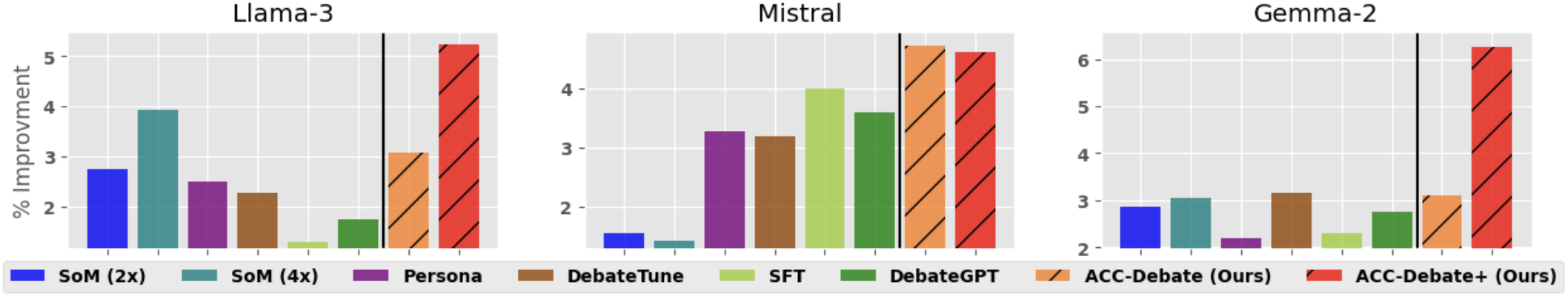
Figure 2: Percent improvement in accuracy after five rounds of debate, compared to a single round. Percent improvement (Eq. \ref{eq:improve}).
The performance gains were consistent across varying datasets and debate scenarios, indicating the robustness of the ACC-Debate method.
Implications and Future Work
The ACC-Debate framework signifies progress in harnessing the potential of LLMs for collaborative tasks. Its structured approach to debate training opens avenues for enhancing collaboration in real-world applications, such as decision-making systems and complex problem-solving environments.
The implications extend to developing more sophisticated AI systems capable of nuanced reasoning and effective teamwork. Future research may explore scalability to larger models and adaptation to more complex task domains beyond question-answering.
Conclusion
The ACC-Debate framework exemplifies a significant advancement in multi-agent reinforcement learning, focusing on improving collaboration among LLMs. By embedding debate as a learned behavior rather than relying on it as an emergent property, ACC-Debate paves the way for more capable, collaborative artificial intelligence systems.

