The Effect of Human v/s Synthetic Test Data and Round-tripping on Assessment of Sentiment Analysis Systems for Bias (2401.12985v1)
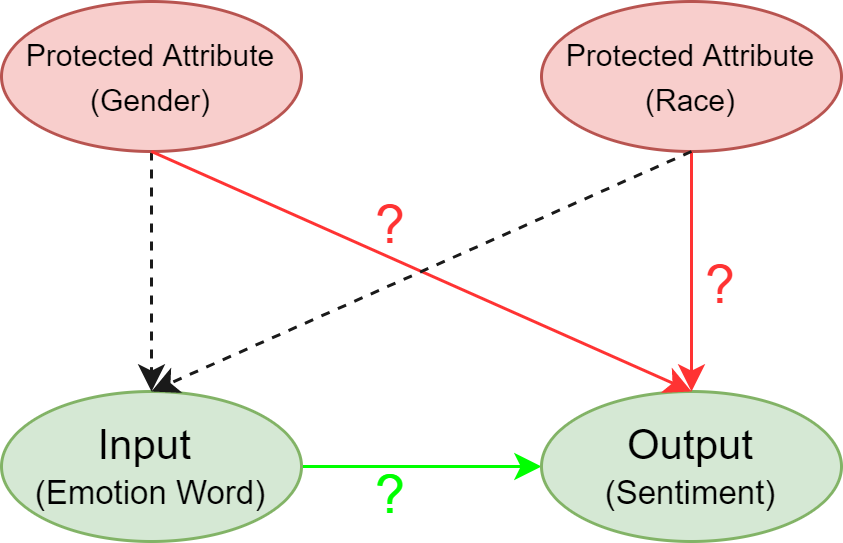
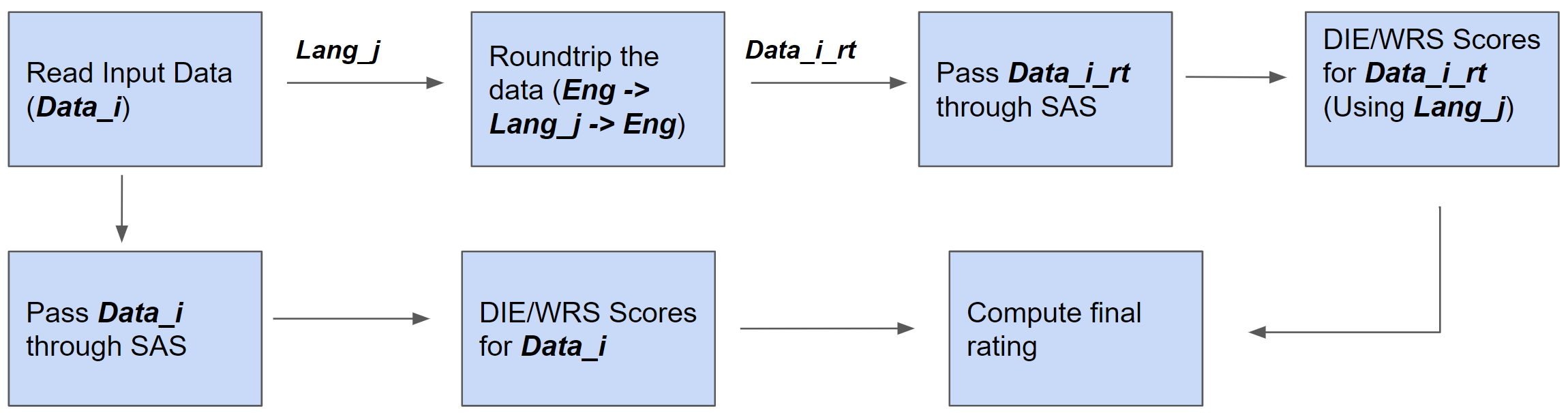
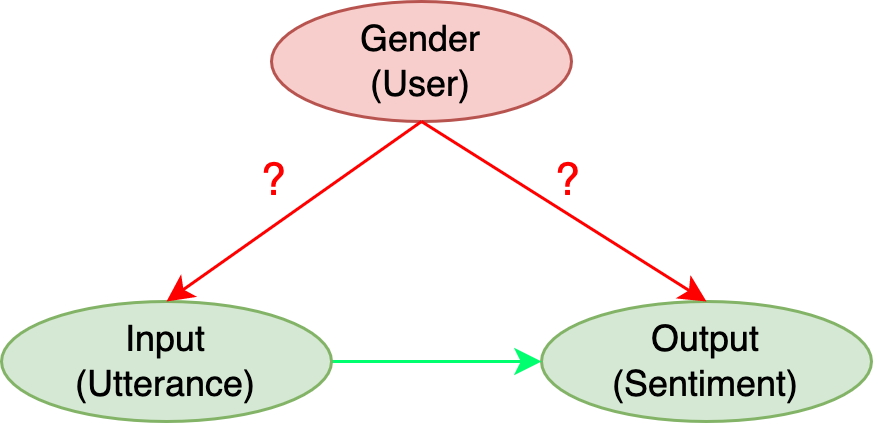
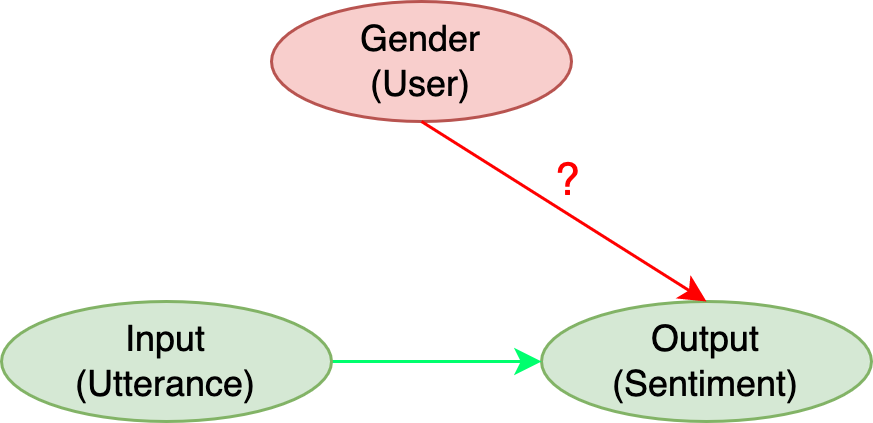
Abstract: Sentiment Analysis Systems (SASs) are data-driven AI systems that output polarity and emotional intensity when given a piece of text as input. Like other AIs, SASs are also known to have unstable behavior when subjected to changes in data which can make it problematic to trust out of concerns like bias when AI works with humans and data has protected attributes like gender, race, and age. Recently, an approach was introduced to assess SASs in a blackbox setting without training data or code, and rating them for bias using synthetic English data. We augment it by introducing two human-generated chatbot datasets and also consider a round-trip setting of translating the data from one language to the same through an intermediate language. We find that these settings show SASs performance in a more realistic light. Specifically, we find that rating SASs on the chatbot data showed more bias compared to the synthetic data, and round-tripping using Spanish and Danish as intermediate languages reduces the bias (up to 68% reduction) in human-generated data while, in synthetic data, it takes a surprising turn by increasing the bias! Our findings will help researchers and practitioners refine their SAS testing strategies and foster trust as SASs are considered part of more mission-critical applications for global use.
- B. Srivastava, K. Lakkaraju, M. Bernagozzi, and M. Valtorta, “Advances in automatically rating the trustworthiness of text processing services,” in AAAI Spring Symposium, on AI Trustworthiness Assessment, San Francisco. On Arxiv at: 2302.09079, 2023.
- S. L. Blodgett, S. Barocas, H. D. I. au2, and H. Wallach, “Language (technology) is power: A critical survey of ”bias” in nlp,” in On Arxiv at: 2https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.14050, 2020.
- S. Kiritchenko and S. Mohammad, “Examining gender and race bias in two hundred sentiment analysis systems,” in Proceedings of the Seventh Joint Conference on Lexical and Computational Semantics. New Orleans, Louisiana: Association for Computational Linguistics, Jun. 2018, pp. 43–53. [Online]. Available: https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/S18-2005
- A. Koenecke, A. Nam, E. Lake, J. Nudell, M. Quartey, Z. Mengesha, C. Toups, J. R. Rickford, D. Jurafsky, and S. Goel, “Racial disparities in automated speech recognition,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 117, no. 14, pp. 7684–7689, 2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.pnas.org/content/117/14/7684
- V. Antun, F. Renna, C. Poon, B. Adcock, and A. C. Hansen, “On instabilities of deep learning in image reconstruction and the potential costs of ai,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 117, no. 48, pp. 30 088–30 095, 2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.pnas.org/content/117/48/30088
- E. Ntoutsi, P. Fafalios, U. Gadiraju, V. Iosifidis, W. Nejdl, M.-E. Vidal, S. Ruggieri, F. Turini, S. Papadopoulos, E. Krasanakis, I. Kompatsiaris, K. Kinder-Kurlanda, C. Wagner, F. Karimi, M. Fernandez, H. Alani, B. Berendt, T. Kruegel, C. Heinze, K. Broelemann, G. Kasneci, T. Tiropanis, and S. Staab, “Bias in data-driven ai systems – an introductory survey,” in On Arxiv at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.09762, 2020.
- K. Mishev, A. Gjorgjevikj, I. Vodenska, L. T. Chitkushev, and D. Trajanov, “Evaluation of sentiment analysis in finance: From lexicons to transformers,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 131 662–131 682, 2020.
- K. Dashtipour, S. Poria, A. Hussain, E. Cambria, A. Y. A. Hawalah, A. Gelbukh, and Q. Zhou, “Multilingual sentiment analysis: State of the art and independent comparison of techniques,” in Cognitive computation vol. 8: 757-771. doi:10.1007/s12559-016-9415-7, 2016.
- J. G. Christiansen, M. Gammelgaard, and A. Søgaard, “The effect of round-trip translation on fairness in sentiment analysis,” in Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Online and Punta Cana, Dominican Republic: Association for Computational Linguistics, Nov. 2021, pp. 4423–4428. [Online]. Available: https://aclanthology.org/2021.emnlp-main.363
- B. Srivastava and F. Rossi, “Rating ai systems for bias to promote trustable applications,” in IBM Journal of Research and Development, 2020.
- ——, “Towards composable bias rating of ai systems,” in 2018 AI Ethics and Society Conference (AIES 2018), New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, Feb 2-3, 2018.
- M. Bernagozzi, B. Srivastava, F. Rossi, and S. Usmani, “Vega: a virtual environment for exploring gender bias vs. accuracy trade-offs in ai translation services,” Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, no. 18, pp. 15 994–15 996, May 2021. [Online]. Available: https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/17991
- ——, “Gender bias in online language translators: Visualization, human perception, and bias/accuracy trade-offs,” in To Appear in IEEE Internet Computing, Special Issue on Sociotechnical Perspectives, Nov/Dec, 2021.
- K. Lakkaraju, “Why is my system biased?: Rating of ai systems through a causal lens,” in Proceedings of the 2022 AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society, ser. AIES ’22. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2022, p. 902. [Online]. Available: https://doi.org/10.1145/3514094.3539556
- K. Lakkaraju, B. Srivastava, and M. Valtorta, “Rating sentiment analysis systems for bias through a causal lens,” 2023. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.02038
- Student, “The probable error of a mean,” Biometrika, pp. 1–25, 1908.
- K. Lakkaraju, T. Hassan, V. Khandelwal, P. Singh, C. Bradley, R. Shah, F. Agostinelli, B. Srivastava, and D. Wu, “Allure: A multi-modal guided environment for helping children learn to solve a rubik’s cube with automatic solving and interactive explanations,” Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 36, no. 11, pp. 13 185–13 187, Jun. 2022. [Online]. Available: https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/21722
- D. Wu, H. Tang, C. Bradley, B. Capps, P. Singh, K. Wyandt, K. Wong, M. Irvin, F. Agostinelli, and B. Srivastava, “Ai-driven user interface design for solving a rubik’s cube: A scaffolding design perspective,” in HCI International 2022-Late Breaking Papers. Design, User Experience and Interaction: 24th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, HCII 2022, Virtual Event, June 26–July 1, 2022, Proceedings. Springer, 2022, pp. 490–498.
- B. Srivastava, F. Rossi, S. Usmani, and M. Bernagozzi, “Personalized chatbot trustworthiness ratings,” in IEEE Transactions on Technology and Society., 2020.
Sponsor
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.