- The paper introduces MemRec, a system that decouples reasoning from memory management to overcome cognitive and computational bottlenecks.
- It employs a three-stage pipeline—collaborative retrieval, grounded reasoning, and asynchronous propagation—to achieve state-of-the-art metrics.
- Empirical evaluations across various domains demonstrate significant performance improvements and cost-efficiency over traditional recommender models.
Collaborative Memory-Augmented Agentic Recommendation: A Comprehensive Analysis of MemRec
Introduction and Motivation
The proliferation of agentic recommender systems (AgentRS) driven by advanced LLMs has fundamentally transformed how user preferences are stored, interpreted, and leveraged. MemRec (2601.08816) introduces a paradigm shift from isolated, self-reflective semantic memory structures to a collaborative, global memory graph architecture. Traditional frameworks maintain discrete, entity-centric memories that fail to exploit the high-order connectivity of collaborative filtering. MemRec explicitly addresses the dual bottlenecks of cognitive overload—resulting from unfiltered context—and prohibitive computational costs—due to brute-force graph propagation—by introducing an architectural decoupling of reasoning and memory management.
Existing systems are confined within isolated channels where agents access only personal or item-specific memories.


Figure 1: (a) Conventional agents operate on isolated read/write channels for user and item memories. (b) MemRec employs collaborative operations via a unified memory graph, enabling global connectivity.
The rationale behind MemRec is to synthesize salient collaborative signals while maintaining efficiency and relevance, thus unlocking the benefits of community-level recommendation reasoning.
MemRec Architecture
The central innovation is the decoupling of two functions:
- LLMRec: Reasoning agent, specializing in interpretation and ranking.
- LMMem: Dedicated lightweight memory manager, orchestrating collaborative graph evolution and context curation.
MemRec operates on a three-stage pipeline:
- Collaborative Memory Retrieval: Adopts a curate-then-synthesize strategy, guided by zero-shot LLM-generated domain-adaptive rules. Raw collaborative neighborhoods are filtered for informativeness, mitigating the cognitive overload imposed by verbose context windows.
- Grounded Reasoning: Employs structured preference facets synthesized from curated neighbors, allowing the reasoning agent to generate rankings and rationales informed by community-level patterns.
- Asynchronous Collaborative Propagation: Inspired by Label Propagation, this mechanism batches updates for self-reflection and neighbor enrichment, reducing interaction complexity to O(1).

Figure 2: MemRec’s modular agentic pipeline decouples reasoning from memory operations, achieving scalable collaborative augmentation in three stages.
This decoupled architectural strategy offers substantial flexibility for both deployment and extensibility, supporting configurations ranging from cloud APIs to on-premise open-source stacks.
Methodological Innovations
Collaborative Signal Distillation
The system leverages LLM-as-Rule-Generator for neighbor curation, shifting away from heuristic random walks and opaque GNN-based attention mechanisms. This methodological approach enables rapid, interpretable domain adaptation: rules are synthesized based on aggregated domain statistics and injected as high-speed filters during inference, ensuring low-latency, high-relevance context selection.
Memory synthesis operates via a tiered representation—prioritizing full semantic memory for the target user, and condensed representations for neighbors—to maximize the information bottleneck’s relevance.
Efficient Memory Evolution
MemRec optimizes the collaborative propagation of semantic insights post-interaction. Updates to the memory graph are orchestrated in a single batched operation, writing new reflections for the user, the item, and selected neighbors. This asynchronous protocol circumvents prohibitive computational costs while guaranteeing continuous graph enrichment.
Empirical Evaluation
MemRec achieves statistically significant SOTA results across four domains (Books, Goodreads, MovieTV, Yelp) and all ranking metrics (H@1, H@3, H@5, NDCG@K). Most notably, relative improvements over the strongest baselines reach:
- +28.98% on Goodreads H@1
- +19.75% on MovieTV H@1
- +15.77% on Yelp H@1
These results establish MemRec's dominance in both sparse and dense interaction regimes, consistently superseding traditional graph-based models and recent agentic approaches relying on isolated memory.
Cognitive Overload Mitigation
Ablation and comparative analysis demonstrate that naive agents attempting monolithic reasoning over raw, uncurated collaborative context plateau in performance due to cognitive and instruction adherence bottlenecks.

Figure 3: MemRec mitigates information bottlenecks, surpassing Naive and Vanilla LLM approaches in H@1 across multiple datasets.
Decoupling allows MemRec to sustain substantial gains, confirming the centrality of architectural separation for scalable, high-accuracy collaborative recommendation.
Efficiency and Deployment Flexibility
MemRec configurations define a new Pareto frontier, achieving optimal trade-offs between performance, cost, and latency. The cloud–OSS configuration approaches ceiling performance at a fraction of proprietary LLM cost; vector-based reranking provides ultra-low-latency alternatives.

Figure 4: MemRec establishes a superior cost–performance landscape, dominating the trade-off frontier for LLM-powered agentic recommenders.
Empirical token breakdowns further reveal an input-biased operational design, aligning with commercial pricing asymmetries and yielding practical cost reductions.
Explanation and Interpretability
GPT-4o-based evaluations of generated rationales indicate MemRec substantially improves both specificity and relevance of explanations. The integration of collaborative signals leads to marked increases in explanation quality, with statistically significant improvements over isolated-memory baselines.

Figure 5: MemRec’s collaborative context yields improved rationale specificity and relevance; all gains significant with p<0.001.
Ablations and Hyperparameter Sensitivity
Ablation studies verify that each collaborative mechanism—memory retrieval, domain-adaptive curation, and asynchronous propagation—contributes measurably to overall system precision. Disabling collaborative reading incurs up to 9.9% degradation in H@1. Hyperparameter sweeps confirm robust optimality in neighborhood and facet selection ranges.
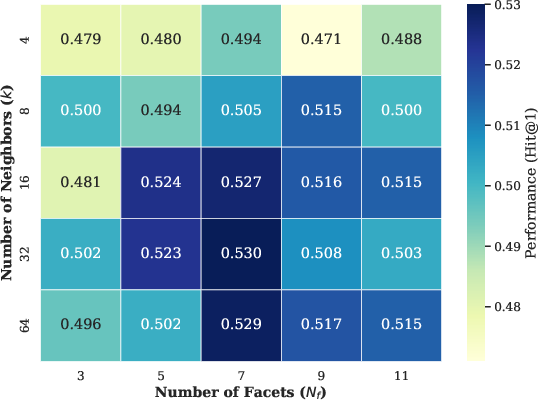
Figure 6: MemRec exhibits a performance plateau around k=16 neighbors and Nf=7 facets, confirming architectural robustness.
Hit@3 is further validated as robust under these settings.
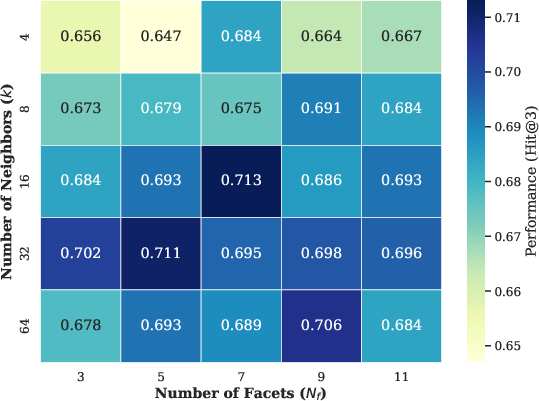
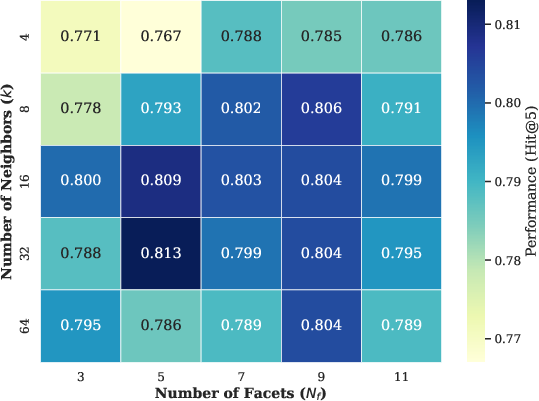

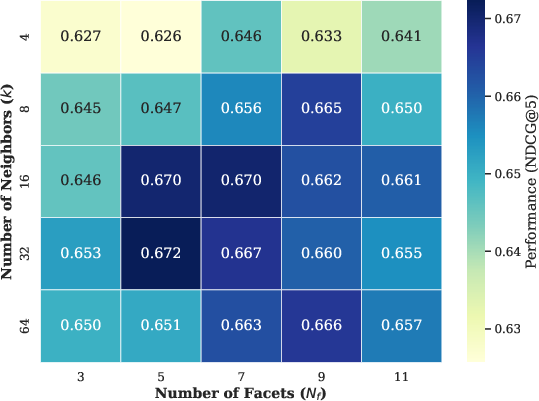
Figure 7: Hit@3 metric trends corroborate MemRec’s stability across hyperparameter settings.
Related Works Contextualization
MemRec advances beyond prior memory architectures in LLM agent systems, which focus on temporal, factual, or conversational domains, by directly targeting the collaborative graph connectivity critical to recommendation. While generative agents, MemGPT, Zep, and RAG-GNN frameworks offer memory solutions for general reasoning, none address agentic recommendation’s need for efficient collaborative signal propagation and dynamic memory evolution. MemRec fills this gap through explicit graph model integration, modular agentic design, and collaborative context curation.
Theoretical and Practical Implications
This paradigm shift from isolated to collaborative agentic memory unlocks high-signal community trends and serendipitous discovery potential, long recognized as central in CF theory. Practically, MemRec’s modular decoupling supports scalable privacy-preserving deployments, domain-adaptive rule injection, and hybrid integration with existing RAG and tool-use pipelines. Theoretically, MemRec demonstrates that cognitive and computational bottlenecks in LLM-augmented recommendation can be mediated by separating memory propagation from reasoning, and by structuring collaborative knowledge as evolving graphs rather than mere collections of siloed semantic entities.
Future developments will likely involve scaling collaborative memory to web-scale graphs, refining multi-hop propagation mechanisms, and pursuing open-source, privacy-preserving implementations compatible with federated learning and local deployment requirements.
Conclusion
MemRec formalizes a collaborative, memory-augmented agentic recommender framework achieving substantial empirical gains, operational efficiency, and deployment flexibility. The decoupled architecture enables effective high-order signal synthesis and scalable graph evolution, establishing new standards for cost–performance trade-offs and rationale quality. This research lays the groundwork for further exploration of agentic recommendation at web scale, with direct implications for the design of future LLM-powered recommendation systems.










