- The paper introduces a collaborative-guided multimodal fusion framework that integrates visual, textual, and collaborative signals into unified item representations.
- It leverages a residual quantization VAE for tokenizing item features and employs an LLM for constrained, autoregressive generative recommendation.
- Experimental results show up to 26.6% improvements in HR@10 and NDCG@10, validating the framework’s enhanced performance and cold-start robustness.
Collaborative-Enhanced Multimodal Generative Recommendation: A Technical Analysis
Introduction and Motivation
CEMG—Collaborative-Enhanced Multimodal Generative Recommendation—addresses persistent limitations in generative recommendation, specifically the superficial inclusion of collaborative signals and the late or loose fusion of multimodal item features. Traditional generative frameworks typically tokenize items via unimodal signals, often leading to decoupled content-collaboration modeling and reduced generalization for cold-start or long-tail items. CEMG proposes a unified semantic space for item representations via collaborative-guided multimodal fusion combined with residual quantization-based tokenization and an LLM-based end-to-end generation approach (2512.21543).
Framework Overview and Architecture
CEMG comprises three primary components: the Multimodal Encoding Layer, Unified Modality Tokenization, and End-to-End Generative Recommendation.

Figure 1: The overall architecture of the CEMG framework, visualizing collaborative-guided multimodal fusion, codebook-based tokenization, and LLM-based generation.
The Multimodal Encoding Layer extracts features from images (via a VGG encoder), text (BERT encoder), and user-item collaborative interactions (LightGCN). These are integrated in a multimodal fusion layer where the collaborative representation modulates attention over content modalities, delivering a unified representation xi per item.
This fused xi is discretized by a Residual Quantization VAE, which generates M codebook token indices as a sequential semantic identifier for each item, adapting discrete latent modeling to the recommendation context.
In the generative stage, a T5 LLM is fine-tuned on user-item interaction histories where item IDs are replaced by their semantic code sequences. Recommendation is reframed as conditional sequence prediction with constrained decoding to ensure valid item generation.
Deep Multimodal-Collaborative Fusion
A distinguishing aspect of CEMG is the use of a collaborative-guided attention mechanism, a departure from prior fusion schemes that treat collaboration as a late addition or token alignment post-hoc. In CEMG, the LightGCN-generated collaborative embedding eiC acts as the query in an attention schema, modulating the relative importance of visual (eiV) and textual (eiT) features. The final item embedding concatenates a collaboration-attended multimodal sum with the collaborative embedding, tightly interleaving content and user preference structure.
This synergy is critical for capturing item substitutability and user-taste nuances not evident from content alone, an advance over the shallow fusion mechanisms in previous work such as LETTER [wang2024learnable] and MMGRec [mmgrec].
Unified Modality Tokenization via RQ-VAE
The residual quantization VAE tokenizes each item's fused representation into a sequence of M tokens by iteratively assigning codebook elements to each stage's residual. Crucially, the encoder-decoder structure and the training objective (reconstruction loss, VQ commitment loss, diversity loss) guarantee that semantic compression preserves both modality content and collaborative structure.
The ablation results (Figure 2) confirm that removing either collaboration, visual, or text features degrades HR@10 and NDCG@10 notably, with the collaborative ablation yielding the largest drop. This validates the necessity of all three modalities and collaboration-aware fusion.

Figure 2: Ablation analysis demonstrating material drops in top-k recommendation metrics when collaborative or content features are ablated.
Generative Recommendation with LLMs and Codebook Tokens
The foundation of the generative approach is a conditional language modeling schema: the LLM receives as prompt a chronological sequence of past item code tokens and predicts the semantic code token sequence for the next item. Decoding is constrained using a trie to restrict outputs to valid item tokenizations, ensuring catalogue consistency and search space pruning.
This end-to-end, autoregressive semantics-to-item mapping overcomes the genericity and adverse transfer risk of standard LLM-based recommenders that operate on item titles or IDs without structural alignment.
Experimental Results and Analysis
CEMG is evaluated against both discriminative (SASRec, MMSRec, MISSRec) and generative (TIGER, LETTER, MMGRec) baselines on Amazon Beauty, Sports, and Yelp datasets.
Numerical Highlights:
- On all datasets, CEMG yields a 14.5%-16.7% absolute increase in HR@10 and a 19.2%-26.6% increase in NDCG@10 over the strongest baselines. All improvements are statistically significant at p<0.05.
- Cold-start performance is 15–22% higher in both metrics compared to content and generative baselines.
Strong claims: The results demonstrate that deep, collaborative-guided fusion of multimodal data and joint semantic tokenization confer substantial gains over both unimodal generative and discriminative multimodal models.
Efficiency assessment reveals that CEMG achieves a favorable trade-off: slightly higher training cost than the simplest generative models but significantly faster inference due to fixed-length token generation and prefix-constrained decoding.
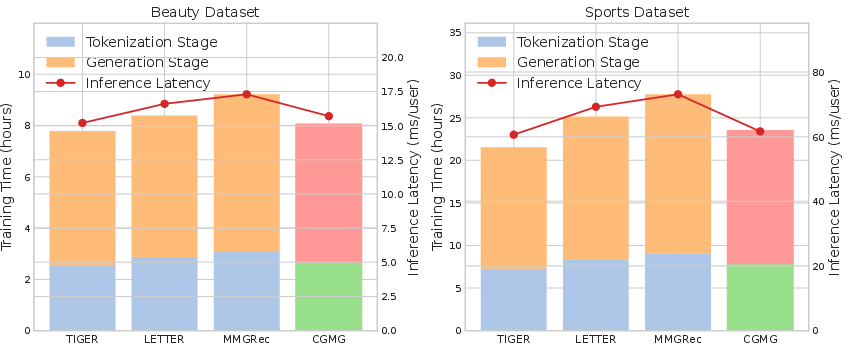
Figure 3: Training and inference computational efficiency of CEMG compared to prior generative recommender models.
Hyperparameter and Sensitivity Analysis
Parameter analysis (Figure 4) shows that moderate numbers of codebook layers (M=4) and codebook sizes (K=512) yield optimal HR@10, with diminishing returns (and even performance drops) at larger scales due to sequence modeling difficulty and overfitting. The quantization and diversity losses have clear sweet spots, confirming the importance of these regularization terms for balanced, high-quality tokenization.
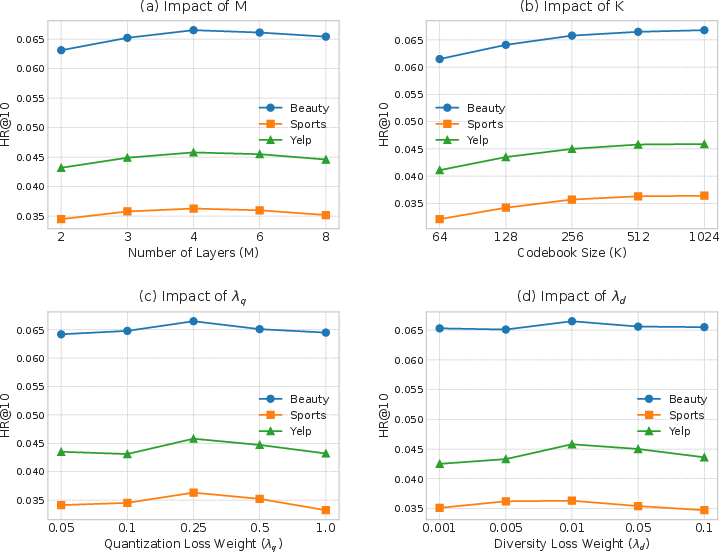
Figure 4: Sensitivity of CEMG’s HR@10 to codebook layers, codebook size, quantization (VQ) loss weight, and diversity loss weight.
Implications and Future Directions
CEMG sets a new technical direction for generative recommendation by:
- Realizing tight, collaborative-guided modality fusion for unified representation learning.
- Leveraging codebook-based semantic compression for transferable, interpretable item identifiers.
- Enabling constrained autoregressive generation to enforce recommendation validity.
These choices have practical implications for efficient, cold-start-robust, and catalogue-aligned deployment in real-world recommendation systems, notably in domains with rich visual and textual content.
Future work may pursue adversarial robustness (given the increased collaborative reliance), more advanced decoding for error correction, and more efficient or explainable fusion/tokenization modules, especially for noisy or adversarial multimodal input (2512.21543).
Conclusion
CEMG advances generative recommendation by integrating collaborative context into every stage of multimodal item representation and tokenization, leveraging LLMs for efficient and accurate code sequence generation. Strong empirical gains, particularly in generalization and cold-start scenarios, substantiate the claim that deep, collaboration-aware modality fusion is essential as the field transitions from shallow fusion to fully generative, multitask recsys paradigms. The framework also points toward new directions for migration of LLM centric architectures into high-precision, efficiency-critical recommendation deployments.



