- The paper presents ImageCritic, a model that corrects fine-grained inconsistencies in generated images by leveraging reference-guided post-editing.
- It employs innovative attention alignment loss and a detail encoder within an automated multi-agent chain to enhance correction precision.
- Experimental results demonstrate substantial gains in CLIP similarity, mAP, and other metrics, validating its effectiveness across diverse generative pipelines.
Consistency Critic: Correcting Inconsistencies in Generated Images via Reference-Guided Attentive Alignment
Introduction
The paper presents ImageCritic, a reference-guided post-editing model designed to rectify inconsistencies and inaccuracies in generated images, particularly in fine-grained details such as texts and logos. Contemporary customized image generation approaches—especially those utilizing diffusion models—often introduce visible artefacts or fail to maintain structural and semantic fidelity when reproducing objects from a reference image. This is attributed mainly to information bottlenecks in encoder–decoder architectures and limitations in spatial alignment. ImageCritic aims to address this by proposing a unified correction framework built on a novel dataset, enhanced attention mechanisms, and an automated agent chain for robust multi-round editing.
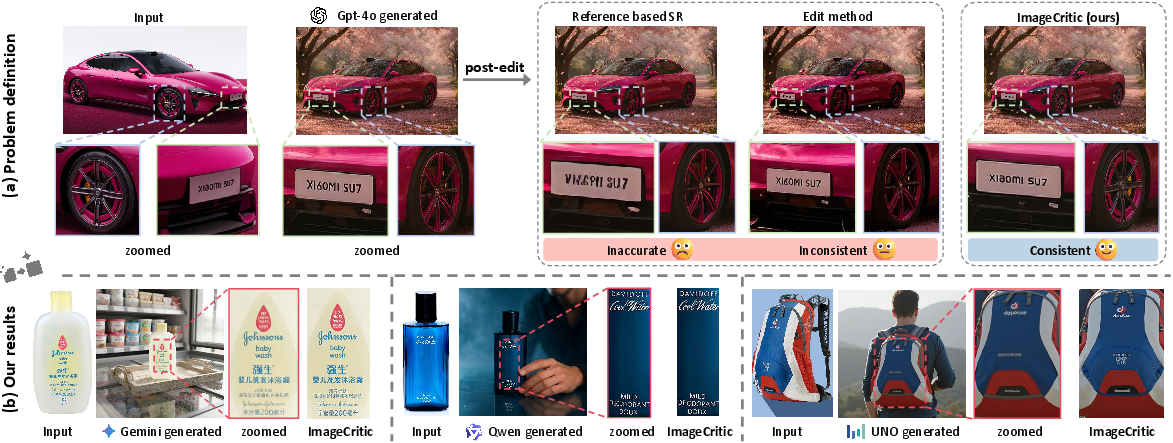

Figure 1: Visual illustrations showing improved fine-grained detail consistency and spatial alignment in generated images corrected by ImageCritic, compared to alternative post-editing and super-resolution approaches.
Dataset Construction and Benchmarking
A critical challenge in correcting generated image inconsistencies is the lack of datasets tailored to high-fidelity reference–target pairs emphasizing precise local details. Existing datasets such as Subjects200K and UNO-1M focus primarily on global object consistency, often neglecting subtle discrepancies. To address this, the paper introduces a dataset of reference-degraded-target triplets, constructed via VLM-based filtering, explicit object grounding, and controlled inpainting degradation. This workflow simulates realistic generative artefacts and provides substantive supervision for learning nuanced corrections.
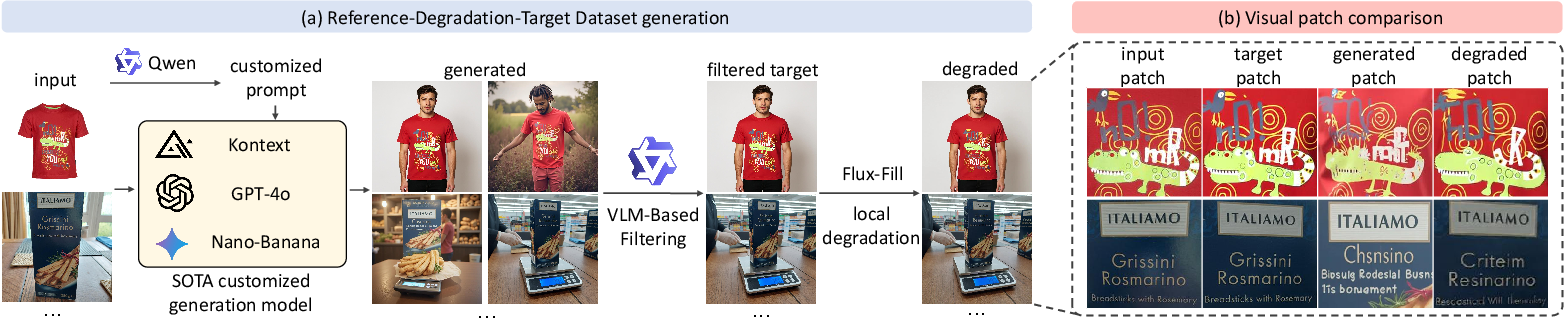
Figure 2: Data curation pipeline demonstrating the use of VLM filtering, degradation via inpainting, and regional alignment for simulating fine-grained inconsistencies in custom-generated images.
Notably, the dataset encompasses 10k high-quality triplets, covering multilinguality, diverse scenes, and variable object viewpoints. A new evaluation benchmark, CriticBench, is introduced, focusing on challenging cases with intricate details and textual elements, supplementing the standard DreamBench++ for broader comparative analysis.
Methodology and Architectural Components
ImageCritic builds on a DiT-based editing backbone, leveraging multimodal attention for spatial and semantic fusion of text and image tokens. The architecture introduces two principal innovations:
- Attention Alignment Loss (AAL): Supervised via region masks, AAL disentangles and aligns the attentional focus between the reference and input branches at the level of double-stream layers. This promotes effective identification and localization of regions requiring restoration, circumventing the prevalent issue of coupled/conflicting attentional cues that leads to suboptimal corrections.
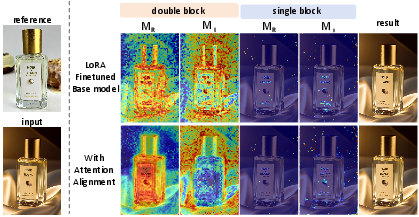
Figure 3: Attention visualization showcasing improved disentanglement after applying attention alignment loss, enabling more precise localization in fine-grained regions.
- Detail Encoder (DE): A coupling mechanism that integrates image-specific representations into the text trigger tokens, resolving ambiguities and enhancing prompt conditioning when handling structurally divergent inputs. This ensures robust reference-image understanding and correct object association during correction steps.

Figure 4: Demonstrates the necessity of the detail encoder for accurate correspondence recovery when structural discrepancies exist between input and reference images.
Additionally, ImageCritic is embedded in a fully automated multi-agent chain, orchestrating sub-tasks from inconsistency detection, region localization, reference retrieval, to iterative correction. The agent framework supports both autonomous and human-in-the-loop operation, adapting the correction workflow interactively for complex real-world scenarios.
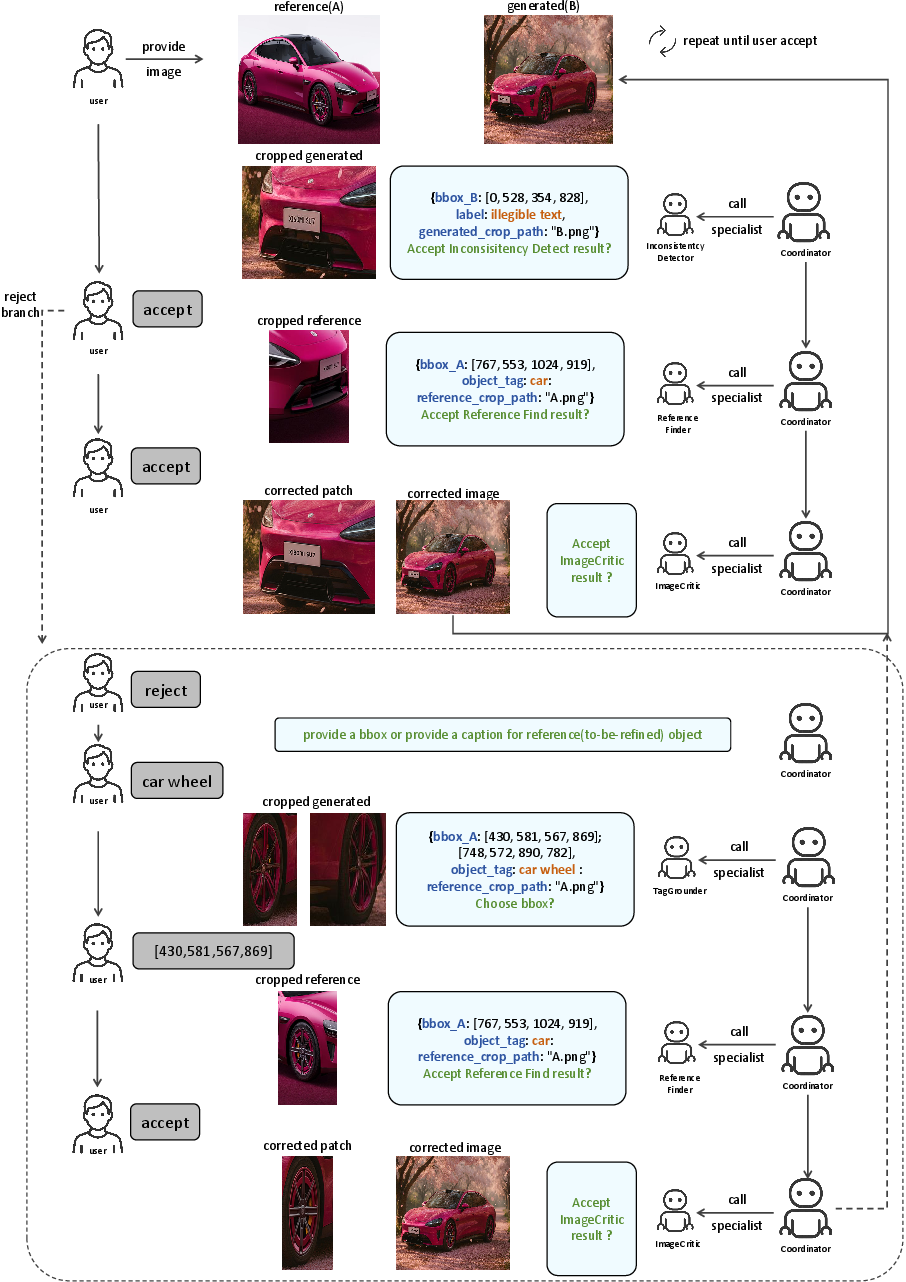
Figure 5: Illustration of the multi-agent image correction workflow, delineating detection, matching, and iterative patch restoration steps.
Experimental Results
ImageCritic demonstrates robust quantitative and qualitative gains across several open-source and closed-source generation pipelines (XVerse, Dreamo, MOSAIC, Uno, Qwen-Image, NanoBanana, GPT-Image). The method substantially improves metrics for CLIP image similarity, DINO, and DreamSim scores on both CriticBench and DreamBench++, consistently outperforming comparative baselines for detail restoration and overall coherence.

Figure 6: Visual comparisons show superior local consistency after correction by ImageCritic across different generative models.
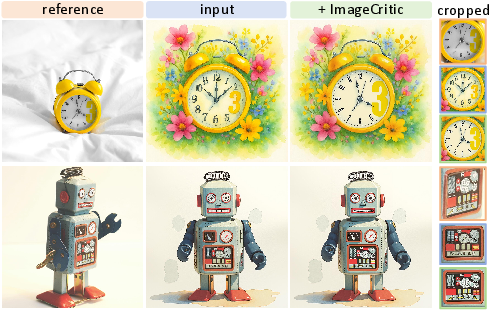
Figure 7: Robust generalization examples highlighting style and illumination preservation in diverse viewpoints, categories, and stylizations.
Ablation studies confirm the synergistic contribution of both Attention Alignment Loss and Detail Encoder. Isolated addition of either yields incremental improvements, but their combination leads to further substantial gains in fine-grained consistency scores.
Agent-Based Localization and Correction
The agent chain's efficacy for automated region localization is validated by mean IoU of 75.3% and mAP@50 of 88.4% against human-labeled ground truth, indicating high accuracy in bounding box prediction and patch selection.
Implications and Future Directions
The introduction of ImageCritic and its underlying dataset represents a substantial step toward solving fine-grained consistency challenges in image generation. The reference-guided correction approach is highly extensible, permitting integration into existing generative systems as an automated post-processing step. The deep multimodal attention mechanisms, coupled with adaptive agent workflows, suggest future applicability in broader domains—multilingual document layout correction, real-world product visualization, and personalized editing workflows. Extensions might target generative video correction and continuous multimodal content streams, leveraging similar reference-guided, region-level alignment strategies.
Conclusion
ImageCritic sets a new benchmark for reference-guided correction of generative image inconsistencies, combining a rigorously constructed dataset, advanced attention alignment, and agent-based automation. Extensive evaluation confirms its effectiveness in restoring detail fidelity and maintaining structural coherence, with substantial improvement over prevailing approaches. The methodology and dataset offer substantive resources and paradigms for future high-consistency generative modeling research.

Figure 8: Additional visual results illustrate the method’s robustness for multilingual, multi-scene image correction, corroborated by text recognition alignment using OCR outputs.









