- The paper introduces CWMDT, which decouples digital twin extraction, LLM-guided reasoning, and video diffusion to generate counterfactual video trajectories.
- The methodology employs structured scene representations and multi-hop intervention propagation to ensure precise spatial grounding and semantic alignment.
- Experimental results show significant improvements in temporal coherence and spatial localization on benchmarks like RVEBench and FiVE, demonstrating robust hypothetical scenario generation.
Counterfactual World Models via Digital Twin-Conditioned Video Diffusion
Conventional world models simulate environment dynamics by predicting the temporal evolution of visual observations, extrapolating future states from a single factual trajectory. These models, particularly those based on video diffusion, operate using entangled pixel-space representations that obscure semantic and relational properties. Such an approach is fundamentally limited in handling counterfactual reasoning–i.e., generating plausible scene evolutions under hypothetical modifications (interventions) to objects or relationships. This capability is essential for evaluating physical agents and systems under varied, unseen conditions and for robust scenario planning.
Counterfactual world models (CWMs) redefine the classical paradigm by treating interventions as explicit inputs, thereby predicting multiple alternate futures conditioned on specified hypothetical changes. The paper formalizes CWMs as mappings from observed visual states and interventions to probability distributions over hypothetical video sequences, thereby decoupling reasoning about “what could happen” from the constraints of direct pixel-level manipulation.
CWMDT Framework and Methodological Innovations
CWMDT (Counterfactual World Model with Digital Twin Representation Conditioned Diffusion Model) advances the field by decomposing counterfactual simulation into three functionally distinct stages:
- Digital Twin Construction: Vision foundation models extract compositional scene descriptions (objects, attributes, spatial configurations, semantic categories, and trajectories) from video frames and serialize them as structured text representations.
- Counterfactual Reasoning: An LLM processes intervention queries at the digital twin level, propagating modifications across predicted temporal sequences. This leverages world knowledge embedded in the LLM for multi-hop spatial-relational reasoning and generates modified digital twin sequences representing plausible hypothetical scenarios.
- Video Diffusion Synthesis: A fine-tuned video diffusion model, conditioned on edited initial frames and the modified digital twin sequence, generates the corresponding pixel-space counterfactual trajectories. This separation ensures consistency between the logical effects of interventions and their visual manifestation.
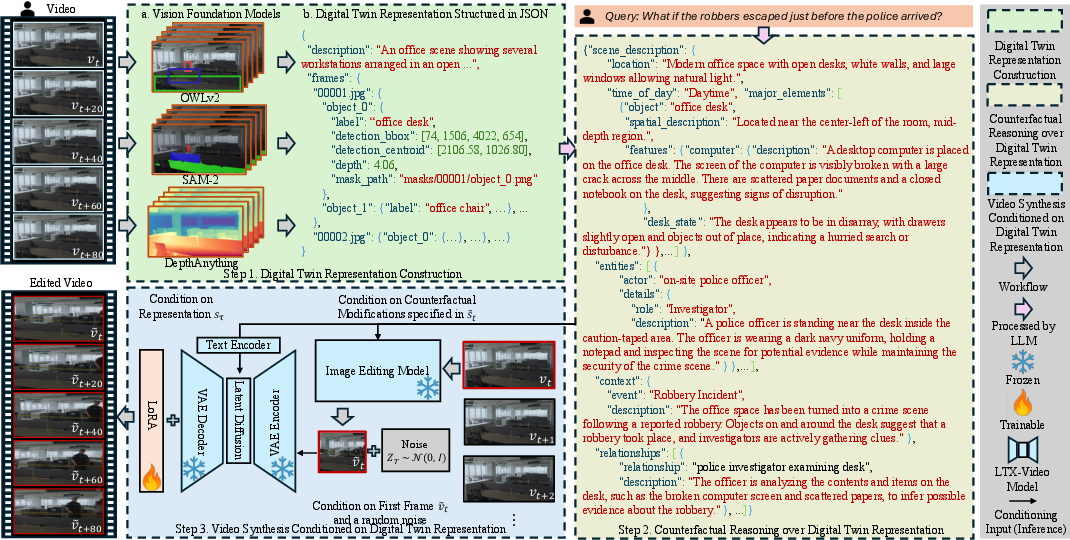
Figure 1: Method overview for CWMDT: perception as digital twin extraction, reasoning over digital twins with an LLM for intervention propagation, and synthesis via video diffusion conditioned on edited scene descriptions.
This modular architecture enables targeted, controlled interventions, preserves spatial and semantic coherence, and readily generates multiple plausible futures for a given scenario and intervention.
Experimental Results and Quantitative Analysis
Reasoning-Intensive Benchmarks
CWMDT is evaluated on RVEBench and FiVE, both crafted to test complex editing and multi-hop reasoning requirements. RVEBench consists of videos paired with queries requiring counterfactual reasoning at increasing complexity levels; FiVE focuses on fine-grained, object-level video editing and temporal coherence.
CWMDT establishes state-of-the-art performance across all competitive metrics:
- GroundingDINO (Spatial Grounding): CWMDT attains 29.16–33.33% on RVEBench and 30.18% on FiVE, greatly exceeding the nearest alternative (9.94–22.81%).
- LLM-as-a-Judge (Semantic Alignment): CWMDT yields 58.81–64.06% on RVEBench, 63.02% on FiVE, surpassing baselines by 20+ points.
- CLIP-Text (Semantic Alignment to Intervention Descriptions): CWMDT delivers 26.18–30.59%, outperforming all baselines (≤25.31%).
- CLIP-F (Temporal Coherence): CWMDT achieves near-perfect scores (97.87–98.85%), confirming that compositional structure does not compromise dynamic consistency.
Baseline video editing and synthesis approaches (e.g., InstructV2V, FlowDirector, AnyV2V, InstructPix2Pix) degrade heavily at higher reasoning complexities and fail to spatially localize interventions or propagate them coherently over time.

Figure 2: Qualitative comparison demonstrating CWMDT's superiority in executing and propagating interventions while baseline methods remain factually constrained.

Figure 3: CWMDT generates diverse, physically coherent counterfactual trajectories from a single intervention, in contrast to visually inconsistent or failed baselines.

Figure 4: Visualization of multiple plausible counterfactual scenarios for a single video source, illustrating the probabilistic nature of CWMDT’s output.
Ablations
Ablation studies show that removal of digital twin representations or LLM-based intervention reasoning sharply reduces spatial grounding and semantic alignment. Scaling down the LLM backbone results in diminished performance across all metrics, quantifying the value of high-capacity reasoning. The implementation of an edited initial frame (as opposed to conditioning on unmodified inputs) is crucial for temporal and visual consistency.
Causal Reasoning Benchmark
On CausalVQA, explicit augmentation with CWMDT-generated counterfactual videos boosts model performance for counterfactual, anticipation, and hypothetical questions (up to 17.5% absolute improvement; best-in-class open-model scores), establishing that compositional intervention reasoning provides actionable signal even outside direct video editing contexts.
Architecture and Digital Twin Representation Specification
Digital twin representations include global scene summaries, object-centric spatial trajectories, attribute annotations, per-frame semantic captions, and detailed numerical traces encoding area, centroid drift, and depth evolution (Figure 5). The LLM modifies descriptions, spatial couplings, and temporal dynamics to maintain physical and semantic coherence under hypothetical interventions.

Figure 5: Evolution and editing of digital twin representations: from original, to condensed, to LLM-modified states reflecting interventions and spatiotemporal propagation.
Implications and Future Directions
CWMDT demonstrates that explicit decomposition (perception → reasoning → synthesis) and structured scene representations dramatically augment the controllability and tractability of video world models for hypothetical scenario generation. Strong quantitative results highlight the limitation of pixel-based, entangled representations and validate digital twins and LLM-driven reasoning as critical enhancements.
The framework opens opportunities for safe autonomous operation in embodied AI, simulation-based planning in robotics, and robust scenario analysis in physical AI deployments. Theoretically, it suggests that structured representation and decoupled reasoning-synthesis may be necessary for generalizing world models to out-of-distribution interventions. Practically, future work can extend digital twin representations to cover richer physical attributes and integrate uncertainty modelling in LLM reasoning to sample generative coverage of plausible futures.
Conclusion
CWMDT formalizes counterfactual reasoning in world models and operationalizes it through digital twin-conditioned video diffusion. This architecture delivers strong empirical gains in spatial grounding, semantic fidelity, and controllable counterfactual video generation over conventional pixel-space approaches. Digital twin representations and LLM reasoning emerge as necessary components for advanced, intervention-driven simulation capabilities, with broad implications for decision-making and robust physical AI evaluation.






