- The paper introduces a novel hybrid approach that integrates cooperative reinforcement learning within MPPI control for enhanced multi-robot collision avoidance.
- It employs a safety-constrained update mechanism that biases the sampling towards intelligent, collision-free trajectories, achieving a 100% success rate in key scenarios.
- Experimental results demonstrate superior navigation efficiency and reduced task completion time compared to classical methods in both sparse and dense environments.
CoRL-MPPI: Advancements in Multi-Robot Collision Avoidance
Introduction
The paper "CoRL-MPPI: Enhancing MPPI With Learnable Behaviors For Efficient And Provably-Safe Multi-Robot Collision Avoidance" (2511.09331) presents a novel approach for addressing decentralized collision avoidance in multi-robot systems. The focus of this research is the integration of Cooperative Reinforcement Learning (RL) with the Model Predictive Path Integral (MPPI) control, leveraging the advantages of both methods to enhance navigation efficiency and safety. This hybrid solution aims to overcome the limitations intrinsic to standard MPPI, particularly its reliance on uninformed random sampling, which can lead to suboptimal trajectories and potential collisions.

Figure 1: The figure illustrates the core idea of our method for decentralized collision avoidance. The left panel shows the baseline MPPI controller, where random rollouts (yellow) lead to potential collisions (red crosses) and suboptimal control (red trajectory). The right panel depicts proposed fusion of RL and MPPI, where learned policy rollouts (blue) bias the sampling distribution toward more cooperative and collision-free behaviors, improving final control performance while retaining the theoretical guarantees of MPPI.
Methodology
Model Predictive Path Integral (MPPI)
MPPI is a sampling-based optimization framework that generates control sequences through stochastic perturbations and evaluates them based on a defined cost function. It provides strong theoretical guarantees and flexibility to handle complex motion models and cost functions. In multi-robot systems, MPPI faces challenges due to its dependence on random control sampling, which struggles in densely populated environments, as most trajectories may not exhibit cooperative behavior.
Cooperative Reinforcement Learning (RL)
Cooperative RL has demonstrated capabilities in learning strategic behaviors in multi-agent scenarios. By anticipating other agents' actions, RL-trained policies can facilitate efficient navigation and conflict negotiation. Despite these strengths, RL policies often face difficulties in generalization beyond trained environments and lack the formal safety guarantees of model-based controllers.
CoRL-MPPI Framework
CoRL-MPPI employs a hybrid architecture, embedding a pre-trained RL policy within the MPPI control framework to adjust the sampling distribution towards more intelligent trajectories. This integration enables the preservation of MPPI's safety guarantees while benefiting from RL's cooperative strategies. The synergy between RL's high-level strategic knowledge and MPPI's robust planning ensures improved navigation performance.
Safety and Efficiency
The paper introduces a safety-constrained update mechanism for the distribution parameters within CoRL-MPPI, ensuring probabilistic safety with respect to neighboring robots. By solving an optimization problem, control inputs are adjusted to meet predefined safety levels while maintaining proximity to nominal parameters [dergachev2024decentralized].
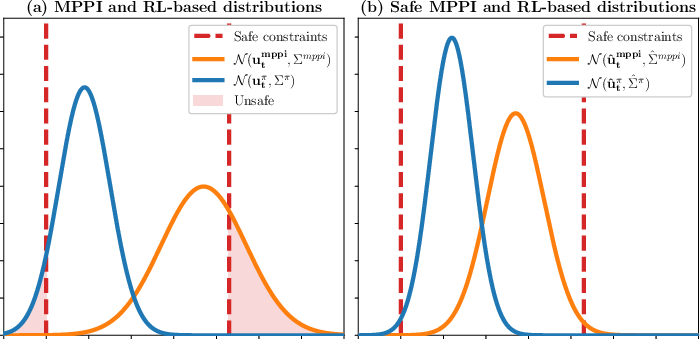
Figure 2: Visualization of safety-constrained update of distribution parameters. The probability mass of unsafe controls (red region) is reduced to meet the required confidence level.
Experimental Evaluation
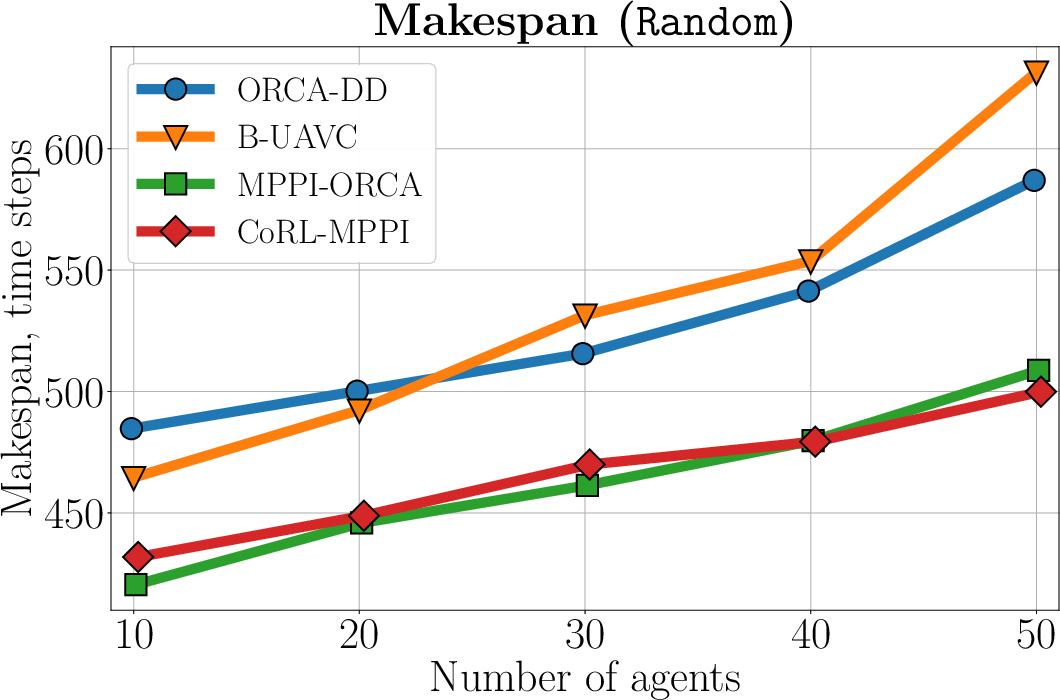
The authors conducted rigorous experiments in various scenarios, including Random, Circle, and Mesh environments, to evaluate the efficacy of CoRL-MPPI against classical methods like ORCA, BVC, and MPPI-ORCA. The simulations demonstrated CoRL-MPPI's superiority in achieving higher success rates and efficiency, particularly in complex interactions necessitating cooperative behavior.
Results


Figure 4: The average makespan of the evaluated algorithms across the Random, Circle, and Mesh (Dense) scenarios. Only instances with a 100\% successful runs are included. The lower is better.
Conclusion
CoRL-MPPI represents a significant advancement in multi-robot collision avoidance, enhancing MPPI with learnable behaviors for effective and safe navigation in decentralized systems. The hybrid framework adeptly combines the strategic capabilities of RL with MPPI's planning robustness, demonstrating superior performance across complex simulation environments. Future work may explore real-world applications, additional safety optimizations, and adaptive policy learning to further enhance generalization in diverse conditions. The successful integration of RL into MPPI paves the way for more intelligent and cooperative multi-robot systems, potentially influencing future developments in robotic autonomy.