- The paper demonstrates that using expanded GPT prompts improved JQL query accuracy from 17.14% to 48.57%.
- The study outlines a three-phase workflow: JQL generation, field selection, and natural language response construction.
- The research highlights that lower temperature settings yield more deterministic and reliable GPT outputs for structured queries.
Using GPT to Build a Project Management Assistant for Jira Environments
The paper "Using GPT to build a Project Management assistant for Jira environments" introduces JiraGPT Next, a project management assistant designed to enhance the functionality of Jira by integrating GPT-based natural language processing. The authors aim to reduce the complexity project managers face when interacting with Jira, relieving them of the need to master intricate programming languages and facilitating the querying of project data through natural language inputs.
Introduction to JiraGPT Next
JiraGPT Next operates as a smart layer over existing Jira environments, harnessing GPT models to interpret and convert user queries into Jira Query Language (JQL). This process simplifies data retrieval from Jira's extensive database, allowing for more intuitive project management. The assistant focuses on translating natural language requests into actionable JQL queries, conducting analyses, and furnishing users with comprehensible, natural language responses.
User Interface and Interaction
The user interface of JiraGPT Next is structured to distinguish between functionalities aimed at end users and developers. Managers can input queries in a central text area, supported by features like query complexity toggling to manage costs. On the other hand, a developer-focused panel facilitates debugging and configuring parameters like temperature settings and LLM selection.
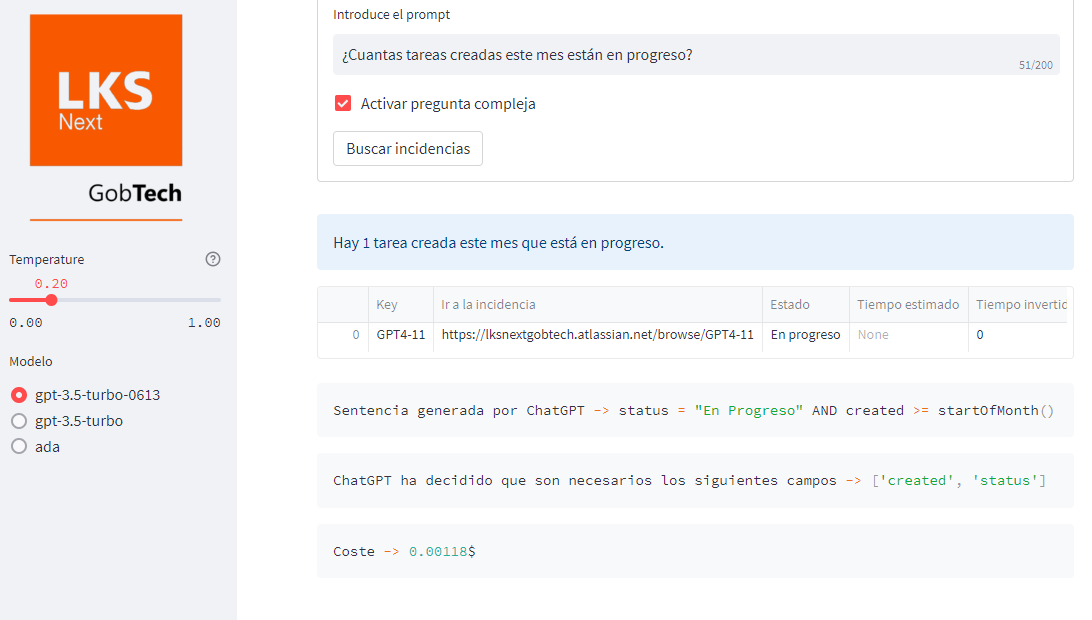
Figure 1: Screenshot of JiraGPT Next with the results to the query ``How many tasks created this month are in progress?'' (In Spanish).
Workflow Phases
The internal workflow of JiraGPT Next is segmented into three distinct phases:
- JQL Generation: User queries are fed into GPT with crafted prompts to produce JQL queries, which are subsequently executed within Jira.
- Field Selection: Analyzes the returned Jira data fields via GPT to identify those necessary for constructing a meaningful response.
- Natural Language Response Construction: GPT synthesizes a coherent natural language response using the refined dataset from preceding phases.
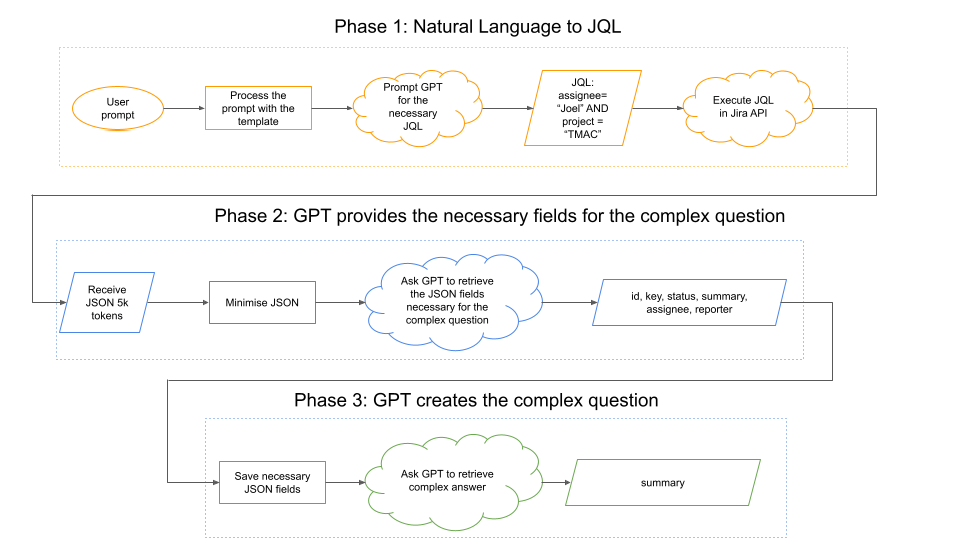
Figure 2: Phases of the JiraGPT Next internal process.
Evaluation of GPT Prompts
The authors performed an evaluation focused on the first phase of the system—JQL generation—to assess the accuracy and efficiency of different prompting strategies. Through iterative tests, they found that fuller prompts, despite higher token costs, produced more accurate JQL queries. A detailed analysis revealed that accuracy improved from 17.14% using a minimal prompt to 48.57% with an expanded prompt structure containing multiple task-oriented examples.
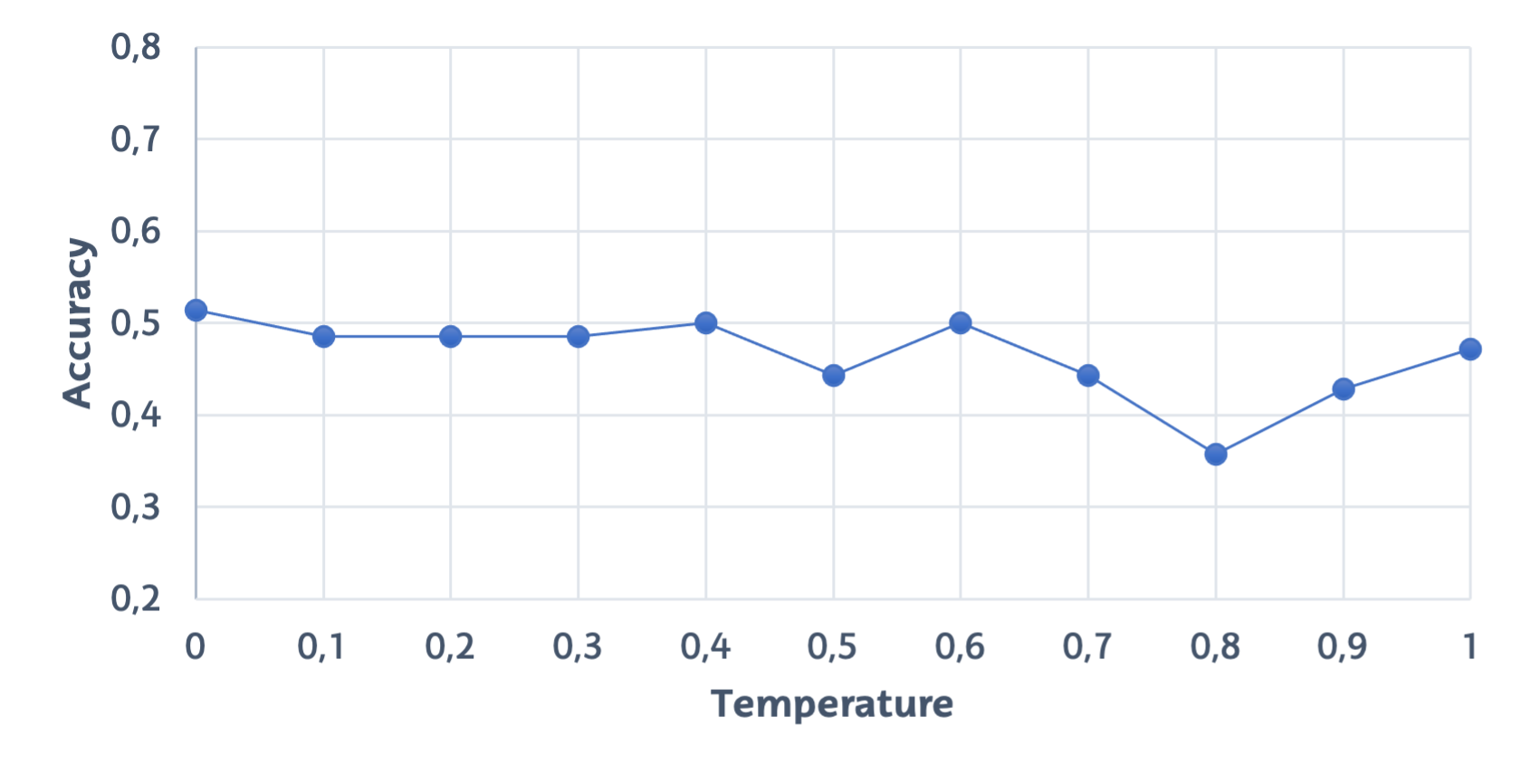
Figure 3: Accuracy of the full prompt with different temperature values.
Impact of Temperature on GPT Output
The paper also explored how the temperature setting affected the model's output randomness and coherence, revealing that lower temperatures (close to 0) resulted in more deterministic and reliable responses for structured query generation tasks. This insight could guide the parametrization of future LLM-based assistants.
JiraGPT Next is compared with other AI-powered project management tools such as Kubiya.ai, Microsoft 365 Copilot, and Albus, highlighting its lower operating costs and seamless integration with Jira. The evaluation emphasizes its potential for democratizing Jira usage by making project management workflows more intuitive and accessible.
Conclusion
JiraGPT Next stands as a promising advance in AI-augmented project management toolkits, offering significant benefits in terms of user accessibility and query efficiency within Jira environments. The research emphasizes careful prompt design and cost management, essential for deploying LLMs effectively in real-world applications. Future developments will focus on optimizing prompt strategies and exploring alternative LLM architectures like Gemini and Llama, alongside enhancing usability and functionality based on user feedback.


