- The paper introduces a systematic criterion for identifying atomic arbitrage transactions on Polygon using multi-swap mechanisms that ensure net profit.
- The analysis leverages Python-driven scrutiny of 23 million blocks from Jan 2023 to Oct 2024 to quantify MEV extraction and evaluate transaction strategies.
- The paper finds that FastLane arbitrage, yielding about 13% of AA MEV, highlights a strategic shift towards more efficient, auction-based methods.
Introduction
The integration of blockchain technology has reshaped financial ecosystems, accentuating challenges like Maximum Extractable Value (MEV) on platforms such as Polygon. This paper examines the intricacies of MEV, especially focusing on Atomic Arbitrage (AA) transactions. Leveraging a dataset comprising 23 million blocks over 22 months, it provides insights into the behavioral patterns of AA transactions and the factors facilitating MEV extraction on the Polygon blockchain.
MEV Taxonomy and Arbitrage Mechanisms
MEV on Polygon, like on Ethereum, involves strategic transaction ordering by validators to exploit financial opportunities. The paper classifies MEV into atomic, semi-atomic, and statistically driven strategies, highlighting that AA transactions ensure risk-free profit through multi-swap mechanisms executed within a single transaction. Backrunning, a focal point of MEV, exploits mempool visibility, allowing transactions to be strategically placed for profit, often facilitated by spam-based or auction-based (e.g., Flashbots) approaches.
Criterion for Identifying Arbitrage Transactions
To systematically classify AA transactions, the paper introduces a criterion requiring at least two asset swaps per transaction, ensuring net positive asset change and transaction profitability post-fee consideration. This heuristic aids in distinguishing genuine arbitrage strategies from mere financial maneuvers.
Empirical Analysis of AA Transactions on Polygon
Transaction Examples
In practice, AA transactions leverage cross-market price discrepancies to yield profit without assuming risk. For instance, an arbitrage between Uniswap V2 and V3 on Polygon yielded 0.3121 WMATIC as profit, demonstrating a typical transaction where liquidity pools facilitate profitable cross-asset swaps.
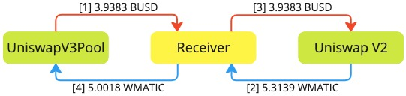
Figure 1: Plain arbitrage between Uniswap V3 and V2 on Polygon netted 0.3121 WMATIC profit (transaction 0xc6591b9.. in block 58,329,504)
Data Collection and Methodology
Employing data from a remotely hosted Polygon node, the paper utilizes Python scripts to analyze transaction blocks from January 2023 to October 2024. This facilitates identification of AA transactions across Uniswap V2, V3, and related DeFi protocols. Moreover, it differentiates between FastLane and spam-based AA transactions, delineating their respective contributions to MEV.
Results and Analysis
Trends and Numerical Results
AA transactions contributed approximately 12M USD in extracted MEV on Polygon, predominantly through efficient FastLane mechanisms which accounted for 13% of total AA MEV. This shift highlights evolving preferences towards structured strategies that minimize network disruption.
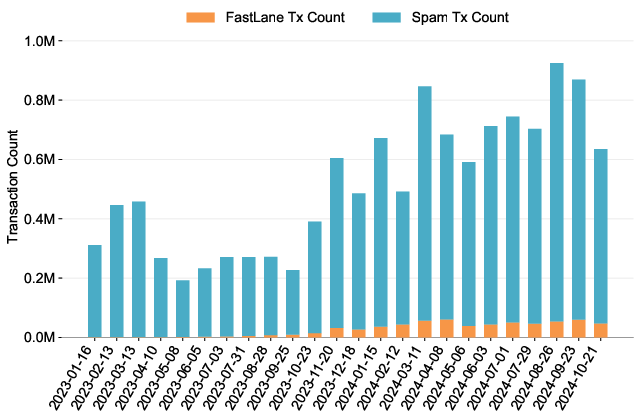
Figure 2: AA Transactions Count Over Time
The data presents increasing awareness and adoption of auction-based methods over spam, as reflected in the composition and outcome of MEV strategies. Despite lower transaction counts, FastLane AA transactions exhibit higher MEV realization, attributed to their bid-induced prioritization.
Evolution of Transaction Dynamics
The FastLane method's effectiveness, marked by a high return on reduced transactions, underscores its strategic relevance. While spam-based transactions persist due to their prevalence, shifting network dynamics emphasize profitability efficiency over volume.
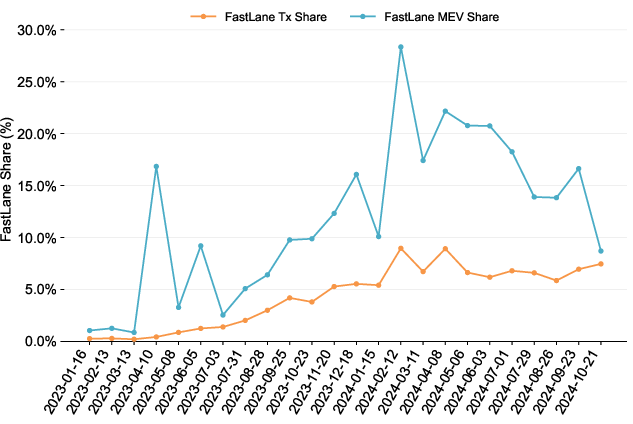
Figure 3: AA Fastlane Transactions and MEV Share Over Time
Conclusion
The paper provides an extensive examination of MEV dynamics on Polygon, revealing a pragmatic shift towards structured, auction-based arbitrage strategies. It suggests the emerging potential of optimized transaction methods in diminishing network load while maximizing MEV. Future implications involve advancing MEV prevention at the transaction initiation stage, indicating a transition from mere extraction to preemptive optimization.
The research underscores ongoing MEV challenges and advocates for enhanced decentralized protocols balancing economic incentives and fairness. As transaction mechanisms evolve towards solver-centric models, initiatives like CoW Swap and FastLane Atlas may reframe the future landscape of MEV execution strategies, paving the way for fairer, efficient blockchain ecosystems.


