- The paper introduces MLED, a framework that fuses LLM-driven textual embeddings with GNN-based graph representations for enhanced fraud detection.
- It employs type-level and relation-level enhancers to dynamically integrate node and edge data, improving metrics like AUCROC and F1-score.
- Experimental results show that MLED achieves significant performance gains with minimal computational overhead on diverse datasets.
Multi-Level LLM Enhanced Graph Fraud Detection
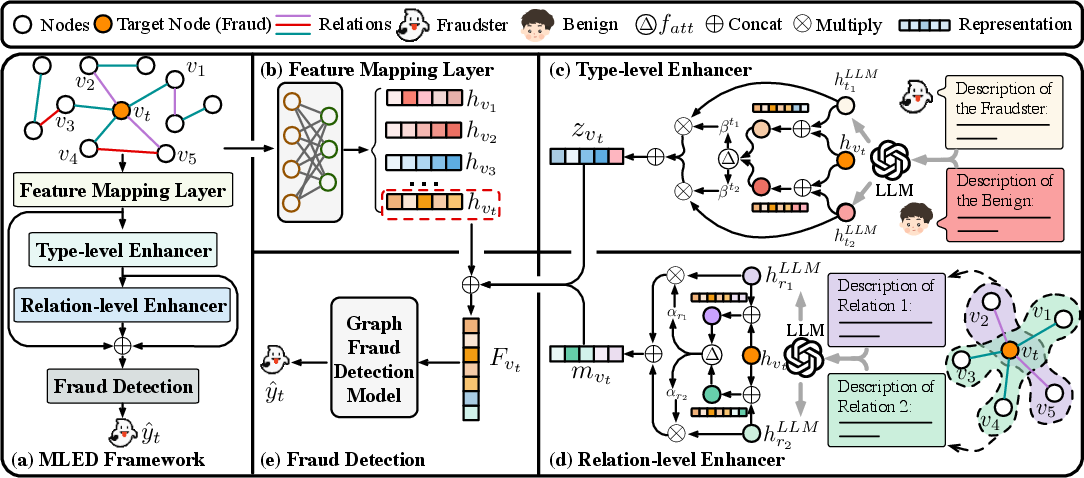
The paper "Can LLMs Find Fraudsters? Multi-level LLM Enhanced Graph Fraud Detection" discusses a novel framework called MLED designed to improve graph fraud detection techniques by integrating the powerful capabilities of LLMs with Graph Neural Networks (GNNs). This framework aims to leverage textual embeddings and graph structures to enhance the ability to distinguish fraudsters from benign entities.
Framework Overview: MLED
MLED's core concept is the multimodal fusion of LLMs and GNNs to enhance graph fraud detection. The framework consists of two key components: a type-level enhancer and a relation-level enhancer. These components are responsible for integrating external knowledge from LLMs and refining the detection capabilities of existing graph structures.
Methodology
Preliminaries
The framework targets multimodal graphs where nodes can have complex relationships and multimodal attributes. A graph fraud detection problem is posed as an imbalanced binary classification task, focusing on detecting suspicious nodes within a network.
Feature Mapping and Enhancers
Using a feature mapping layer, MLED projects input nodes into a unified representation space. The subsequent enhancers use LLM-generated semantic embeddings to enrich node representations on multiple levels:
Fraud Detection Process
The integrated node representations from both type and relation level are combined using weighted sums. This comprehensive node depiction is then classified to predict whether a node is fraudulent or benign, incorporating MLED into existing GNN-based fraud detection pipelines.
Experimental Results
MLED's efficacy is demonstrated through extensive experiments on both multi-relation and single-relation datasets, including Amazon and YelpChi, achieving remarkable improvements over the state-of-the-art:
- On multi-relation datasets, MLED shows an increase in metrics such as AUCROC and F1-score, enhancing the ability to separate fraudsters from benign entities.
- The framework's integration also carries negligible additional time overhead, shown by an average increase in training time of less than 0.3 seconds per epoch.
- Visualization analyses and parameter studies reveal that MLED's multi-level enhancements lead to clearer cluster definitions and resilient performance against varying hyperparameter settings.
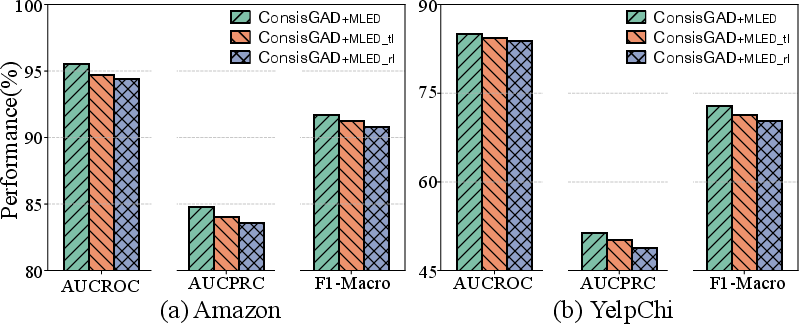
Figure 3: Ablation study results on various MLED variants with the SOTA method.

Figure 4: Efficiency analysis on the Amazon and YelpChi datasets.
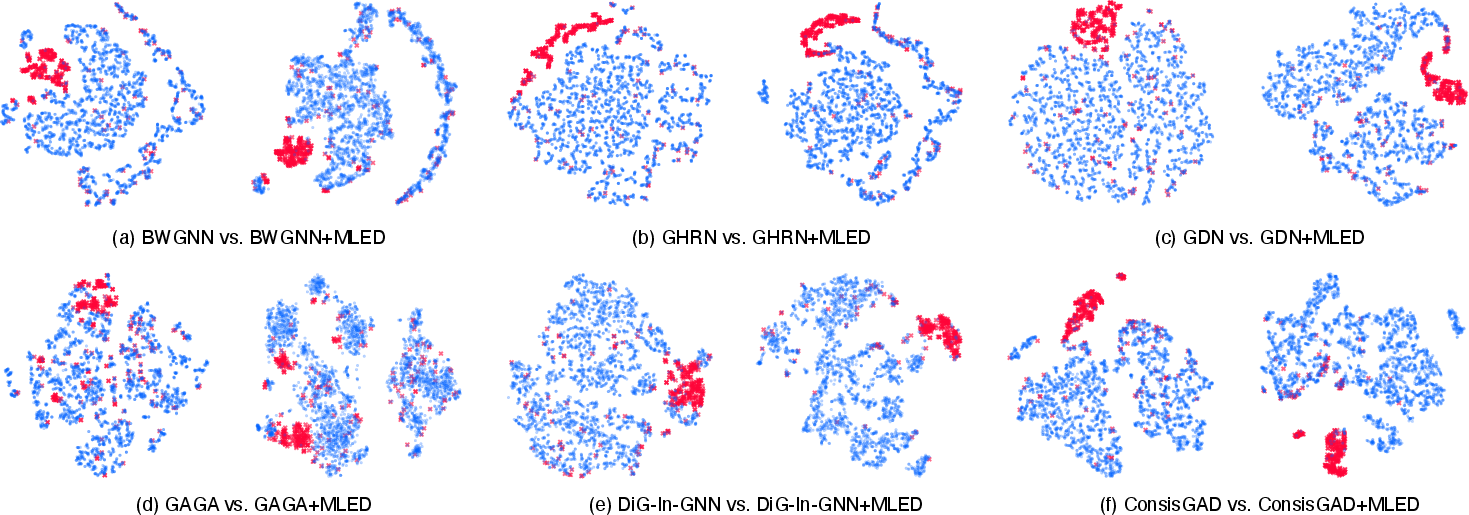

Figure 5: The visualization analysis on the Amazon dataset, where red represents fraudsters blue represents benign entities. Each pair of subfigures consists of baselines (left) and baselines enhanced by MLED (right).
Conclusion
MLED introduces a pioneering approach to fraud detection by innovatively merging LLM-driven textual insights with structural graph data, significantly improving detection accuracy across diverse datasets. It showcases the potential of applying multimodal learning for complex real-world tasks, suggesting further exploration in dynamically integrating linguistic and structural data for other graph-based applications.