- The paper introduces IDEIA’s generative AI system that integrates Google Trends and Gemini APIs for real-time editorial ideation, achieving up to 70% time savings.
- It employs a modular, containerized architecture with Node.js, React, Docker, and PostgreSQL to ensure scalability and rapid iteration.
- Empirical deployment demonstrated significant operational gains while highlighting challenges in API integration and ethical content generation.
IDEIA: A Generative AI System for Editorial Ideation in Digital Journalism
System Overview and Architectural Design
IDEIA introduces a generative AI-powered workflow to address the increasing demand for speed and thematic relevance in digital journalism. Developed with modularity and scalability as primary design principles, the system integrates Google Trends API for real-time topic monitoring with Google Gemini API for automated headline and summary generation. Node.js underpins the back-end logic; React, accelerated by Vite, delivers a responsive single-page front-end; and PostgreSQL ensures robust data persistence. The entire stack is containerized using Docker and orchestrated via an automated CI/CD pipeline powered by GitHub Actions and Vercel, employing Jest for backend component testing.
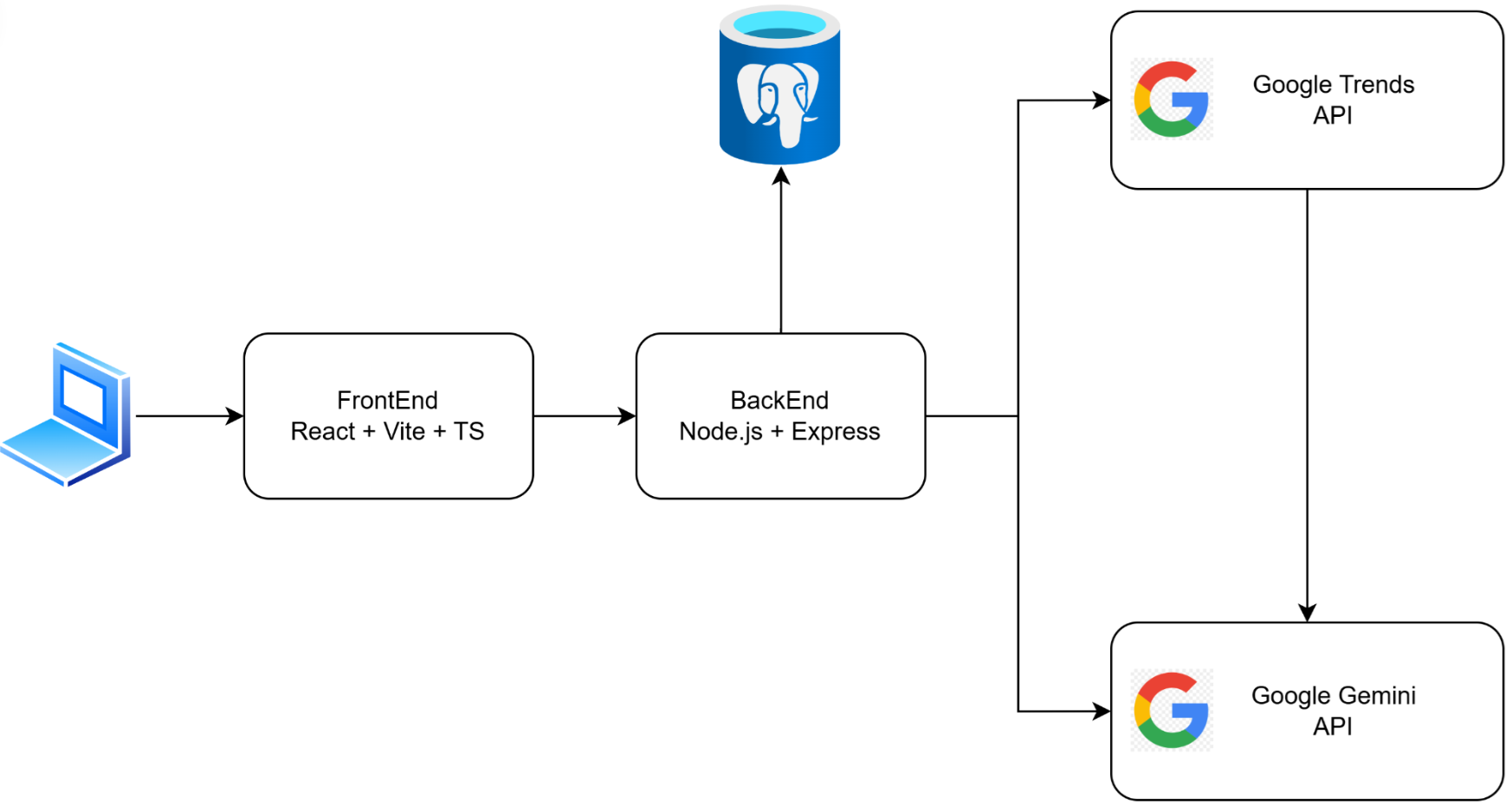
Figure 1: Logical architecture of the application, illustrating integration between modules and third-party APIs.
This architecture enables rapid feature iteration while maintaining separation between UI, business logic, and data layers. The React front-end interfaces with RESTful endpoints, leveraging hooks for asynchronous state management. Integration challenges with the Gemini API were resolved via the official Google SDK to standardize prompt construction and authentication. Persistent Docker volumes ensure data integrity across container lifecycles.
Front-End Implementation and User Experience
IDEIA's interface was developed in ReactJS with CSS-in-JS encapsulation and Framer Motion for advanced visual transitions and user feedback. The design prioritizes institutional branding fidelity and accessibility, offering seamless switching between dark and light themes and an adaptive layout for diverse devices.
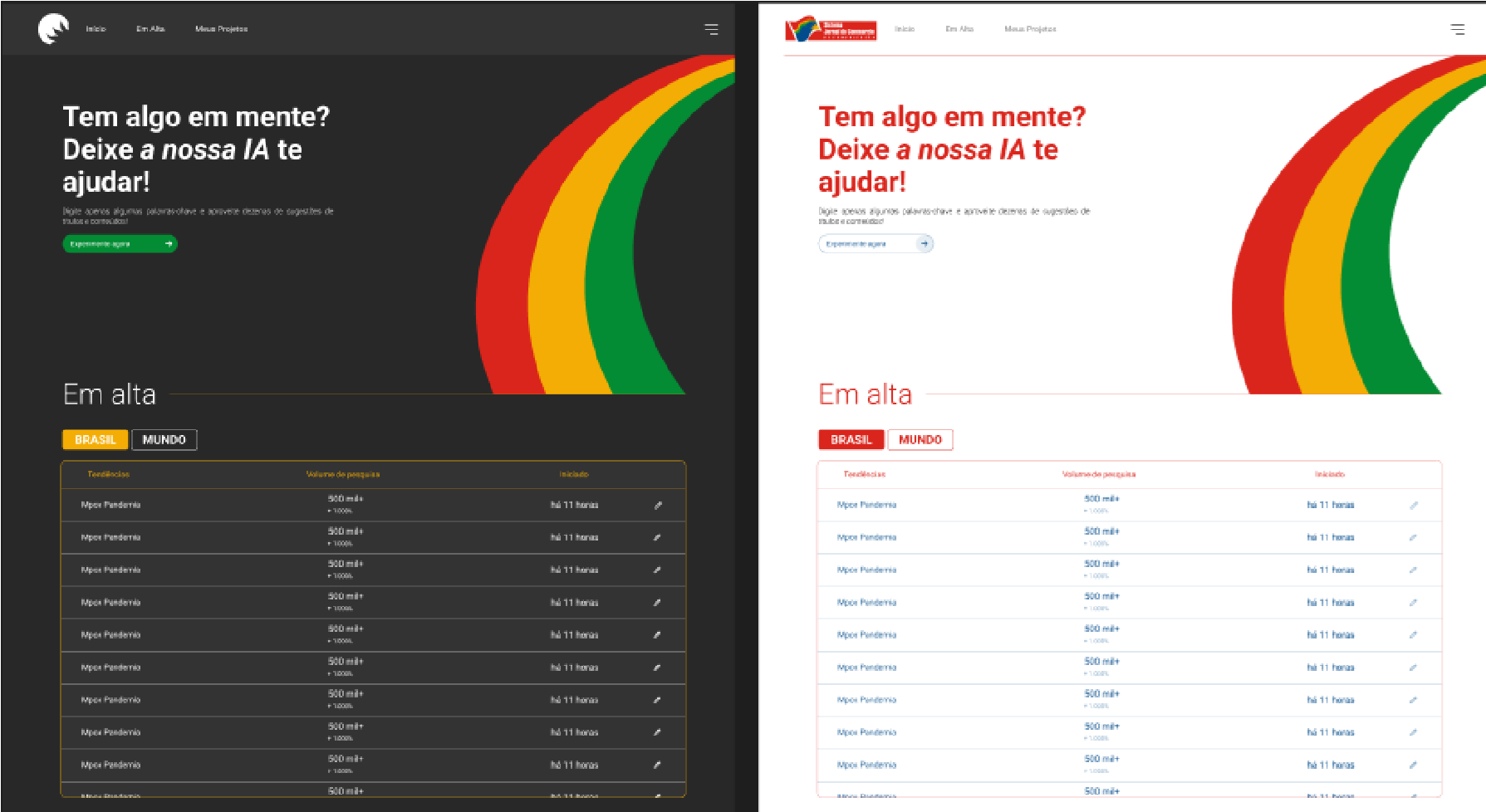
Figure 2: Layout of the home page of the project (landing page), supporting both dark and light themes.
Figure 3: Initial interface of the system (landing page), merging institutional identity with modern graphical elements.
Screen flow prototyping was performed with Figma, ensuring early validation of user interactions and hierarchy of information. Axios is employed for robust asynchronous communication, allowing instantaneous data updates, particularly for trending topics extracted from the Google Trends API, which refresh at 10-minute intervals.
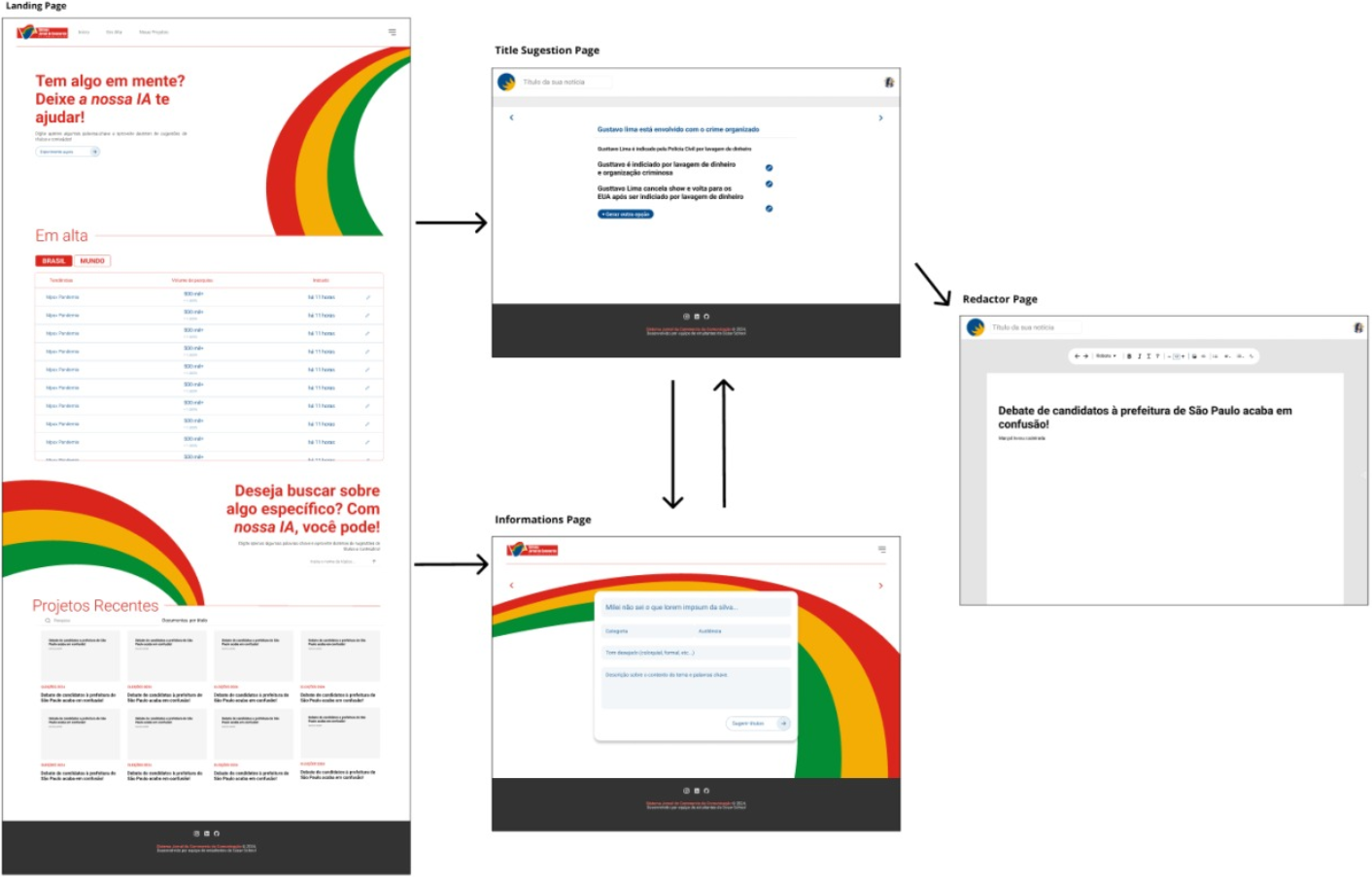
Figure 4: Main screen flow of IDEIA from trend selection to editorial drafting.
Development, Deployment, and CI/CD Practices
The project followed Scrum-based agile development, with sprint-based task management via Trello and version control in GitHub. The CI/CD pipeline automates unit and integration tests (via Jest) and deploys validated builds to Vercel following merges to the main branch, with build logs exposed to the team for traceability.
Critical technical challenges included:
- Asynchronous state management in React, mitigated through judicious hook placement.
- Integration errors with Google Gemini API, overcome by formalizing prompt formats and endpoint calls.
- Persistent PostgreSQL storage in Docker, resolved through explicit volume configuration.
- Use of Gherkin for BDD, which streamlined acceptance testing by aligning functional expectations across stakeholders.
Editorial Impact and Operational Gains
Empirical deployment in SJCC's editorial teams demonstrated a marked reduction in time-to-story development. Automating the screening and ideation stage displaced substantial cognitive load, freeing journalists for higher-order editorial tasks. The reported up to 70% time savings and increases nearing 100% reduction in manual trend search effort validate the productivity gains.
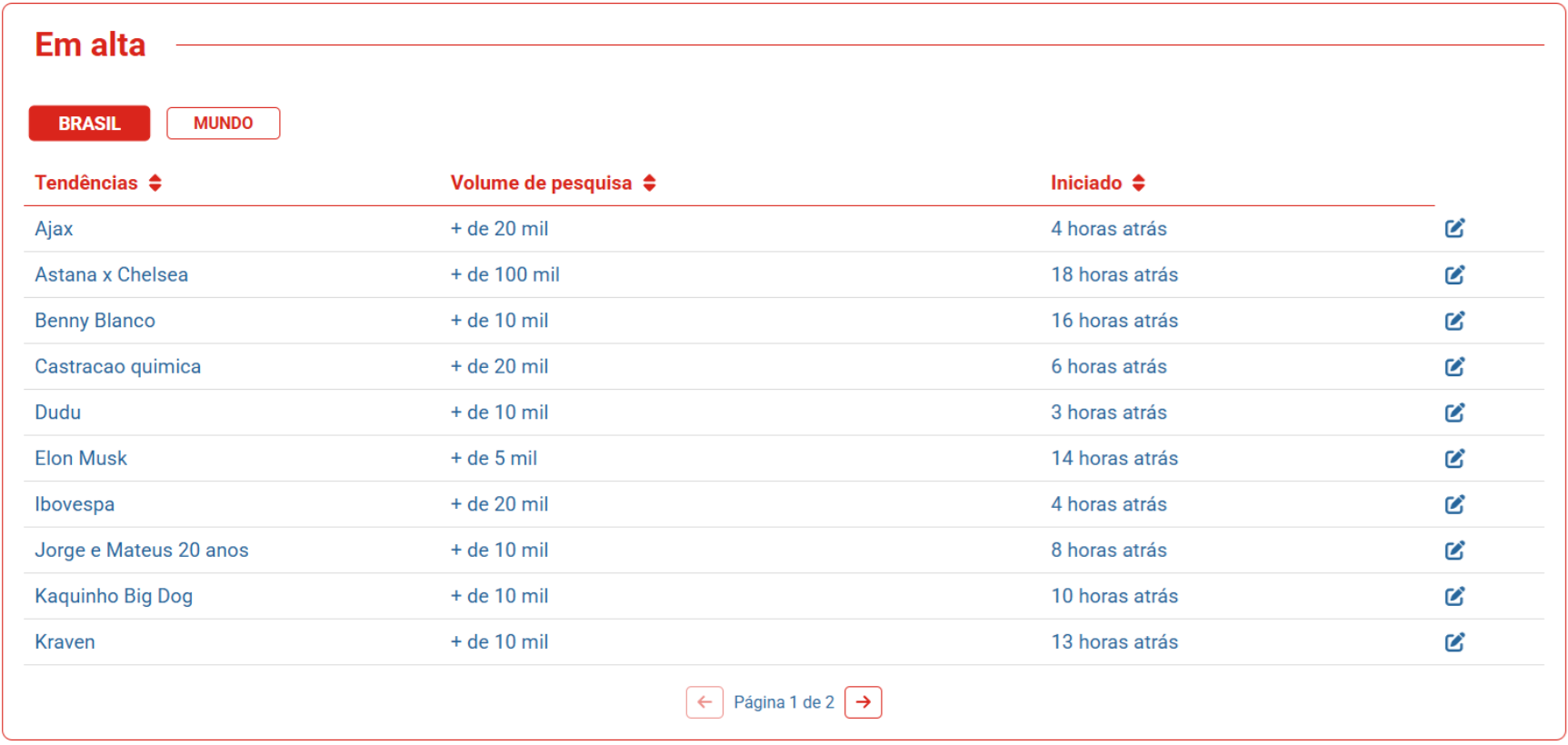
Figure 5: Trends table dynamically generated from Google Trends, enabling real-time monitoring of hot topics.
IDEIA's real-time integration with Google Trends offered the editorial staff immediate visibility into emerging topics, facilitating data-driven story selection. The Gemini API's generative capabilities produced headlines and summaries contextualized to current informational landscapes, and the editorial flow permitted further refinement and editing, sustaining quality control and human oversight.
Technical and Ethical Implications
IDEIA's architecture is inherently flexible, supporting replication across departments and sectors (e.g., digital marketing, education). Nevertheless, several limitations are acknowledged: the requirement for extended statistical validation of productivity metrics; adaptation to multilingual and varying editorial demands; and open challenges in algorithmic transparency, editorial accountability, and upholding human authorship in content produced via generative AI.
The system provokes broader questions surrounding the ethical deployment of generative models in creative workflows. Mechanisms for provenance, explainability, and style personalization are potential avenues for future extension. Incorporating analytics modules (e.g., Google Analytics) can quantitatively assess editorial impact and guide further optimization.
Conclusion
IDEIA provides a modular, production-ready generative AI system for optimizing editorial ideation in digital journalism. Its integration of real-time trend monitoring and automated headline/summaries has produced substantial organizational efficiencies within the SJCC. The logical separation of layers, containerized deployment, and continuous delivery pipeline ensure maintainable scalability. While initial qualitative and quantitative results are strong, long-term empirical evaluation and ethical frameworks for content generation remain critical for sustained adoption. The future scope includes expanding personalization features, integrating impact analytics, and generalizing the architecture for cross-sectoral applications.




