- The paper introduces a novel framework integrating AI, blockchain, and IoT to create self-governing, trustless systems.
- It presents a multi-layered architecture using real-time analytics and token-based governance for secure machine-to-machine transactions.
- The framework’s implications include improved asset management, reduced intermediaries, and a shift toward decentralized economic models.
Trustworthy Decentralized Autonomous Machines: A New Paradigm in Automation Economy
Introduction
Decentralized Autonomous Machines (DAMs) constitute an innovative paradigm in the automation economy by integrating AI, Blockchain technology, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. DAMs operate as self-governing economic agents within Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN), extending autonomy into the physical field and enabling trustless systems for managing Real and Digital World Assets (RDWAs). The integration of AI-driven decision-making, IoT-enabled operational autonomy, and blockchain-based governance is pivotal in transitioning from trust-based to trustless economic models, offering scalable, transparent, and equitable solutions for asset management.
Technological Foundations and Driving Forces
The technical realization of DAMs is rooted in the convergence of several technological paradigms, including DePIN, AI, blockchain, and IoT. The framework leverages community-driven networks for distributed data, compute, and governance, while employing AI for real-time decision-making and adaptation. This multi-layered architecture integrates physical operations, intelligent decision-making, and blockchain-based governance to facilitate autonomous machine operations in decentralized, trustless systems.
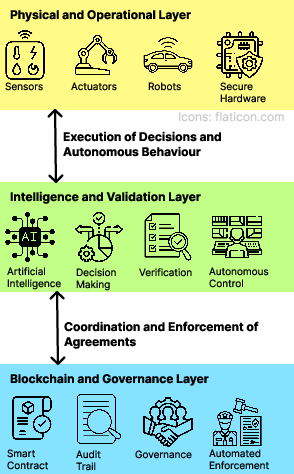
Figure 1: Layered Representation of a DAM.
DePIN exemplifies decentralized governance and token-incentivized participatory models in managing physical infrastructure such as wireless networks and energy grids. Projects like Helium and Filecoin demonstrate this model by incentivizing contributions to physical networks with token rewards. The integration of AI and blockchain within IoT systems enhances intelligent, secure, and autonomous operations. AI-driven smart contracts enable automated economic transactions without intermediaries. Additionally, blockchain technology ensures data integrity and security in trustless machine-to-machine interactions.
Transition to Trustless Economic Models
DAMs play a central role in transitioning from trust-based to trustless economic frameworks. Traditional economic systems rely heavily on intermediaries to facilitate trust, which incurs high costs and single points of failure. Blockchain technology provides transparency and resilience by enabling decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms that execute transactions with on-chain visibility and reduced counter-party risk.
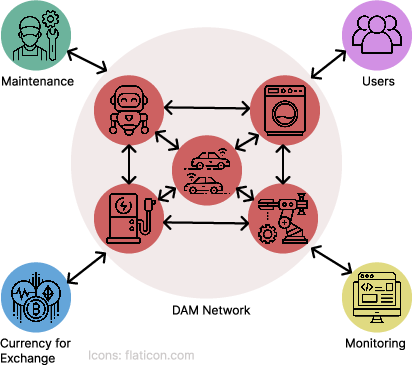
Figure 2: Interactions within a DAM Network, with internal M2M and external interactions.
AI enhances these systems by optimizing blockchain operations and enabling secure autonomous transactions. AI-driven real-time analytics and decision-making reduce reliance on intermediaries and enhance security, ensuring reliable machine-to-machine transactions. Despite existing scalability challenges within blockchain frameworks, emerging solutions such as Layer-2 technologies and cross-chain interoperability promise to enhance the scalability and integration across diverse systems.
Socio-Economic Implications
The socio-economic implications of DAMs are profound, offering potential shifts in how wealth is generated and distributed. Automation through DAMs promotes efficiency by reducing intermediaries and enabling direct peer-to-peer exchanges. They reshape asset ownership through tokenization, allowing fractional ownership and lowering entry barriers for individual investors.

Figure 3: Venn Diagram illustrating the Spectrum of the Impact of DAMs.
Conversely, DAMs may accelerate automation to levels disruptive to existing labor markets, requiring retraining and adaptative policies. Potential risks of wealth concentration among early adopters and governance controversies necessitate careful consideration in decentralized networks. The rise of DAMs also demands adaptive regulation within the insurance industry, where blockchain and AI innovations could optimize policy delivery and risk management.
Conclusion
DAMs exemplify a transformative integration of AI, blockchain, and IoT by rethinking the management of Real and Digital World Assets. They address inefficiencies in centralized systems and facilitate democratized access to economic infrastructure. However, widespread adoption demands overcoming technical challenges such as scalability, security vulnerabilities, and interoperability barriers, alongside socio-economic considerations related to potential labor market disruptions and wealth distribution in decentralized systems. Therefore, effective governance, equitable tokenomics, and proactive policy responses are essential to harnessing their full potential in bridging physical and digital realms.




