- The paper introduces REGLUE, a novel framework that fuses VAE latents with both global and local semantic cues, achieving outstanding FID improvements.
- The paper employs a nonlinear compression of multi-layer VFM features to efficiently align and fuse disparate modalities, reducing computational overhead.
- The paper demonstrates significant gains in convergence speed and image quality on ImageNet compared to traditional latent diffusion models.
Unified Modeling of Local and Global Semantics with REGLUE for Entangled Diffusion
Introduction
The paper "REGLUE Your Latents with Global and Local Semantics for Entangled Diffusion" (2512.16636) establishes a new framework for generative modeling by integrating both reconstruction-optimized VAE latents and semantics-optimized Vision Foundation Model (VFM) representations within a unified latent diffusion architecture. The approach overcomes limitations in existing Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs), which rely solely on VAE latents and provide only indirect semantic supervision. REGLUE extends previous techniques by entangling global image representations and compact local semantics via a nonlinear compressor, enabling the model to efficiently leverage information from multiple abstraction scales during both training and generation.
Methodology
The REGLUE framework is built upon the Scalable Interpolant Transformer (SiT) diffusion backbone, extended to model three entangled modalities: (i) VAE image latents, (ii) nonlinear compressed local patch-level VFM semantics, and (iii) a global VFM token ([CLS]). All semantic sources are jointly noised and fused, with features spatially aligned and projected into common embedding spaces. The fusion design avoids unnecessary self-attention overhead by merging channels, and a lightweight MLP head provides external alignment between hidden states and clean VFM teacher representations, following an auxiliary cosine similarity loss.
Crucially, patch-level VFM features from the last multiple layers are aggregated and compressed via a shallow, frozen convolutional autoencoder, yielding a low-dimensional, spatially-structured semantic tensor. This design both reduces channel imbalance (relative to naively fusing raw features) and preserves nonlinear structure, in contrast to baseline methods using linear PCA projections.
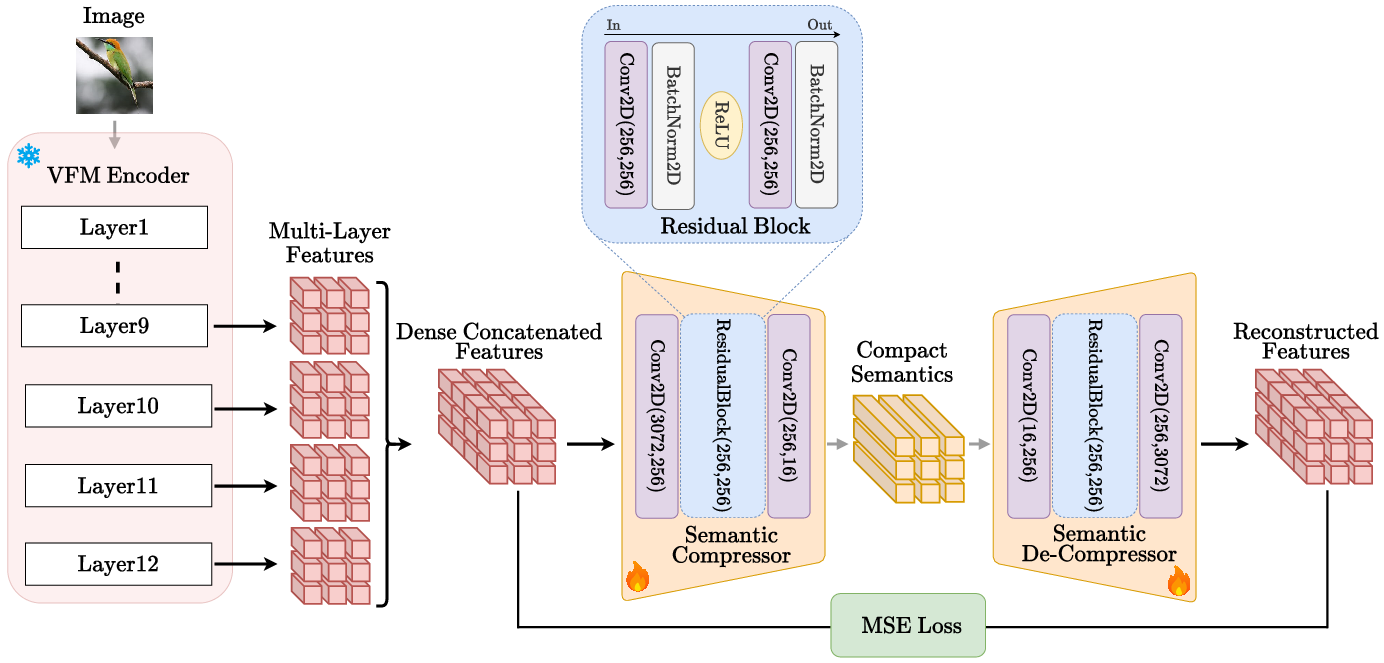
Figure 1: Semantic compressor structure: convolutional aggregation of multi-layer VFM features into a compact, reconstructive semantic embedding.
Training proceeds under a multimodal velocity prediction objective with jointly noised modalities and an auxiliary REPA-style representation alignment loss at an intermediate Transformer block.
Convergence Behavior and Numerical Results
REGLUE demonstrates strong improvements in sample quality and convergence speed across extensive evaluations on ImageNet 256×256. Notably, REGLUE achieves:
- FID 14.5 at 300K steps and FID 12.9 at 400K with SiT-B/2, significantly outperforming SiT-B/2 baseline (FID 33.0), REPA (24.4), ReDi (21.4), and REG (15.2) under identical training budgets.
- On SiT-XL/2 REGLUE attains FID 2.5 at 1M steps, matching or surpassing state-of-the-art methods and hitting REG's 1M-step FID with only 70% of the iterations.
- Consistently superior behavior in data-limited settings, with larger FID gaps over REG under aggressive dataset pruning.
Qualitatively, the model reaches high-fidelity image generation at significantly earlier stages of training in comparison to strong baselines.








Figure 2: REGLUE achieves high synthesis fidelity at very early training epochs, as visually reflected in the evolution of generations from 50K to 400K steps.
Empirical Analysis of Semantic Modeling Design
The paper conducts a systematic analysis of semantic signal choices and demonstrates:
- Local (patch) semantics outperform global tokens: Directly modeling compressed local patch-level semantics yields an absolute 7.1 FID reduction over global-only counterparts, even exceeding global modeling + alignment (REG).
- Nonlinear compression is essential: CNN-based semantic compression preserves critical VFM information, both raising downstream discriminative probing accuracy and lowering FID, as compared to ReDi-style PCA projections.
- Joint global-local-latent modeling is complementary: Adding the global [CLS] token and REPA alignment on top of local modeling further reduces FID. Alignment to global tokens alone is numerically unstable, requiring local anchors.
- Multi-layer VFM aggregation provides additional gain: Combining features from the last four VFM layers before compression outperforms last-layer-only variants.
Semantic Compressor Impact and Probing
The semantic compressor architecture is designed for high throughput and reconstructiveness. Ablation studies identify an optimal range of 16 output compression channels for balancing discriminative fidelity and generative performance. Downstream probing (e.g., attentive probing on ImageNet, frozen DPT semantic segmentation on Cityscapes) demonstrates that compressed non-linear features nearly recover the semantics of full VFM representations while enabling stable joint modeling with VAE latents, outperforming linear compression in both probing accuracy and FID.
Implications and Future Directions
REGLUE delivers empirical evidence that spatially-structured, compact VFM features, combined with reconstruction-optimized latents and a global semantic anchor, enable accelerated convergence and superior sample quality with minimal compute overhead. The results support a paradigm where learned, nonlinear semantic tokenizers are critical for scalable and efficient latent diffusion, and where global and local cues must be modeled in tandem to maximize generative signal.
Practically, this framework can be extended to other domains and modalities, including multimodal diffusion pipelining (e.g., joint image-text, image-video generation), data-scarce regimes, or scenarios requiring robust transfer of semantic structure. The architecture is agnostic to the choice of VFM; improvements track advances in foundation model pretraining.
Theoretically, the work illustrates the ongoing collapse of the distinction between discriminative and generative modeling via dense joint entanglement, suggesting future studies on more intricate architectures for semantic tokenizers, global context blenders, or task-adaptive external alignment.
Conclusion
REGLUE introduces a unified modeling strategy that leverages both global and local VFM semantics with VAE latents inside a single diffusion backbone, enabled by a compact, nonlinear semantic compressor. This architecture yields robust improvements in FID, convergence rate, and data efficiency as evidenced by systematic ablations and state-of-the-art ImageNet results. The methodology sets a new standard for semantic supervision and compositionality in latent diffusion models, and its analysis raises promising lines of inquiry for universal, semantics-driven generative modeling.


