- The paper presents LMCache as an efficient KV cache layer that reduces redundant computations through cross-query context reuse.
- It leverages batched operations, compute-I/O overlapping, and zero-copy transfers to minimize latency and maximize throughput.
- The architecture integrates a data plane and control plane to manage cache movement across hardware layers, proving scalability in enterprise environments.
LMCache: An Efficient KV Cache Layer for Enterprise-Scale LLM Inference
Introduction
The paper "LMCache: An Efficient KV Cache Layer for Enterprise-Scale LLM Inference" (2510.09665) addresses significant inefficiencies in current LLM inference systems. Typically, each user query is processed independently by a single inference engine instance, leading to redundant computations and underutilized resources. LMCache introduces an efficient open-source solution for KV caching, allowing for resource sharing across queries and engines, thereby optimizing performance and reducing latency.
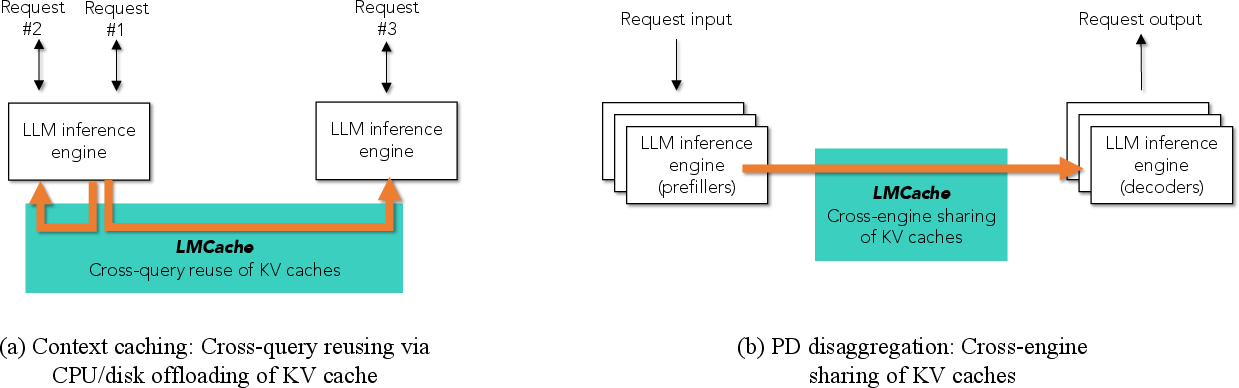
Figure 1: LMCache supports both context caching (KV cache offloading and sharing across queries) and PD disaggregation (cross-engine transfer of KV caches).
Motivation
The proliferation of enterprise applications utilizing LLMs has shifted the bottleneck from training to inference costs and delays. This paper highlights that inference becomes the primary limitation due to increasing input and output lengths, driven by user interactions, multimodal inputs, and newer LLMs with extensive context windows. The redundant computation involved in recomputing the same prompt prefix across different queries adds to these costs. In interactive applications, reducing Time-to-First-Token (TTFT) is essential for maintaining a quality user experience.
KV Caching as a Solution
The paper proposes extending KV caching beyond single-query lifecycles to enable cross-query context reuse and prefill-decode (PD) disaggregation. These optimizations rely on efficiently moving KV cache segments across different memory hierarchies, including GPU memory, CPU DRAM, and networks such as Ethernet and NVLink.
LMCache makes several contributions:
- Optimized Performance: Incorporates batched operations, compute-I/O overlapping, and minimizes data copies to achieve high throughput and efficiency.
- Standardized Interface: A modular KV cache connector maintains compatibility with evolving inference engines.
- Management Interface: Offers APIs for KV cache orchestration, allowing efficient utilization and control across storage and network layers.
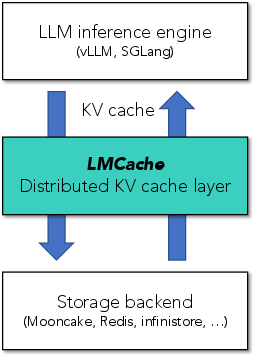
Figure 2: LMCache sits between LLM inference engines and heterogeneous storage/network devices.
Architecture and Implementation
LMCache's architecture integrates with LLM inference engines to manage KV cache movement, as depicted in the end-to-end system workflow (Figure 3). It features a data plane (LMCache Worker) and a control plane (LMCache Controller), providing standardized interfaces for optimized data movement and resource management.
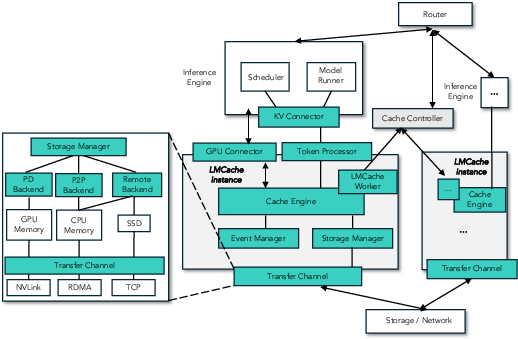
Figure 3: End-to-end system workflow for LMCache.
To handle I/O inefficiencies, LMCache employs batched operations with configurable chunk sizes, layer-wise pipelining to overlap computation with data transfer effectively, and zero-copy operations to reduce memory overhead (Figure 4).
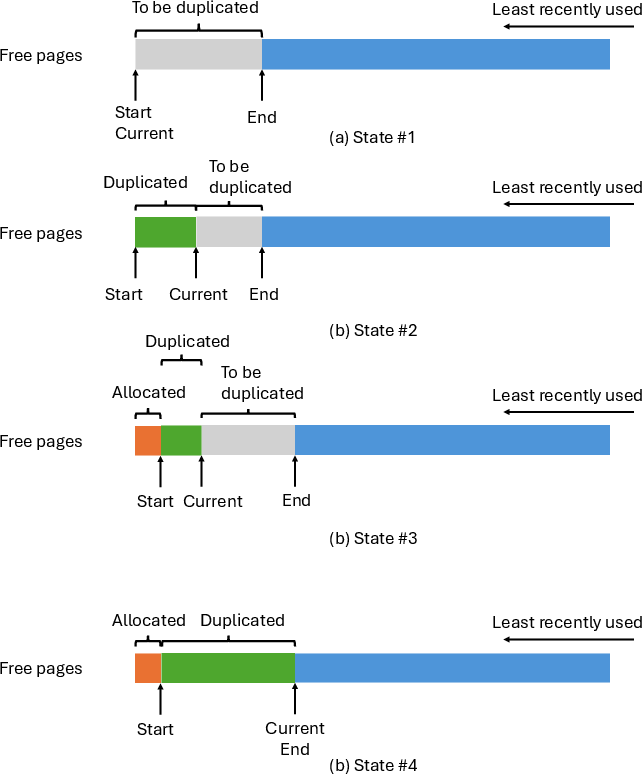
Figure 4: Illustration of dynamic offloading in LMCache.
LMCache's evaluation demonstrates its superiority in reducing latency and improving throughput across various scenarios compared to existing systems and commercial offerings. In single-node CPU offloading, LMCache achieves significantly higher throughput and lower TTFT. Through centralized storage servers and PD disaggregation, it exhibits substantial improvements in efficiency and resource utilization.
Among the highlights:
- Single-Node Evaluation: LMCache reduces mean latency and achieves higher throughput by leveraging CPU offloading and optimized cache management.
- Remote Backend Evaluation: Utilizes hierarchical storage to maximize cache hit ratios and minimize time-to-load delays from remote servers.
- PD Disaggregation: Outperforms native PD implementations by effectively managing KV cache transfers between prefiller and decoder stages.
Real-World Application
In production environments, LMCache's capabilities have been adapted for large-scale deployments, including emerging use cases like recommendation systems and chatbots. The paper notes the importance of adaptive strategies for KV cache loading, given bandwidth and context length considerations.
Conclusion
LMCache presents a robust and efficient solution for KV caching in LLM inference, significantly enhancing performance by addressing inefficiencies in current systems. Its open-source availability and rapid adoption in industry highlight its practical value and potential as a foundation for next-generation LLM infrastructures that consider AI-native data, such as KV caches, as integral components.
The work contributes a compelling argument for the broader adoption of AI-native data as a substrate for scalable LLM inference, facilitating a shift toward persistent, cache-aware computation models that ensure efficient, reliable, and cost-effective AI service delivery.





