TreePrompt: Leveraging Hierarchical Few-Shot Example Selection for Improved English-Persian and English-German Translation (2510.03748v1)
Abstract: LLMs have consistently demonstrated strong performance in machine translation, especially when guided by high-quality prompts. Few-shot prompting is an effective technique to improve translation quality; however, most existing example selection methods focus solely on query-to-example similarity and do not account for the quality of the examples. In this work, we propose TreePrompt, a novel example selection approach that learns LLM preferences to identify high-quality, contextually relevant examples within a tree-structured framework. To further explore the balance between similarity and quality, we combine TreePrompt with K-Nearest Neighbors (K-NN) and Adaptive Few-Shot Prompting (AFSP). Evaluations on two language pairs - English-Persian (MIZAN) and English-German (WMT19) - show that integrating TreePrompt with AFSP or Random selection leads to improved translation performance.
Sponsor
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Knowledge Gaps
Below is a concise, actionable list of the paper’s knowledge gaps, limitations, and open questions that remain unresolved.
- Validate label reliability: quantify intra-model and inter-model agreement for the LLM-based 1/0/−1 example-quality labels (e.g., report Cohen’s kappa across GPT‑4o, GPT‑3.5, DeepSeek and across multiple runs with temperature 0).
- Control prompt sensitivity: measure how labeling outcomes vary with different scoring prompts, instruction phrasing, and chain-of-thought vs. no-CoT, and establish a robust, prompt-agnostic scoring protocol.
- Avoid test-set leakage: TreePrompt uses test sentences to guide example labeling/selection; redesign to use a separate development set for labeling and freeze the example library before evaluating on a disjoint test set.
- Establish compute-fair comparisons: report wall-clock time, number of LLM calls, ANN/KNN query counts, and cost per point of COMET improvement for all methods; compare under matched compute budgets.
- Statistical rigor: report confidence intervals and statistical significance for metric differences (bootstrap on test sentences) and average results over multiple random seeds for initial sampling.
- Human evaluation: complement automatic metrics with human adequacy/fluency/MQM or DA assessments, especially for Persian where COMET may misjudge quality.
- Low-resource metric calibration: test metrics better suited to low-resource settings (e.g., COMETKiwi, xCOMET, Prism), or train/tune a Persian-aware COMET variant and assess metric–human correlation.
- Error analysis: provide a qualitative taxonomy of error types (terminology, agreement, reordering, idioms, named entities) and analyze how TreePrompt-selected examples mitigate or exacerbate them.
- Ordering effects: evaluate and learn the optimal ordering of demonstrations (e.g., by difficulty, domain, length, topical coherence); quantify sensitivity to permutation of selected examples.
- Label granularity and strategy: compare the current ternary label to pairwise preference ranking or listwise learning-to-rank; test whether pairwise wins improve selection quality and stability.
- Use of negative examples: examine whether explicitly including some −1 examples as “contrastive” demonstrations improves robustness, or whether filtering them yields the best outcome.
- Diversity vs. redundancy: incorporate explicit diversity controls (e.g., MMR, clustering constraints) in the tree expansion; measure redundancy and its effect on translation quality.
- Embedding choice for retrieval: benchmark RoBERTa against multilingual encoders (LaBSE, e5‑multilingual, mUSE, MPNet multilingual, BGE‑m3) and cross-lingual alignment methods, especially for English–Persian.
- Retrieval features: test source-only vs. source+target bilingual embeddings and bilingual lexical features; assess whether including target-side signals improves selection.
- Tree search design: ablate depth vs. breadth, branching factor, and stop criteria; introduce utility-based stopping (e.g., stop when marginal COMET gain on a dev set falls below a threshold).
- Parameter sensitivity: provide systematic ablations for R (initial random size), k (neighbors), iterations, and threshold of positive labels; publish performance–cost curves to guide practitioners.
- ANN at scale: evaluate FAISS/HNSW/ScaNN for approximate search; measure quality–speed tradeoffs on larger prompt-source corpora (e.g., 100k+ sentence pairs).
- Budgeted selection: develop a budget-aware TreePrompt variant that maximizes quality under a fixed LLM-call budget and compare its efficiency to AFSP/KNN.
- Re-ranker identity bias: using the same LLM for reranking and translation risks preference feedback loops; test with a separate scorer (e.g., a smaller LLM or a learned QE model) and compare outcomes.
- Cross-model transfer: assess whether a TreePrompt-selected example library built with one LLM (e.g., GPT‑4o) transfers to other LLMs; identify conditions for cross-model generalization.
- k-shot sensitivity: the study fixes k=5; evaluate performance across k (e.g., 1–16) and identify model- and language-specific optima.
- Domain robustness: test on out-of-domain sets (legal, medical, conversational) and measure how selection strategies adapt; add domain-aware selection signals if needed.
- Language coverage: extend to typologically diverse and low-resource pairs (e.g., English–Amharic, English–Vietnamese), scripts (Arabic, Devanagari), and morphologically rich languages; analyze per-language effects.
- Dataset size and diversity: expand beyond 9k prompt-source/500 test sentences; evaluate on larger, more varied corpora and multiple domains to strengthen generalizability claims.
- Baseline breadth: compare against stronger or newer selection methods (e.g., influence-function-based demo selection, SELF‑ICL/STaR, gradient-based retrieval, SELECT) and document relative gains.
- Generalization from single-query scoring: TreePrompt labels examples relative to one query at a time; study whether labels generalize across queries and design query-agnostic quality scoring procedures.
- Overfitting to test distribution: measure performance when the test distribution shifts after building the example library (e.g., different topics/domains) to test robustness of learned preferences.
- Data contamination checks: verify that selected examples are not near-duplicates of test references or memorized by the LLM; include de-duplication and similarity filters to prevent contamination.
- Safety and content filtering: add toxicity/PII filters for selected examples; quantify any effect on translation quality.
- Efficiency via distillation: explore training a lightweight classifier/QE model to mimic the LLM’s labeling, reducing LLM calls while preserving selection quality; report the distillation gap.
- Multi-sentence/document-level extension: examine whether TreePrompt scales to document-level MT with coherence constraints and cross-sentence phenomena (coreference, discourse markers).
- Transparent reporting: release code, prompts, seed values, and full hyperparameter grids to improve reproducibility and enable rigorous comparison by future work.
Practical Applications
Overview
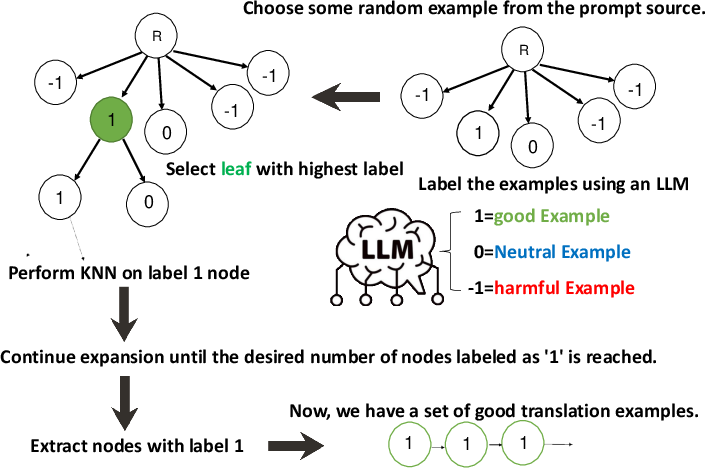
TreePrompt is a hierarchical, LLM-preference–guided few-shot example selection method that blends semantic similarity (via KNN over RoBERTa embeddings) with direct LLM scoring of example quality (labels 1/0/−1). It improves machine translation prompting by curating fewer but higher-quality examples and is especially helpful for low-resource language pairs. Below are practical applications and workflows derived from the paper’s findings and method.
Immediate Applications
The following applications can be deployed now with standard LLM APIs, off‑the‑shelf embedding models, and vector search tools.
- Translation Memory Optimizer for Localization
- Sectors: software/localization, media/entertainment, e-commerce
- Workflow/Product: A “TreePrompt Selector” plugin for Translation Management Systems (e.g., Smartling, memoQ, Lokalise) that pre-filters translation memories and selects 5-shot exemplars for LLM MT; optionally integrates AFSP or a reranker for final selection.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Access to a reliable LLM for labeling; RoBERTa or SBERT embeddings; FAISS/ANN index; curated bilingual corpora; costs manageable via batching/caching.
- Low-Resource Language Translation Enhancement
- Sectors: NGOs, public health, emergency response, government
- Workflow/Product: A deployment-ready pipeline that uses TreePrompt to build high-quality example sets for low-resource language advisories (e.g., English↔Persian), improving clarity for critical communications.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Human-in-the-loop for quality assurance; domain-specific examples; potential misalignment of COMET with true quality in low-resource settings.
- Customer Support Ticket Translation
- Sectors: software/SaaS, customer service/BPO
- Workflow/Product: Dynamic few-shot selection from prior ticket translations; LLM labels best exemplars; KNN retrieves similar cases; AFSP finalizes prompt per ticket.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Privacy safeguards; anonymization; real-time vector retrieval; LLM latency and cost control.
- Subtitle and Media Localization
- Sectors: media/entertainment
- Workflow/Product: Curate exemplar subtitle pairs via TreePrompt before translating episodes/movies; reduces post-editing time and stylistic inconsistency.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Domain/style consistency; timecode-aware pipelines; human review for colloquialisms.
- LLM-Driven Reranker for Translation Memories
- Sectors: localization QA/tooling
- Workflow/Product: Use LLM-generated labels (−1/0/1) as a “memory hygiene” signal to retag or suppress harmful/low-quality examples; integrate with AFSP for retrieval.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Reliable LLM preference labeling; access to memory metadata; organizational buy-in to prune legacy TMs.
- Academic Corpus Curation for MT Research
- Sectors: academia
- Workflow/Product: A reproducible TreePrompt-based data curation script to build high-quality exemplar subsets from large bilingual corpora; facilitates fair benchmarking and low-resource studies.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Open data licensing; embedding model availability; standardized scoring prompts.
- Multilingual Chatbot Fallback Translation
- Sectors: software/customer service
- Workflow/Product: For chats in unsupported languages, TreePrompt selects examples on the fly to guide LLM translation; AFSP balances fluency/accuracy.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Contextual privacy; robust session caching; fast ANN retrieval.
- Domain-Specific Glossary Preservation
- Sectors: finance, legal, healthcare
- Workflow/Product: TreePrompt selects examples rich in domain terminology; reduces term drift in few-shot LLM MT.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Domain-annotated corpora; glossary injection; post-edit QA.
- Data Quality Auditing for Bilingual Corpora
- Sectors: data engineering, AI tooling
- Workflow/Product: Label-based filtering pipeline to identify noisy, misaligned or stylistically harmful pairs; produces a “clean subset” for downstream MT or LLM prompting.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: LLM budget; clear flagging/removal policies; versioned corpus management.
- EdTech Bilingual Exercise Generation
- Sectors: education
- Workflow/Product: Select high-quality example pairs to seed bilingual exercises and translations in language-learning platforms.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Age/level-appropriate corpora; teacher QA loop; content licensing.
- Developer SDK for Few-Shot Example Selection
- Sectors: software/AI
- Workflow/Product: A Python SDK exposing TreePrompt + AFSP/KNN workflows (embeddings, FAISS, LLM labeling, caching, reranking), with config templates and metrics logging.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Standardized APIs (OpenAI/Anthropic/DeepSeek); embedding model weights; devops for indexing and cache persistence.
- Compliance-Friendly Prompt Curation
- Sectors: legal, finance
- Workflow/Product: Automated redaction and compliance checks followed by TreePrompt selection; ensures few-shot examples do not leak sensitive information.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: De-identification preprocessor; audit trails; regulatory review.
Long-Term Applications
These require further research, scaling, benchmarking, or development to be robust and broadly adoptable.
- Cross-Task Example Selection Beyond Translation
- Sectors: software/AI
- Workflow/Product: Extend TreePrompt to summarization, code generation, clinical note normalization, or classification; unified “Example Selector” microservice for any in-context LLM operation.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Task-specific labeling prompts; new evaluation metrics; domain datasets.
- Preference Scorer Model to Replace LLM Labeling
- Sectors: software/AI, privacy-first industries
- Workflow/Product: Train a smaller “preference model” on LLM labels to emulate 1/0/−1 scoring; reduces cost and latency; viable for on-prem deployments.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Sufficient labeled data; careful distillation and bias analysis; periodic recalibration to new LLMs.
- Online, Self-Optimizing Few-Shot Selection
- Sectors: software/AI, localization
- Workflow/Product: Real-time adaptation with A/B testing, COMET/CHRF feedback, and reinforcement signals; continuous prompt optimization under drift.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Streaming metrics; robust feedback loop; safeguards against overfitting and metric gaming.
- Human-in-the-Loop Interactive Tree Curation
- Sectors: localization, academia
- Workflow/Product: UI that visualizes the selection tree, lets linguists approve expansions, adjust KNN parameters, and enforce style/glossary rules.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Usability design; role-based access; version control of curated sets.
- Data-Centric Fine-Tuning for NMT/LLMs
- Sectors: AI/ML
- Workflow/Product: Use TreePrompt to curate high-quality fine-tuning subsets; couple with domain adaptation pipelines to reduce training data volume without quality loss.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Training infrastructure; method validation across model families; robust generalization studies.
- Low-Resource Evaluation Standards and Metrics
- Sectors: academia, policy
- Workflow/Product: Develop metrics better aligned with human judgment for low-resource languages; guidelines for governmental language-access programs to adopt preference-aware prompt curation.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Multi-language human evaluations; cross-institution collaboration; metric standardization.
- Privacy-Preserving/On-Device TreePrompt
- Sectors: healthcare, legal, defense
- Workflow/Product: Local embeddings + preference scorer; secure vector indices; minimize cloud LLM calls; suitable for regulated environments.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Hardware constraints; deployment of compact preference models; secure MLOps.
- Multilingual Search and Cross-Lingual Retrieval
- Sectors: search/ad tech
- Workflow/Product: Use curated exemplars to stabilize in-context query translation for bilingual search; improves recall/precision on long-tail queries.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Query logs and consent; latency budgets; relevance evaluation.
- Multi-Agent LLM Systems with Specialized Selection Agents
- Sectors: software/AI
- Workflow/Product: Agent responsible for example curation (TreePrompt), another for translation, and a third for QA/reranking; orchestrated workflows for complex documents.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Reliable agent coordination; cost governance; failure handling.
- Industrial Documentation Translation (Robotics/Manufacturing/Energy)
- Sectors: robotics, manufacturing, energy
- Workflow/Product: TreePrompt selects examples from domain manuals to preserve technical terminology and safety-critical instructions.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Access to proprietary corpora; strict QA; liability-aware post-editing.
- Financial Reporting and Cross-Border Compliance
- Sectors: finance
- Workflow/Product: Curate examples for IFRS/GAAP terminology and regulatory phrasing; reduce ambiguity in bilingual disclosures.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Regulatory review; domain experts in the loop; audit trails.
- Crisis-Response Translation at the Edge
- Sectors: humanitarian response, public safety
- Workflow/Product: Offline-friendly TreePrompt with local embeddings and cached exemplars for field teams; prioritizes clarity and key phrases.
- Assumptions/Dependencies: Ruggedized hardware; lightweight preference scorer; field validation.
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.