- The paper introduces KeySG, a hierarchical 3D scene graph that enriches nodes with multimodal context from adaptively selected keyframes.
- It employs adaptive keyframe sampling and a multimodal retrieval-augmented generation pipeline to achieve superior open-vocabulary segmentation and complex query grounding.
- Experimental evaluations demonstrate improved recall and efficiency on benchmarks, emphasizing its scalability and potential for advanced robotic scene understanding.
KeySG: Hierarchical Keyframe-Based 3D Scene Graphs
Introduction
In recent developments within robotics, the integration of semantic richness with geometric precision has become crucial for enabling autonomous agents to navigate and operate in complex environments such as homes and offices. The paper "KeySG: Hierarchical Keyframe-Based 3D Scene Graphs" addresses the limitations of current 3D scene graph (3DSG) approaches, particularly their dependence on predefined semantic relationships and scalability constraints when interfacing with LLMs. The proposed KeySG framework innovatively enhances the 3DSG representation by incorporating a hierarchical structure augmented with multimodal contextual information derived from keyframes, facilitating more general and task-agnostic reasoning.
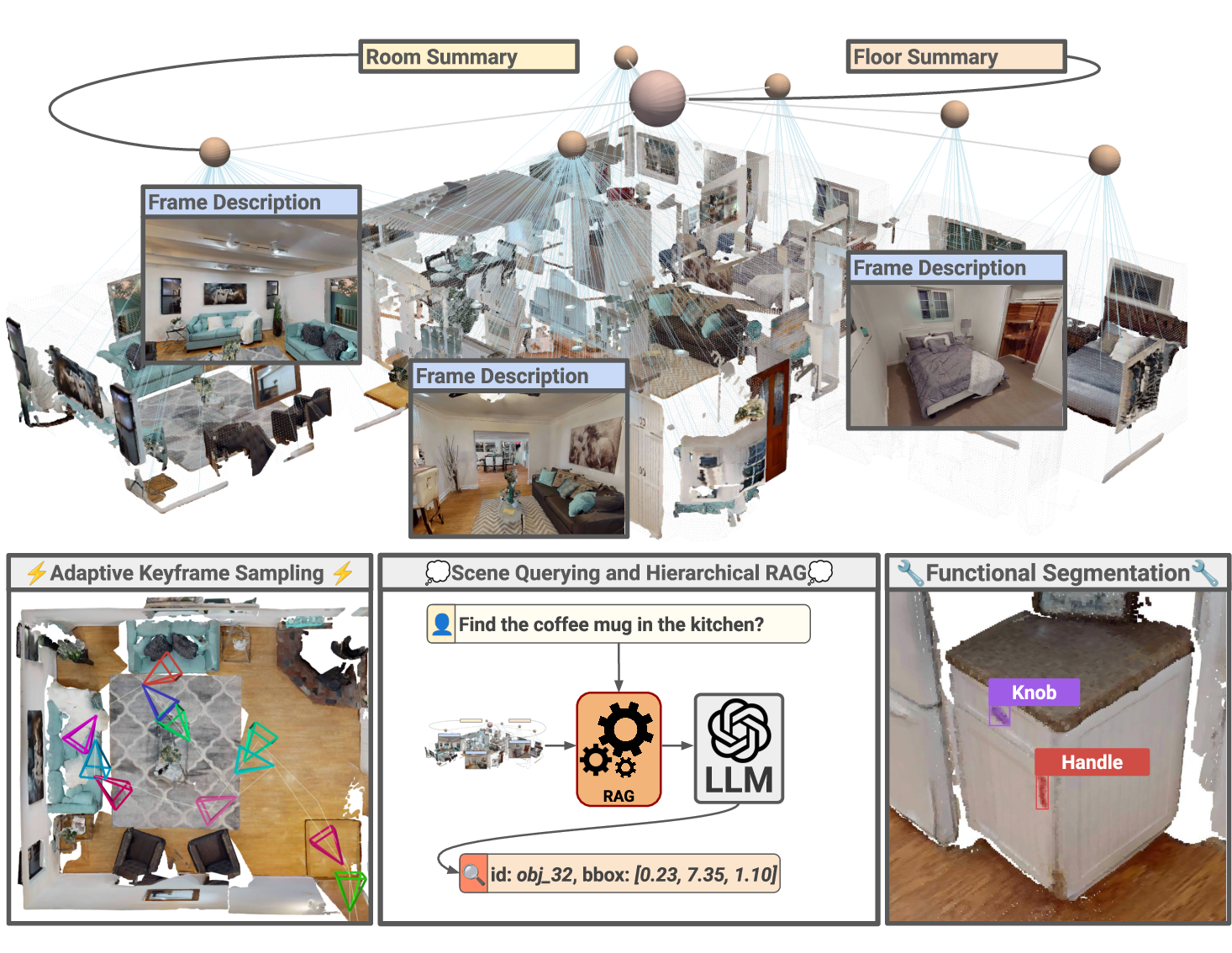
Figure 1: As illustrated (top), KeySG is a hierarchical, keyframe-based 3D scene graph comprising floors, rooms, objects, and functional elements (bottom right). Each node is augmented with contextual information efficiently extracted from scene keyframes via adaptive keyframe sampling (bottom left). Leveraging a multimodal RAG pipeline, KeySG enables users to ask complex natural language queries and receive answers grounded in the 3D scene (bottom middle).
Technical Contributions
KeySG consists of several critical components and methodologies:
- Hierarchical Scene Representation: KeySG models environments at multiple levels, including buildings, floors, rooms, objects, and functional elements. Each node in this hierarchy is enriched with context extracted from selected keyframes, capturing essential geometric, semantic, and functional properties.
- Keyframe Selection for Contextual Enrichment: Recognizing the impracticality of storing entire sequences in large-scale environments, KeySG strategically selects keyframes based on both geometric coverage and visual informativeness. This selection process maximizes the semantic and spatial information captured per room.
- Augmentation with Multimodal Context: By leveraging Vision-LLMs (VLMs), KeySG extracts descriptions and tags from keyframes, which are used in conjunction with open-vocabulary segmentation pipelines for detecting and segmenting 3D objects and associated functional elements.
- Hierarchical Scene Summarization: The extracted descriptions from the keyframes are aggregated within rooms and further summarized at the floor level, ensuring a coherent, high-level description of the scene that can support efficient querying.
- Efficient Scene Querying via RAG: A Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline facilitates efficient querying of the scene graph. This mechanism is pivotal for providing relevant context to LLMs without surpassing their context windows, using a hierarchical retrieval strategy that navigates from general concepts to specific objects.
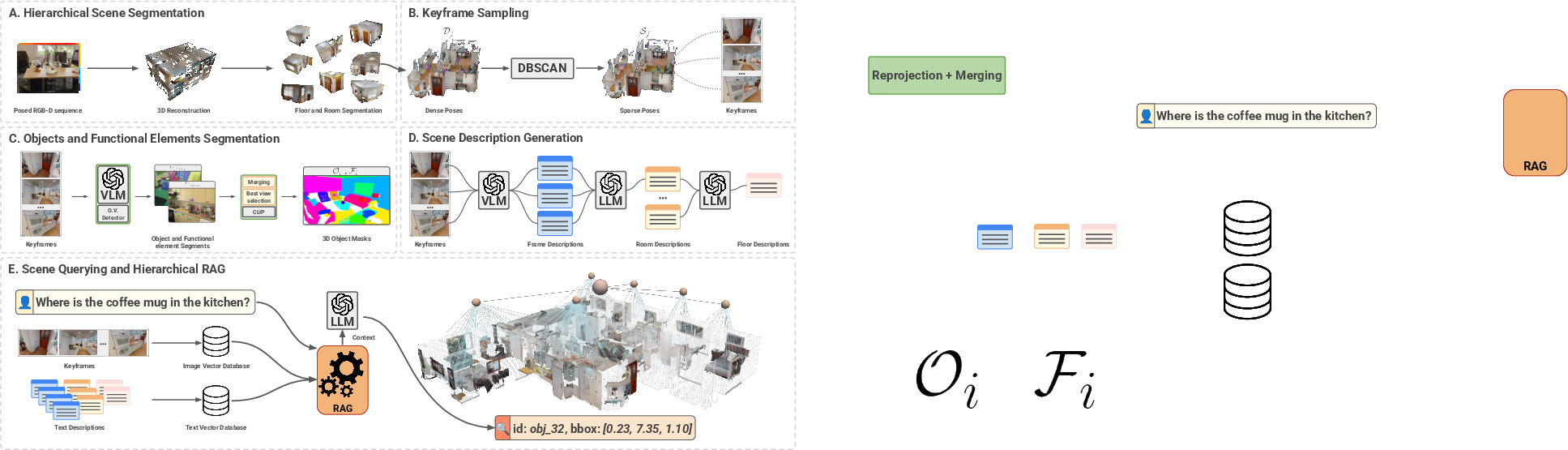
Figure 2: Overview of KeySG showing scene segmentation, keyframe sampling, semantic extraction, hierarchical summarization, and retrieval mechanisms.
Experimental Evaluation
The efficacy of KeySG is demonstrated through extensive evaluations across several benchmarks:
- Open-Vocabulary 3D Segmentation: KeySG excels in 3D semantic segmentation tasks by leveraging CLIP text embeddings for open-vocabulary object recognition, outperforming existing methods on the Replica dataset.
- Functional Element Segmentation: On the FunGraph3D dataset, KeySG demonstrates superior recall in segmenting functional interactive elements, underscoring its capability to generalize to novel task specifications.
- Hierarchical Object Retrieval: In large-scale environments, KeySG effectively retrieves objects using hierarchical queries, showcasing its ability to navigate complex scene structures efficiently.
- Complex Query Grounding: In grounding tasks on the Nr3D dataset, KeySG’s adaptability to diverse natural language queries, including indirect references and non-standard descriptors, highlights its robust semantic comprehension.
Limitations and Future Work
While KeySG is a significant step forward, the framework is constrained to offline processing due to its reliance on large computational models. Moreover, it assumes static environments, lacking adaptability to dynamic changes—a limitation that future research could address through real-time updating of 3DSG representations and incorporating temporal dynamics.
Conclusion
KeySG represents a pivotal advancement in 3DSG frameworks by integrating hierarchical modeling with adaptive, multimodal contextualization, thereby addressing the limitations of static, predefined relationship sets. Its scalable architecture and efficient retrieval mechanisms enable robust semantic reasoning in complex environments, paving the way for more intelligent and versatile robotic systems capable of understanding and interacting with their surroundings in a human-like manner.

