- The paper introduces a unified gradient-based framework for FP4 training, quantifying stabilization and quantization techniques.
- It evaluates approaches like tensor scaling, stochastic rounding, and Hadamard transformations across varied ML tasks to optimize training performance.
- Findings emphasize gradient stability and optimal scale representation as key to balancing computational cost and model accuracy.
Summary of "Elucidating the Design Space of FP4 Training"
Introduction
The paper "Elucidating the Design Space of FP4 training" (2509.17791) addresses the increasing computational demands in training large foundation models, targeting the frontier of 4-bit floating-point (FP4) formats to improve hardware throughput. The authors introduce a unified framework to paper the design space of FP4 training, providing a theoretical analysis on computational costs associated with stabilization techniques used in both forward and backward passes. An extensive empirical paper is conducted across diverse machine learning tasks, focusing on configurations that offer the best performance-to-overhead trade-off. Importantly, techniques combining Hadamard transformations, tensor scaling, and stochastic rounding are identified as promising.
Framework for FP4 Training
The paper proposes a gradient-based framework for microscale quantization, illustrating the mathematical nuances of tensor scaling and quantization. This framework enables a deeper analysis of FP4’s computational costs on training procedures. Specifically, the authors define micro-scaled blocks and explore how different scalar functions and quantization approaches affect model training stability.
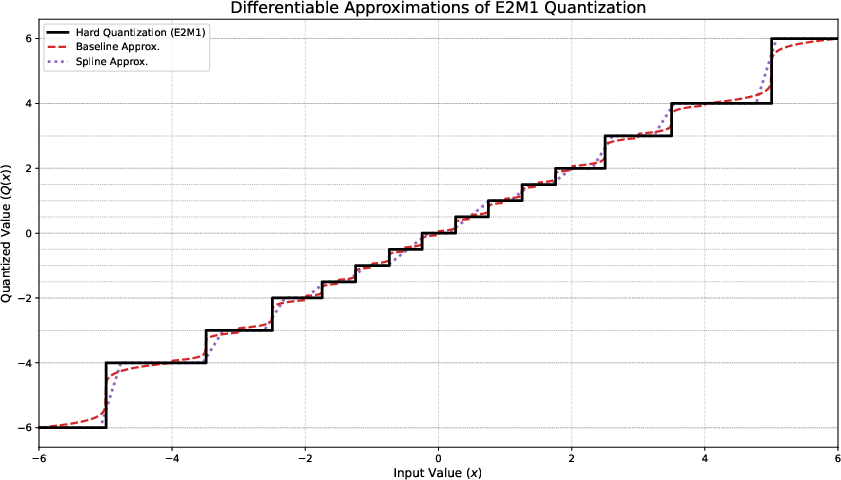
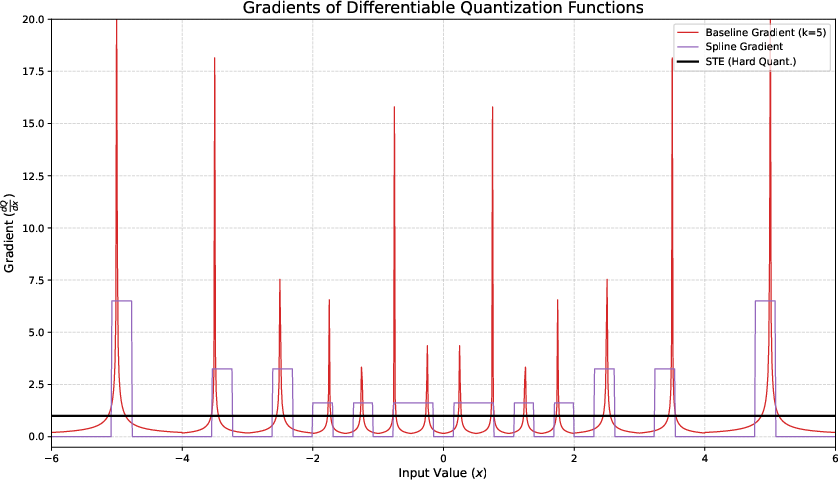
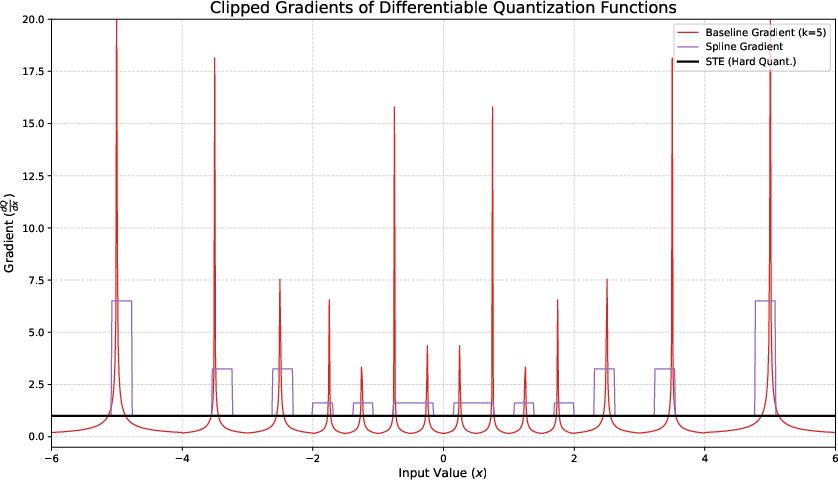
Figure 1: Approximation function $Q_{\text{approx}$.
The framework addresses key choices in calculating gradients, approximating quantization derivatives, and selecting tensor scaling strategies. They highlight the importance of handling zero-valued scales, suggesting alternatives to mitigate quantization errors effectively.
Techniques Evaluated
A broad array of techniques is evaluated for FP4 training:
- Tensor Scaling: The authors propose tensor-wide normalization before block-wise quantization to refine scale precision.
- Rounding Strategies: Various strategies are explored, including round-to-nearest and stochastic rounding, to enhance stability.
- Gradient Approximations: Differentiable relaxations like linear spline approximation and other approximations are introduced to manage non-differentiability in quantization functions.
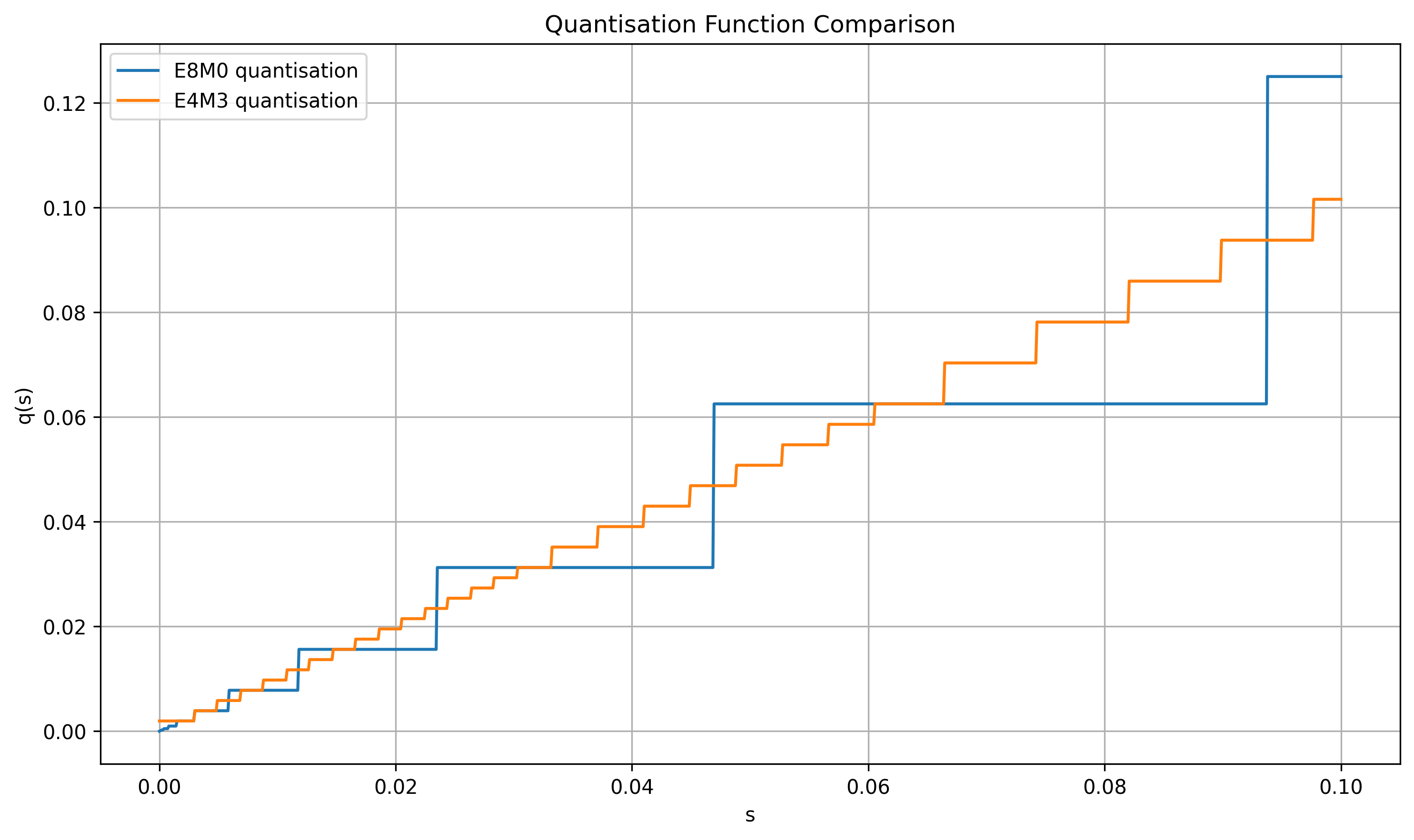
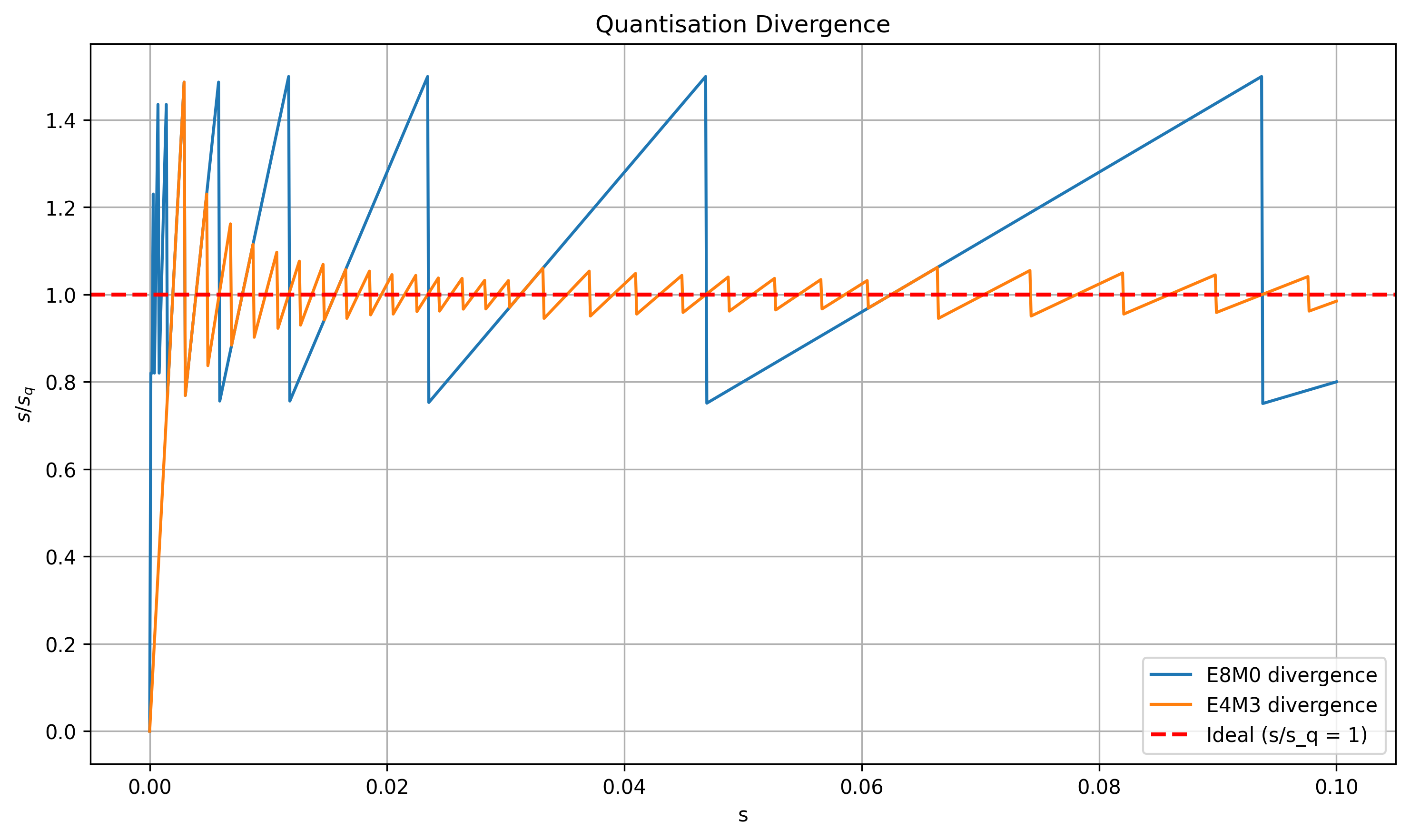
Figure 2: Quantization functions sq=q(s).
The paper further evaluates optimizer-centric adjustments like StableSPAM, which modifies momentum in the Adam optimizer for better stability in low precision contexts, and loss scaling strategies to propagate signals effectively in limited precision formats.
Experiments and Results
Detailed experimental setups involve regression, image classification, diffusion models, and language modeling, with emphasis on balancing performance against computational overhead. The authors demonstrate that only select techniques like Hadamard transformations and tensor scaling consistently deliver value, as illustrated in Pareto-frontier analyses.
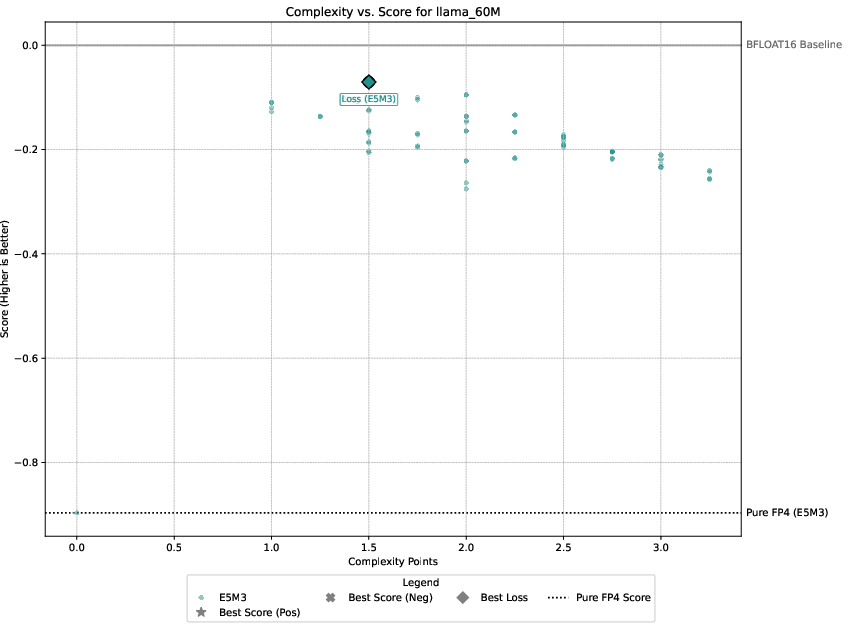
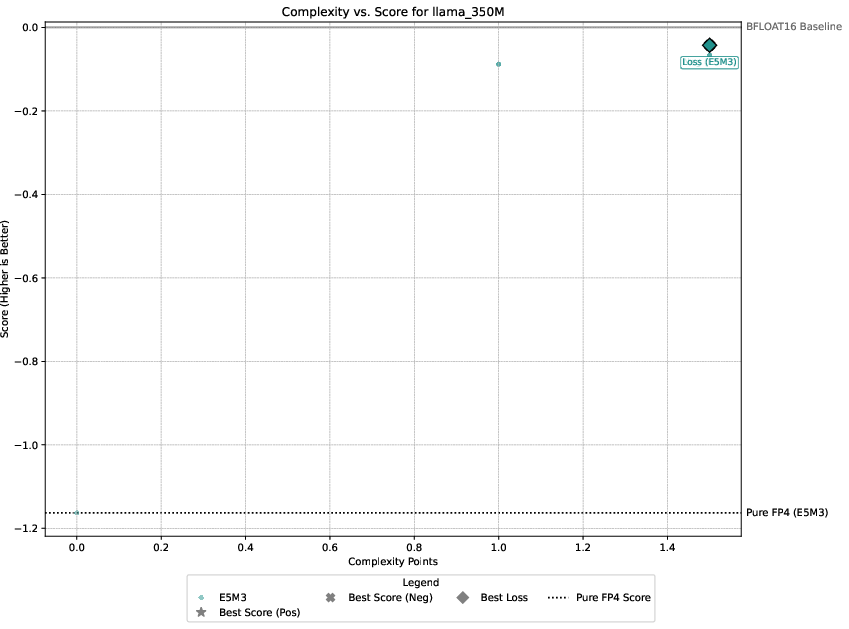
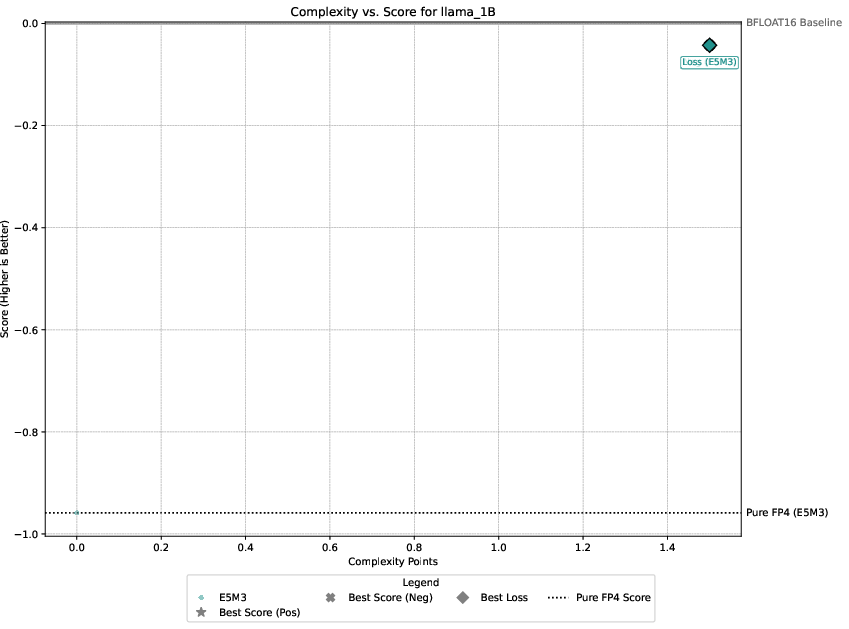
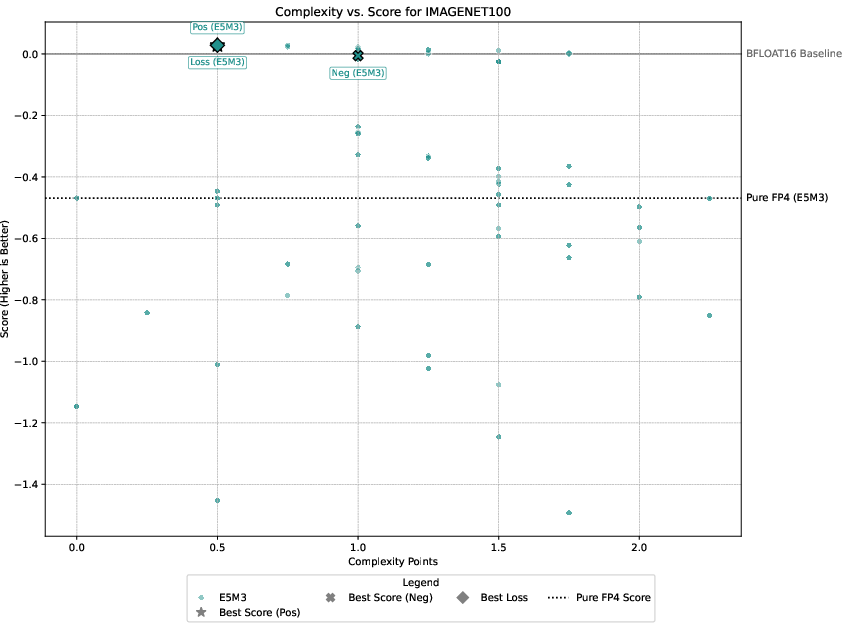
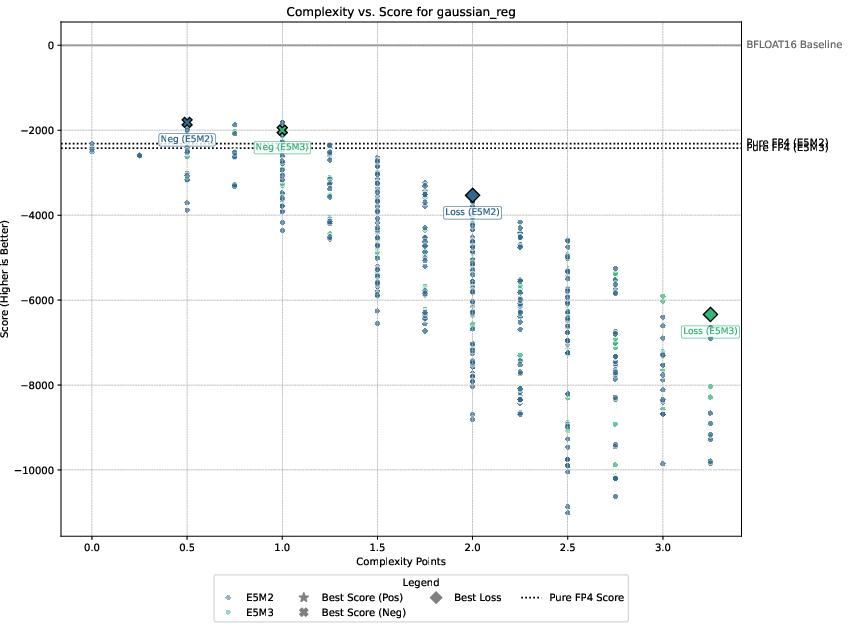
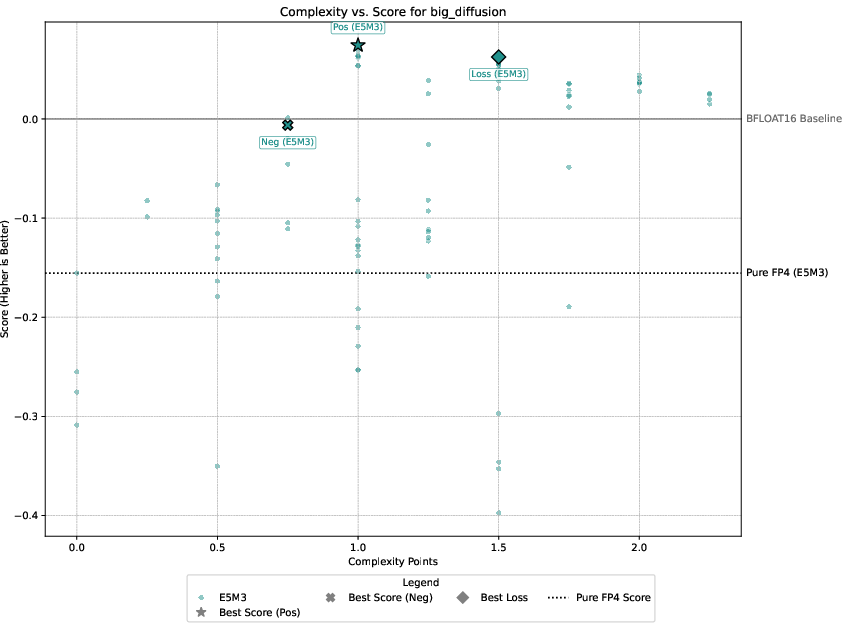
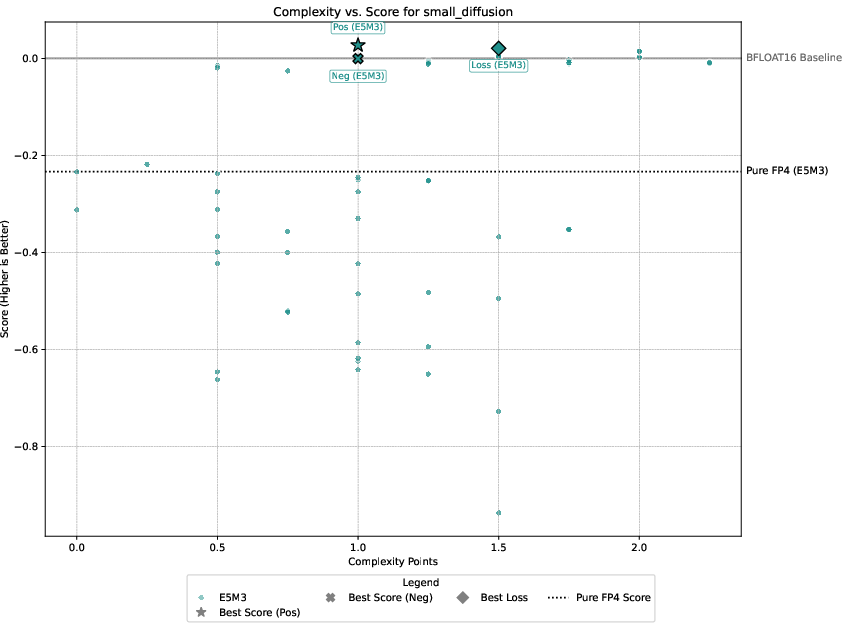
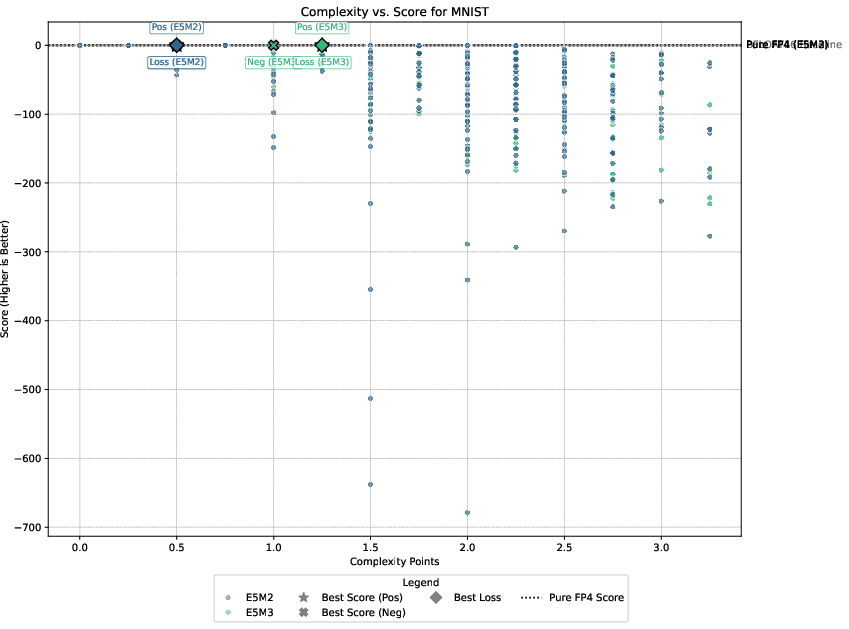
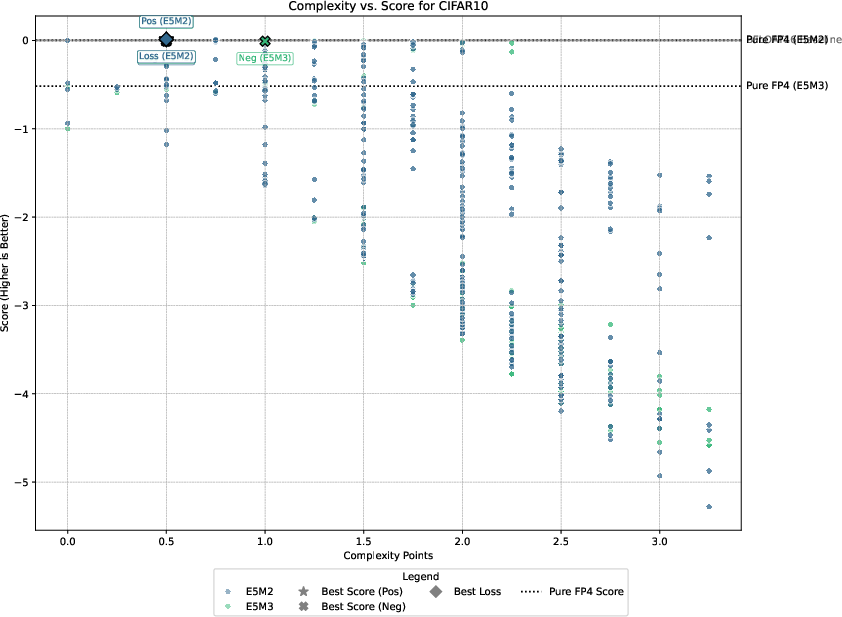
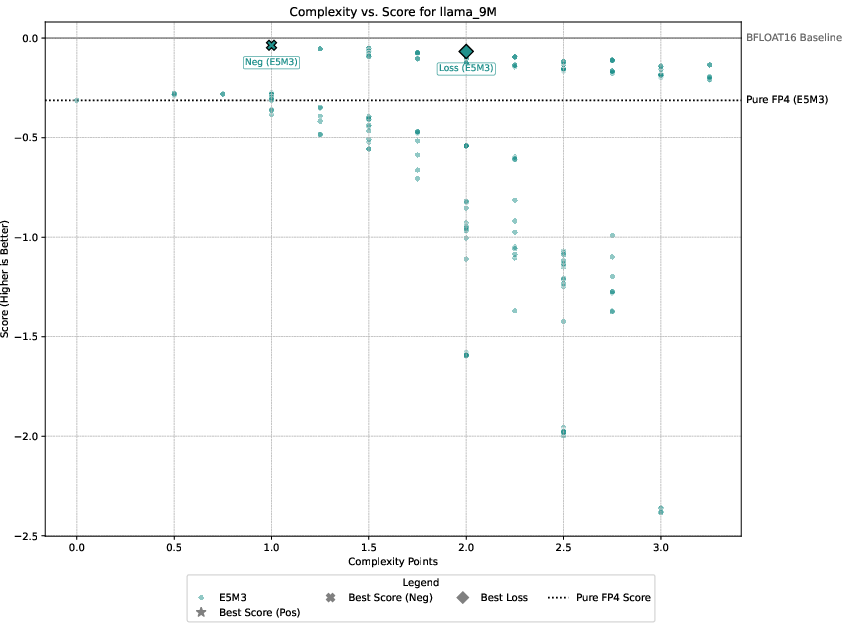
Figure 3: Pareto-frontier plots for each dataset, Omega(c) on the x-axis and S(c) on the y-axis.
Three guiding principles emerge from the analysis: the significance of gradient stability over unbiased gradients, the centrality of scale representation as a bottleneck, and the sparsity of worthwhile performance-overhead configurations.
Conclusion
The paper "Elucidating the Design Space of FP4 training" provides critical insights into FP4 training dynamics, emphasizing a systematic approach to evaluating stabilization methods. It suggests the need for implementing fusable operations such as Hadamard transformation and focusing on scale representation for optimal FP4 training. Additional research directions involve examining hardware support for FP4 and exploring alternative scale formats like UE5M3 with potential for improved range and precision balance.
















