ST-Raptor: LLM-Powered Semi-Structured Table Question Answering (2508.18190v3)
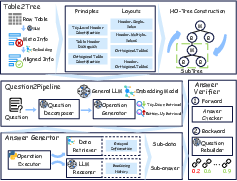
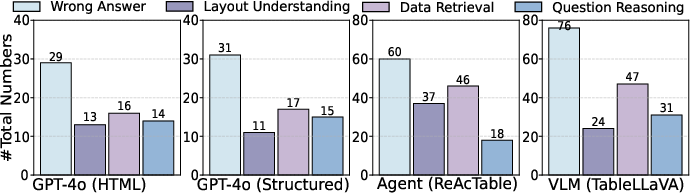
Abstract: Semi-structured tables, widely used in real-world applications (e.g., financial reports, medical records, transactional orders), often involve flexible and complex layouts (e.g., hierarchical headers and merged cells). These tables generally rely on human analysts to interpret table layouts and answer relevant natural language questions, which is costly and inefficient. To automate the procedure, existing methods face significant challenges. First, methods like NL2SQL require converting semi-structured tables into structured ones, which often causes substantial information loss. Second, methods like NL2Code and multi-modal LLM QA struggle to understand the complex layouts of semi-structured tables and cannot accurately answer corresponding questions. To this end, we propose ST-Raptor, a tree-based framework for semi-structured table question answering using LLMs. First, we introduce the Hierarchical Orthogonal Tree (HO-Tree), a structural model that captures complex semi-structured table layouts, along with an effective algorithm for constructing the tree. Second, we define a set of basic tree operations to guide LLMs in executing common QA tasks. Given a user question, ST-Raptor decomposes it into simpler sub-questions, generates corresponding tree operation pipelines, and conducts operation-table alignment for accurate pipeline execution. Third, we incorporate a two-stage verification mechanism: forward validation checks the correctness of execution steps, while backward validation evaluates answer reliability by reconstructing queries from predicted answers. To benchmark the performance, we present SSTQA, a dataset of 764 questions over 102 real-world semi-structured tables. Experiments show that ST-Raptor outperforms nine baselines by up to 20% in answer accuracy. The code is available at https://github.com/weAIDB/ST-Raptor.
Sponsor
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.