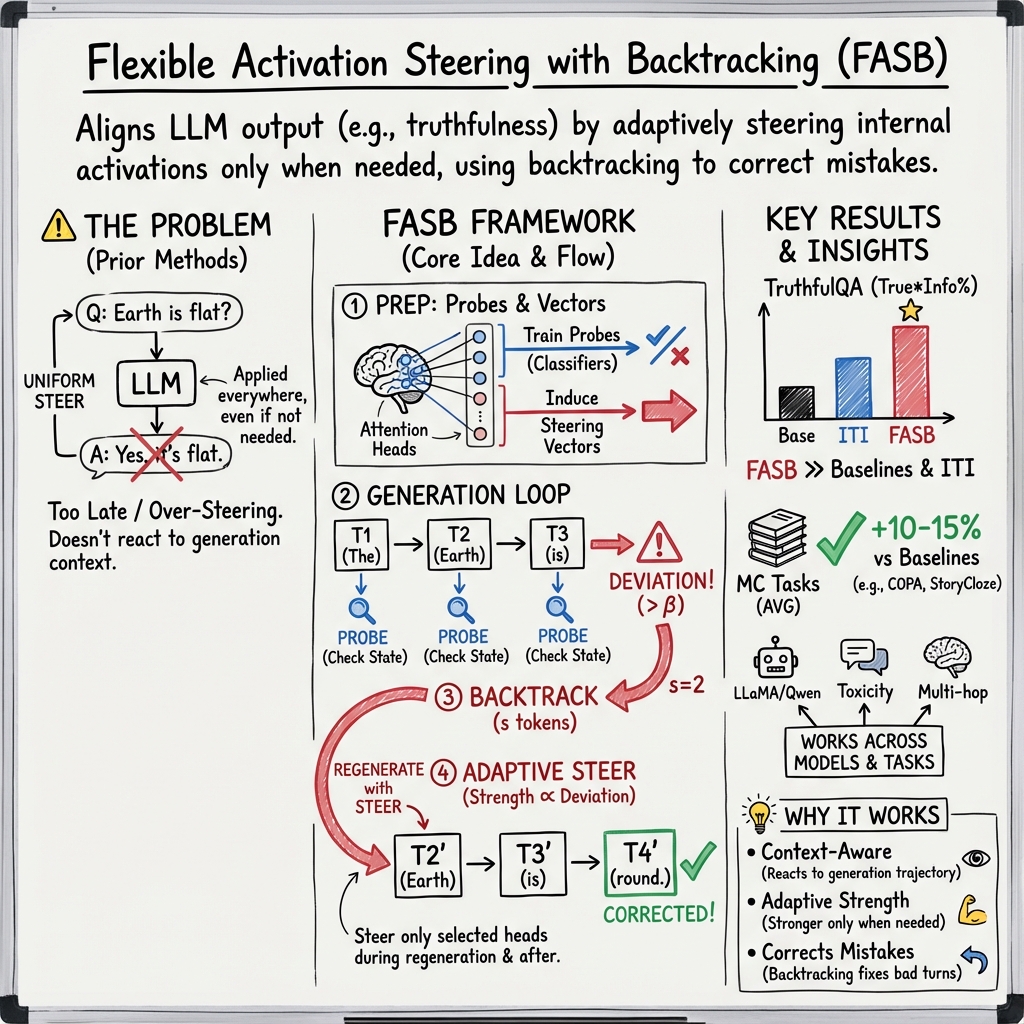
- The paper introduces FASB, a dynamic activation steering method that tracks LLM internal states and employs backtracking to correct deviations during generation.
- It uses a lightweight classifier to identify key attention heads and adjusts intervention strength, thereby enhancing truthfulness and informativeness.
- Experimental results on TruthfulQA and other datasets demonstrate that flexible steering significantly improves output alignment compared to traditional methods.
Steering When Necessary: Flexible Steering LLMs with Backtracking
Abstract
LLMs have achieved high performance in a variety of tasks but aligning their outputs with desired responses remains a challenge. Many existing methods, including instruction tuning and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), require costly fine-tuning. This paper introduces the Flexible Activation Steering with Backtracking (FASB) framework, which dynamically tracks LLMs' internal states during generation, enabling intervention at both necessary times and with appropriate strength. The paper demonstrates superior performance of the FASB method on various datasets like TruthfulQA.
Introduction
Steering LLMs to generate desired outputs is critical for reducing harmful and misleading information in text. Traditional techniques often require large-scale data and high computational overhead. Activation steering offers a more feasible alternative by directly modifying the model's internal activations during inference. However, existing approaches tend to apply interventions uniformly, hindering optimal performance.
The FASB framework introduced here leverages dynamic assessment of both the necessity and strength of intervention by examining LLM's internal states. It incorporates a backtracking mechanism, allowing it to correct deviations in generated tokens promptly. This method avoids the challenges of interventions applied post deviation detection, which often are too late to prevent the model from straying from desired behavior.
Method
FASB operates in two main stages:
- Heads Anchoring and Steering Vectors Inducing: This step identifies attention heads that are closely associated with desired behaviors using probing tools. A lightweight classifier called a probe is trained on these activations, facilitating selection of attention heads for intervention based on their ability to effectively separate the data into desired and undesired outcomes.
- Generation with Flexible Steering and Backtracking: This subsequent step employs classifier-driven state tracking to dynamically assess deviation probability after each token generation. If a deviation is detected, the backtracking mechanism allows for regeneration of previous tokens, steering outputs toward desired behavior with appropriately scaled intervention strength.
Results

Figure 1: The performance of various LLMs on the TruthfulQA benchmark.
Experiments on the TruthfulQA dataset revealed that FASB significantly improved the alignment of outputs when compared to existing methods such as ITI and CAA. It demonstrated marked performance improvements with flexible activation steering and adaptive intervention strength.
Additionally, FASB was tested on multiple-choice datasets, showing consistent results across different response formats. The dynamic intervention mechanism of FASB proved particularly effective when compared to baseline approaches, enhancing both truthfulness and informativeness in LLM outputs.

Figure 2: True*Info scores split across subcategories on LLaMA2-7B-CHAT, sorted by the difference between baseline and probe method. Subcategories with less than 10 questions are not shown.
Model Analysis
A detailed hyperparameter search indicated that both the number of heads selected and intervention strength play crucial roles in performance. Increasing either resulted in improvements in truthful metrics although it could compromise informativeness if pushed too far. The balance between truthfulness and informativeness points to nuanced tuning challenges inherent in steering models toward desired outputs.
Conclusion
The FASB framework offers a pragmatic solution to steering LLM outputs by dynamically determining and adapting intervention strategies through backtracking techniques. This offers both theoretical insights into model behavior during text generation and practical improvements across diverse datasets, enhancing overall alignment while maintaining performance integrity. Future work should focus on refining these methodologies to extend FASB frameworks to further datasets and LLM applications.